Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Discover if chewing gum can boost your oral health with surprising benefits.
Chewing gum has been a popular pastime for decades, but did you know that it can also have a positive impact on your oral health? The science behind chewing gum’s effect on oral health lies in its ability to stimulate saliva production. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids, remineralizing tooth enamel, and washing away food particles and bacteria.
When you chew gum, it stimulates the salivary glands, causing an increase in saliva production. This increase in saliva helps to neutralize acids in the mouth, which can be harmful to tooth enamel. Additionally, saliva is rich in minerals, such as calcium and phosphate, that can help to remineralize tooth enamel, strengthening it and making it more resistant to decay. Chewing gum also aids in the removal of food particles and bacteria from the teeth and gums, reducing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Research has shown that chewing sugar-free gum for at least 20 minutes after meals can significantly reduce the risk of cavities. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Dental Research found that chewing sugar-free gum for 20 minutes after meals reduced the acidity levels in the mouth and increased salivary flow, leading to a reduced risk of cavities. This makes chewing gum a convenient and enjoyable way to help maintain oral health on the go. However, it is important to note that chewing gum should not replace regular brushing and flossing, but rather be used as a complementary tool in your oral hygiene routine.

Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. It is a clear liquid that is continuously produced by our salivary glands, with an average daily production of about 1 to 2 liters. Saliva is made up of water, electrolytes, enzymes, and proteins, and it serves several important functions in our mouths.
One of the primary functions of saliva is to aid in the digestion process. The enzymes present in saliva, such as amylase, help break down food particles and facilitate the initial stages of digestion. Saliva also helps to lubricate food, making it easier to chew and swallow. This process is particularly important for individuals who have difficulty swallowing or have dry mouth conditions.
Additionally, saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal oral health by neutralizing acids in the mouth and preventing tooth decay. When we eat or drink, acids can be produced by bacteria in our mouths or from the food and beverages themselves. Saliva helps to wash away these harmful acids, reducing their impact on tooth enamel. It also contains substances that have antimicrobial properties, which help to control the growth of bacteria and prevent infections in the oral cavity.
Moreover, saliva helps to maintain a healthy pH balance in the mouth. A balanced pH level is essential for the overall health of our teeth and gums. When the pH level becomes too acidic, it can lead to tooth erosion and an increased risk of cavities. On the other hand, a pH level that is too alkaline can disrupt the natural balance of oral bacteria, potentially causing gum disease.
In conclusion, saliva plays a vital role in maintaining oral health. Its functions, such as aiding in digestion, neutralizing acids, and controlling bacterial growth, are crucial for preventing dental problems. Understanding the significance of saliva and taking steps to promote its production and health can greatly contribute to maintaining a healthy mouth.
Chewing gum has long been hailed for its potential as an aid in plaque removal. The act of chewing helps to stimulate saliva production, which in turn can help to wash away harmful bacteria and food particles that contribute to the formation of plaque. Saliva contains enzymes that can break down and neutralize the acids produced by bacteria, preventing them from wearing away tooth enamel and causing decay.
Studies have shown that chewing sugar-free gum for just 20 minutes after a meal can significantly increase saliva flow, effectively reducing plaque build-up. In fact, one study conducted by the American Dental Association found that chewing sugar-free gum after meals reduced the levels of bacteria associated with dental decay by up to 50%. Additionally, the physical act of chewing can help to dislodge food particles that may be stuck between teeth, further aiding in plaque removal.
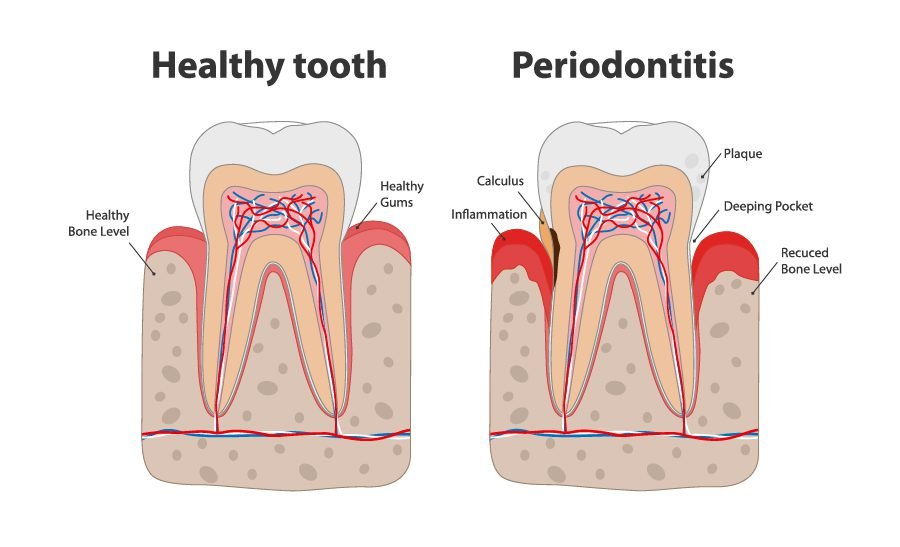
Chewing gum is a popular habit for many people, whether it’s to freshen breath, satisfy a craving, or simply keep the mouth busy. But have you ever wondered about the impact of chewing gum on tooth enamel? The enamel, which is the hard outer layer of the teeth, plays a crucial role in protecting the underlying dentin and pulp from damage and decay.
According to experts, chewing gum, especially sugar-free gum, can actually have a positive effect on tooth enamel. Research has shown that regular gum chewing stimulates the production of saliva, which in turn helps to neutralize acids and rinse away food particles that can contribute to enamel erosion. Additionally, chewing gum can increase saliva flow and enhance the remineralization process, where essential minerals like calcium and phosphate are redeposited onto the enamel, strengthening its structure. However, it’s important to note that excessive chewing or chewing gum that contains sugar can have the opposite effect and contribute to enamel erosion and tooth decay.
Therefore, it’s crucial to choose sugar-free gum and chew it in moderation to reap the benefits while minimizing the risks to tooth enamel.
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a common condition that occurs when the salivary glands do not produce enough saliva to keep the mouth moist. This can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms, including a dry or sticky feeling in the mouth, difficulty in swallowing or speaking, a persistent sore throat, and an increased risk of oral health problems such as tooth decay and gum disease. While there are several causes of dry mouth, including certain medications, radiation therapy, and autoimmune disorders, chewing gum has emerged as a potential aid in preventing and alleviating this condition.
Chewing gum stimulates the production of saliva, known as salivary flow. When you chew gum, the mechanical action of your jaw and tongue increases the flow of saliva in your mouth. This can help to moisten and lubricate the oral tissues, providing relief from the discomfort of dry mouth. Additionally, saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing harmful acid produced by bacteria, washing away food debris and bacteria, and remineralizing the tooth enamel. Therefore, chewing gum can potentially serve as a natural remedy for dry mouth, promoting saliva production and helping to maintain a healthy oral environment.
Chewing gum has long been touted as a solution to bad breath, but does it actually live up to the hype? Well, the answer may surprise you. While chewing gum cannot completely eliminate the underlying causes of bad breath, it can provide a temporary solution by masking unpleasant odors.
One of the main benefits of chewing gum is that it increases saliva production. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health as it helps to wash away food particles and bacteria that can contribute to bad breath. By stimulating saliva flow, chewing gum can help to freshen breath and reduce the presence of odor-causing bacteria in the mouth. Additionally, some chewing gums contain ingredients like menthol or cinnamon that provide a pleasant and minty aroma, further enhancing the breath-freshening effect. However, it’s important to note that chewing gum is not a substitute for proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, as these are the most effective ways to address the root causes of bad breath.
While chewing gum can offer a quick fix for bad breath, it’s important to choose sugar-free options. Sugary gums can actually contribute to dental issues such as tooth decay and cavities. By opting for sugar-free chewing gum, you can enjoy the breath-freshening benefits without compromising your oral health. So, next time you find yourself reaching for a mint, consider grabbing a piece of sugar-free gum instead for a quick and convenient solution to combat bad breath.

Tooth sensitivity is a common dental problem that can cause discomfort and pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and beverages. It occurs when the tooth enamel wears down or when the gum line recedes, exposing the dentin underneath. Many individuals seek solutions to alleviate this sensitivity and improve their quality of life. One potential option that has gained attention is chewing gum.
Chewing gum has been suggested as a potential aid in reducing tooth sensitivity. The act of chewing stimulates the production of saliva, which has several protective properties for the teeth. Saliva helps to neutralize acids in the mouth, remineralize the tooth enamel, and flush away food particles and bacteria. Additionally, saliva contains minerals such as calcium and phosphate, which can help strengthen and protect the teeth. By promoting saliva production, chewing gum may help in reducing tooth sensitivity by providing a protective barrier and aiding in the remineralization process. However, further research is needed to determine the specific effects of chewing gum on tooth sensitivity and its long-term benefits.
Dental cavities, commonly referred to as tooth decay, are a prevalent oral health issue affecting individuals of all ages. The primary cause of dental cavities is the accumulation of plaque on the teeth, which, if left unchecked, can lead to enamel erosion and eventual tooth decay. As oral health professionals, we are constantly seeking ways to combat this problem and promote optimal dental health. One method that has gained attention in recent years is the use of chewing gum.
It is important to note that not all chewing gum is created equal when it comes to its impact on dental health. Sugar-free chewing gum has been found to have a positive influence in preventing dental cavities. The act of chewing stimulates the production of saliva, which plays a crucial role in neutralizing the acids produced by oral bacteria and remineralizing tooth enamel. Additionally, chewing gum can help remove food particles and debris from the teeth, reducing the risk of plaque formation. However, it is essential to choose gum that is sweetened with non-cariogenic substances, such as xylitol, as this can further enhance its protective effects.
Choosing the right chewing gum can play a crucial role in maintaining optimal oral health. Opting for sugar-free chewing gum is particularly important for several reasons. Firstly, sugar-free gum does not contribute to the formation of dental cavities, unlike gum that contains sugar. When we consume sugary foods or drinks, the bacteria in our mouths feed on the sugars and produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. By choosing sugar-free gum, we can enjoy the benefits of chewing gum without the risk of tooth decay.
Secondly, sugar-free gum stimulates the production of saliva, which is essential for maintaining oral health. Saliva helps to neutralize harmful acids, remineralize tooth enamel, and wash away food particles and bacteria that can lead to plaque formation. This natural defense mechanism also helps to prevent dry mouth, a condition that can increase the risk of dental cavities and other oral health problems. By chewing sugar-free gum, we can promote saliva production and support the overall health of our teeth and gums.
In conclusion, selecting sugar-free chewing gum is a wise choice for maintaining optimal oral health. By avoiding the sugars that contribute to dental cavities and embracing the benefits of saliva stimulation, we can enjoy the advantages that chewing gum offers without compromising our teeth and gums. So, next time you reach for a pack of gum, remember to choose sugar-free options to protect your smile and support your oral health.
Chewing gum can be a convenient and enjoyable habit for many people, but it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects it can have on oral health. While chewing gum can have some benefits, such as increasing saliva production and reducing dry mouth, there are also certain factors to consider.
One potential risk of chewing gum is that it can contribute to teeth grinding, also known as bruxism. The repetitive motion of chewing gum can put strain on the jaw joint and cause excessive wear and tear on the teeth. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, jaw pain, headaches, and even damage to dental restorations.
Another concern is the sugar content in some chewing gum products. Regular gum that contains sugar can increase the risk of cavities and tooth decay. The sugar provides a food source for the bacteria in the mouth, which produces acids that can erode the enamel and lead to dental problems. Opting for sugar-free gum is a better choice for oral health, as it doesn’t contribute to decay-causing bacteria.
| Potential Risks/Side Effects | Description |
|---|---|
| Tooth Decay | Chewing gum containing sugar can increase the risk of tooth decay by providing a food source for bacteria in the mouth, which produce acids that attack tooth enamel. |
| Jaw Problems | Excessive chewing, especially with gum that contains sugar or is overly hard, can lead to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, causing pain, clicking, or popping in the jaw joint area. |
| Dental Erosion | Chewing gum with acidic ingredients, such as citric acid or phosphoric acid, may contribute to dental erosion by weakening tooth enamel over time, making teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity. |
| TMJ Discomfort | Prolonged chewing can strain the muscles and ligaments around the jaw joint, leading to discomfort or pain in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). |
| Increased Saliva Production | Chewing gum stimulates saliva production, which can be beneficial for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles. However, excessive saliva production may contribute to nausea or discomfort for some individuals. |
| Potential for Dental Work Damage | Chewing gum excessively or aggressively may dislodge dental work such as fillings, crowns, or bridges, especially if they are loose or poorly fitted. |
| Sugar Alcohol Side Effects | Some sugar-free gums contain sugar alcohols like xylitol or sorbitol, which, when consumed in large amounts, can cause gastrointestinal issues like bloating, gas, or diarrhea. |
| Oral Tissue Irritation | Certain gums may contain ingredients that can irritate oral tissues, leading to discomfort or allergic reactions in some individuals. |
Chewing gum can be a valuable addition to your oral health routine, helping to promote optimal oral health when used correctly. Incorporating chewing gum into your daily routine can help stimulate saliva production, which plays a crucial role in maintaining good oral health. Saliva helps to neutralize acids in the mouth, wash away food particles, and remineralize tooth enamel.
To maximize the benefits of chewing gum for your oral health, it is important to select sugar-free gum. Sugar-free gum eliminates the risk of promoting tooth decay and cavities. When choosing a gum, look for options that carry the American Dental Association (ADA) seal of approval. This seal ensures that the gum has met certain standards for safety and efficacy. Additionally, consider opting for gum with xylitol, a natural sugar substitute that has been shown to have beneficial effects on oral health. Xylitol can help reduce the risk of cavities by inhibiting the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay.
| Time of Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| After meals | Chew sugar-free gum for about 20 minutes |
| Throughout day | Drink water to help rinse away food particles |
| Chew gum after snacks if unable to brush | |
| Before bed | Brush teeth and floss thoroughly |
Chewing gum has long been associated with jaw muscle activity, leading to concerns about its potential impact on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and the development of TMJ disorder. The TMJ is a hinge joint that connects the jawbone to the skull, allowing for the movement needed for activities like chewing and talking. It is essential for maintaining proper jaw function and overall oral health.
While some studies suggest that excessive gum chewing can contribute to jaw muscle fatigue and strain, leading to TMJ dysfunction, the evidence on this topic is limited. The impact of chewing gum on TMJ health is still a subject of ongoing research, and more comprehensive studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions. However, it is worth noting that individuals already experiencing TMJ disorder or jaw pain may want to exercise caution when it comes to chewing gum, as it could potentially exacerbate their symptoms.
In conclusion, the relationship between chewing gum and its impact on jaw muscles and TMJ disorder is still not fully understood. While some concerns have been raised about the potential strain on the TMJ, more research is needed to determine the true extent of this impact. Individuals with existing TMJ disorder or jaw pain may want to consult with a dental professional for personalized advice on whether chewing gum is suitable for their specific situation.
Chewing gum has long been touted as a remedy for various digestive issues, including post-meal acid reflux. But how exactly does it help in alleviating this uncomfortable condition? The answer lies in the mechanism of chewing and its effects on the digestive system.
When you chew gum after a meal, it stimulates the production of saliva. Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing stomach acids that may have refluxed back into the esophagus. Additionally, the act of chewing increases the frequency of swallowing, which helps to push the stomach acid back down and prevent it from causing heartburn.
Furthermore, chewing gum has been shown to increase the production of bicarbonate, a natural buffer that helps to counteract excess stomach acid. This can provide immediate relief from post-meal acid reflux symptoms. However, it’s important to note that chewing gum is not a substitute for medical treatment, especially for individuals with chronic acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Instead, it can be used as a temporary solution or in conjunction with other lifestyle changes and medications as advised by a healthcare professional.
Overall, while chewing gum may provide temporary relief from post-meal acid reflux, it is crucial to address the underlying causes of this condition and seek appropriate medical advice. Regular dental check-ups, a balanced diet, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits are key to maintaining optimal oral and digestive health.
Chewing gum has long been known as a tool for stress relief, providing a simple and convenient way to alleviate tension and promote a sense of relaxation. Many individuals turn to chewing gum as a means to manage stress in their daily lives. But how does this seemingly simple act of chewing gum affect our oral health?
When it comes to stress relief, chewing gum can indeed offer some benefits. One study published in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation found that chewing gum can help reduce stress levels and improve mood. This is believed to be due to the rhythmic motion of chewing, which stimulates the release of hormones that promote relaxation.
However, it is important to note that indulging in chewing gum for stress relief should be done in moderation, as excessive gum chewing may have negative effects on oral health. The constant stimulation of the jaw muscles from excessive chewing can lead to muscle fatigue and discomfort in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Additionally, some chewing gum products contain sugar, which can contribute to dental cavities if proper oral hygiene practices are not followed. Therefore, it is advisable to choose sugar-free gum to minimize the risk of tooth decay.
Chewing gum has long been hailed as a convenient and pleasurable way to freshen breath and improve oral health. But can it truly serve as a viable alternative to brushing and flossing? This is a question that has intrigued dental professionals and researchers alike.
While chewing gum can provide a temporary reprieve from bad breath and stimulate saliva production, it should not be viewed as a substitute for regular brushing and flossing. The mechanical action of brushing and flossing is necessary to physically remove plaque and food particles from the teeth, which gum alone cannot achieve.
That being said, chewing sugar-free gum after meals or snacks can be a useful adjunct to proper oral hygiene practices. Studies have shown that chewing gum for 20 minutes following a meal can help to increase saliva flow and neutralize acids in the mouth, thereby reducing the risk of tooth decay. Additionally, the act of chewing gum can stimulate the release of antibacterial substances in saliva, which can help to inhibit the growth of cavity-causing bacteria. However, it is worth noting that while chewing gum can provide some benefits, it should never replace the foundation of good oral hygiene – regular brushing and flossing.
Chewing gum has long been a favorite pastime for many, providing a burst of refreshing flavor and a satisfying chewing experience. But did you know that chewing gum can also have benefits for your oral health? Studies have shown that chewing gum can help stimulate saliva production, which plays a vital role in maintaining oral health. Saliva helps to neutralize the acids in our mouth, repair damaged tooth enamel, and wash away food particles and bacteria that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
In addition to saliva production, chewing gum has also been found to potentially aid in plaque removal. As we chew, the act of mastication can help dislodge plaque and bacteria from the nooks and crannies of our teeth, making it easier for our saliva to wash them away. Some studies have even suggested that chewing gum after meals can be an effective way to reduce plaque buildup in between brushing sessions. However, it’s important to note that chewing gum should never be a substitute for proper brushing and flossing techniques, but rather a supplemental tool in maintaining good oral hygiene.
Chewing gum can have various effects on oral health, such as increasing saliva production, aiding in plaque removal, preventing dry mouth, potentially reducing bad breath, and helping with post-meal acid reflux.
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids, washing away food particles, remineralizing tooth enamel, and preventing dry mouth.
Yes, chewing gum can potentially aid in plaque removal by stimulating saliva flow, which can help wash away plaque-causing bacteria from the surface of the teeth.
Chewing gum, especially sugar-free gum, does not have a negative impact on tooth enamel. In fact, some studies suggest that certain types of gum can help remineralize and strengthen tooth enamel.
Chewing gum can help prevent dry mouth by stimulating saliva production, which can lubricate the oral tissues and reduce the discomfort associated with dry mouth.
Chewing gum, particularly sugar-free gum, can help reduce bad breath by increasing saliva flow, which can wash away odor-causing bacteria and freshen breath temporarily.
Some research suggests that certain types of chewing gum containing desensitizing agents may help reduce tooth sensitivity by blocking pain signals. However, further studies are needed to establish its effectiveness.
Sugar-free chewing gum can potentially reduce the risk of dental cavities by stimulating saliva production, which helps neutralize acids, wash away food particles, and remineralize tooth enamel.
Sugar-free chewing gum is important for oral health because it does not contribute to tooth decay. Chewing gum containing sugar can increase the risk of cavities.
While chewing gum is generally considered safe, excessive chewing or chewing gum with certain ingredients may lead to jaw muscle fatigue or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. It is important to use moderation and choose gum without harmful additives.
An ideal chewing gum routine for optimal oral health involves chewing sugar-free gum for about 20 minutes after meals or snacks to stimulate saliva flow and aid in the removal of food particles.
Excessive chewing or chewing gum with excessive force can potentially strain the jaw muscles and contribute to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder. It is important to chew gum in moderation and avoid excessive force.
Chewing gum after meals can help with post-meal acid reflux by stimulating saliva production, which helps neutralize stomach acid and reduce the symptoms of acid reflux.
Chewing gum can provide stress relief for some individuals by promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. However, excessive chewing or chewing gum with added sugars may have negative effects on oral health.
Chewing gum cannot replace the importance of brushing and flossing for maintaining good oral hygiene. While it can provide temporary benefits, regular brushing and flossing are essential for removing plaque and preventing dental issues.
It is important to note that excessive chewing or chewing gum with certain ingredients may lead to digestive issues, such as bloating or stomach discomfort. It is advisable to use gum in moderation and consult a dentist if any concerns arise.