Table of Contents
Signs of Healthy Gums

Healthy gums are essential for overall oral health. One of the key indicators of gum health is firm and pink gums. Healthy gums should not be swollen, tender, or bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing. Another sign of well-maintained gums is the absence of persistent bad breath, as this can be a sign of underlying gum disease.
In addition to the physical appearance of the gums, a healthy gum line should snugly fit around each tooth without any signs of recession. Proper gum health is also reflected in the absence of pain or sensitivity in the gum tissue. Regular dental check-ups can help in monitoring the health of your gums and catching any potential issues early on.
Importance of Gum Health
Healthy gums are essential for overall oral health. The gums serve as a protective barrier for the teeth and bone that support them, helping to prevent infections and other dental issues. Neglecting gum health can lead to serious consequences, including gum disease, tooth loss, and even systemic health problems. Therefore, maintaining healthy gums is crucial for both oral health and general well-being.
When it comes to the importance of gum health, prevention is key. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing regularly, attending regular dental check-ups, and following a nutritious diet, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing gum disease. Investing time and effort into gum health not only ensures a beautiful smile and fresh breath but also contributes to a lower risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other serious health conditions.
Common Gum Problems
Gum problems are a common issue that many individuals encounter, impacting their overall oral health. One prevalent gum problem is gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe condition called periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected. This advanced stage of gum disease can lead to bone loss and eventual tooth loss if not addressed promptly by a dental professional.
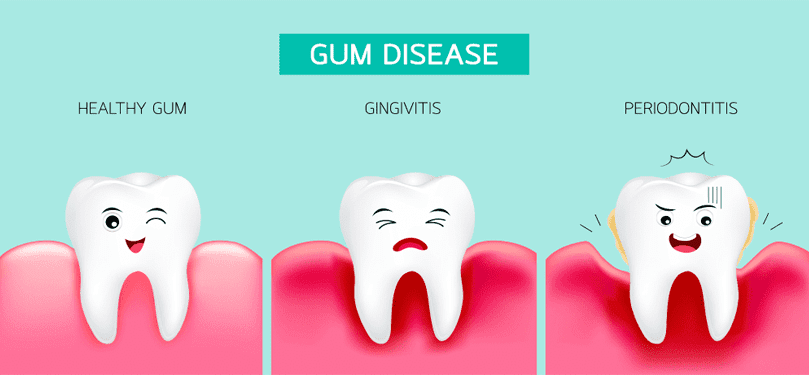
Another common gum problem is gum recession, where the gum tissue pulls back from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. This can result in increased sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, as well as aesthetic concerns due to the appearance of longer teeth. Gum recession can be caused by factors such as aggressive brushing, periodontal disease, or genetic predisposition. Addressing gum problems early through proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups is crucial in preventing these conditions from progressing and affecting your oral health.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene practices that lead to the accumulation of plaque on the teeth and gums. When plaque is not adequately removed through brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which harbors harmful bacteria that irritate the gums and cause inflammation. This initial stage of gum disease is called gingivitis and is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of gum disease known as periodontitis. In periodontitis, the inflammation spreads below the gum line, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth and form pockets that become infected. The body’s immune response to these infections can lead to damage of the surrounding bone and tissues that support the teeth, ultimately resulting in tooth loss if not addressed promptly and effectively. In addition to poor oral hygiene, factors such as smoking, genetics, hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions can also contribute to the development and progression of gum disease.
Preventive Measures for Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common and preventable condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. Implementing preventive measures is crucial to maintaining optimal gum health and preventing the onset of gum disease. One of the key preventive measures for gum disease is maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing the teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and using an interdental cleaner, like dental floss or an interdental brush, to remove plaque and food debris from between the teeth.

In addition to proper oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups play a significant role in preventing gum disease. Professional dental cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be effectively removed through at-home oral care. During dental check-ups, dentists can also identify early signs of gum disease and provide guidance on how to address any oral health concerns. By incorporating these preventive measures into your oral care routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease and maintain optimal gum health.
Proper Brushing Techniques for Gum Health
Brushing your teeth is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal gum health. Proper brushing techniques not only help in removing plaque and food debris but also play a significant role in preventing gum disease. To ensure effective cleaning, hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle against the gum line and use gentle circular motions to massage the gums and clean the teeth thoroughly. Remember to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the inner, outer, and chewing surfaces, for at least two minutes each time you brush.
In addition to the correct brushing technique, it’s essential to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid damaging the gums and enamel. Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed. Incorporating fluoride toothpaste in your brushing routine can also help strengthen your tooth enamel and prevent cavities. Don’t forget to brush your tongue gently to remove bacteria and freshen your breath. By mastering the art of proper brushing, you are taking a proactive step towards promoting gum health and overall oral hygiene.
The Role of Flossing in Gum Health
Flossing is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal gum health. While brushing cleans the surfaces of our teeth, flossing plays a key role in removing plaque and food particles trapped between the teeth and along the gum line. These areas are especially prone to bacterial buildup which, if left unchecked, can lead to gum disease and other oral health issues.

Regular flossing not only helps in preventing gum disease but also contributes to freshening breath and promoting overall oral hygiene. By incorporating flossing into your daily dental routine, you are effectively targeting hard-to-reach areas where bacteria tend to thrive, thus reducing the risk of inflammation and infection in the gums. Remember, a few minutes dedicated to flossing each day can go a long way in safeguarding your gum health and overall well-being.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are an integral part of maintaining optimal oral health. These routine visits allow dental professionals to assess the condition of your gums, teeth, and overall oral cavity, detecting any potential issues early on. Early detection of dental problems can prevent more serious issues from arising, ultimately saving you time, money, and potential discomfort in the long run. Dentists are trained to identify signs of gum disease, cavities, oral cancer, and other oral health concerns during these check-ups, enabling timely intervention and treatment if needed.
In addition to identifying and addressing oral health issues, regular dental check-ups also play a crucial role in preventive care. Through professional cleanings and screenings, dentists can remove plaque and tartar buildup that regular brushing and flossing might miss, reducing the risk of developing gum disease and other dental problems. Furthermore, dental check-ups provide an opportunity for dentists to educate patients on proper oral hygiene practices, including brushing techniques, flossing habits, and the importance of a balanced diet for overall oral health. By attending regular dental appointments, individuals can proactively care for their oral health and contribute to a healthy smile for years to come.
Impact of Diet on Gum Health
A diet plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal gum health. Foods rich in vitamins C and D, as well as antioxidants like green tea, can help reduce inflammation and promote healing in the gums. On the other hand, a diet high in sugars and processed foods can contribute to the development of gum disease by feeding harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Incorporating fibrous fruits and vegetables into your diet can also benefit your gum health by stimulating saliva production and aiding in the removal of plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums. Additionally, consuming foods with high water content, such as cucumbers and watermelon, can help keep your mouth hydrated and wash away food particles that may lead to gum disease. Remember, what you eat not only impacts your overall health but also plays a significant role in the health of your gums.
The Connection Between Gum Health and Overall Health
Maintaining healthy gums is not only vital for your oral well-being but also plays a crucial role in your overall health. Studies have consistently shown a strong connection between gum health and various systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and even pregnancy outcomes. Research suggests that the bacteria and inflammation associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation in other parts of the body and potentially exacerbating existing health issues.
| Aspect of Health | Gum Health |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Health | Gum disease may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. |
| Diabetes | Diabetes increases the risk of gum disease, and gum disease can make diabetes harder to control. |
| Respiratory Health | Gum disease may worsen respiratory conditions like COPD. |
| Pregnancy | Gum disease increases the risk of premature birth and low birth weight. |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Some research suggests a link between gum disease and Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Periodontal disease may be linked to rheumatoid arthritis. |
| Immune System | Poor gum health can weaken the immune system’s ability to fight infections. |
Furthermore, gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of developing conditions like diabetes and heart disease. For instance, individuals with gum disease tend to have a harder time controlling their blood sugar levels, which can worsen diabetic symptoms. Similarly, the inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to the formation of plaque in arteries, potentially leading to heart disease or stroke. By prioritizing your gum health, you are not only safeguarding your smile but also taking a proactive step towards maintaining your overall health and well-being.
Effective Home Remedies for Gum Health
When it comes to maintaining healthy gums, there are several effective home remedies that can help support your overall gum health. One simple yet powerful remedy is saltwater rinse, which can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth. To make a saltwater rinse, mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and swish it around in your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out. This can be done several times a day to promote gum health.
Another beneficial home remedy for gum health is oil pulling, a traditional Ayurvedic practice that involves swishing oil in your mouth to remove bacteria and improve overall oral hygiene. Coconut oil is commonly used for oil pulling due to its antimicrobial properties. Simply swish a tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for about 15-20 minutes, then spit it out and rinse your mouth with water. Oil pulling can be incorporated into your daily oral care routine to help support healthy gums.
Professional Treatments for Gum Disease
For individuals with advanced gum disease, professional treatments are often necessary to alleviate symptoms and prevent further progression of the condition. One common procedure used to treat gum disease is scaling and root planing, also known as a deep cleaning. This process involves the removal of plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line, as well as smoothing out the roots of the teeth to promote gum reattachment and reduce the risk of bacterial accumulation.
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be required to address deep pockets or damaged gum tissue. Procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafting, or soft tissue grafts may be recommended by your dentist or periodontist to restore gum health and improve overall oral hygiene. It is essential to follow post-operative instructions diligently and attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress and ensure the success of the treatment.
The Benefits of Using Mouthwash for Gum Health
Mouthwash is a valuable addition to your daily oral hygiene routine, especially when it comes to promoting gum health. Research has shown that using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the buildup of plaque, which is a leading cause of gum disease. By incorporating mouthwash into your regimen, you can target the bacteria that brushing and flossing might miss, providing an extra layer of defense against gum issues.
Furthermore, mouthwash can aid in reducing inflammation in the gums, which is a common symptom of gingivitis. By swishing with an antimicrobial mouthwash, you can help to kill the harmful bacteria that contribute to gum inflammation, keeping your gums healthy and free from infection. Regular use of mouthwash as part of a comprehensive oral care routine can be an effective way to maintain optimal gum health and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Potential Complications of Ignoring Gum Health
Neglecting the health of your gums can have serious repercussions on your overall well-being. Untreated gum disease can lead to various complications that extend beyond just oral health. One of the main consequences of ignoring gum health is the risk of periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease that can result in tooth loss. This advanced stage of gum disease can also contribute to bone loss in the jaw, which can further exacerbate dental problems.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Initial stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums due to plaque buildup. |
| Periodontitis | Advanced stage of gum disease where infection spreads to the supporting structures of the teeth. |
| Tooth loss | Untreated gum disease can lead to the destruction of the bone and tissues supporting the teeth. |
| Gum recession | The gums may recede or pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and making them more sensitive. |
| Bad breath (halitosis) | Bacteria in the mouth caused by poor gum health can lead to persistent bad breath. |
| Abscesses | Pockets of pus can form in the gums due to bacterial infection, leading to pain and swelling. |
| Cardiovascular complications | Studies suggest a link between gum disease and heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues. |
| Complications during pregnancy | Gum disease during pregnancy can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, and other complications. |
| Diabetes complications | Gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels, leading to complications for diabetic patients. |
| Jawbone deterioration | Advanced gum disease can result in the loss of jawbone density, affecting the structure and stability of the jaw. |
Moreover, research has shown a clear link between gum disease and systemic health issues such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. The inflammation and bacteria associated with untreated gum disease can enter the bloodstream and affect other parts of the body, increasing the risk of developing these serious medical conditions. It is essential to prioritize gum health as part of your overall health and wellness routine to prevent these potentially life-threatening complications.
The Role of Genetics in Gum Health
The health of our gums can be greatly influenced by genetics. Studies have shown that certain genetic factors can predispose individuals to a higher risk of developing gum disease. Research indicates that variations in specific genes can impact the body’s inflammatory response, ultimately affecting the susceptibility of gums to infection and inflammation. This genetic predisposition may make some individuals more prone to gum problems, even with diligent oral hygiene habits in place.
Understanding the role of genetics in gum health can help individuals with a family history of gum disease take proactive measures to prevent its onset. By being aware of genetic influences, individuals can work closely with their dentists to develop personalized oral care plans that address their specific needs and risks. While genetics play a significant role in gum health, it is essential to remember that lifestyle factors, such as diet, oral hygiene practices, and regular dental visits, also play a crucial role in maintaining healthy gums.
Can genetics play a role in gum health?
Yes, genetics can influence an individual’s susceptibility to gum disease. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing periodontal problems, even if they practice good oral hygiene.
How can someone determine if their gum problems are due to genetics?
A dentist can assess your family history and examine your oral health to determine if genetics may be a contributing factor to your gum issues.
Are there genetic tests available to determine one’s risk for gum disease?
While there are some genetic tests available to assess the risk of developing certain oral health conditions, such as periodontitis, they are not commonly used in routine dental practice.
Can genetic factors affect the effectiveness of preventive measures for gum disease?
Genetic factors can influence how well certain preventive measures, such as brushing and flossing, work in maintaining gum health. Individuals with a genetic predisposition to gum disease may need to be more vigilant with their oral hygiene routines.
Is there anything someone with a genetic predisposition to gum disease can do to minimize their risk?
While genetics can play a role in gum health, practicing good oral hygiene, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding tobacco use, and regular dental check-ups can help minimize the risk of developing gum disease, even with genetic factors at play.