Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
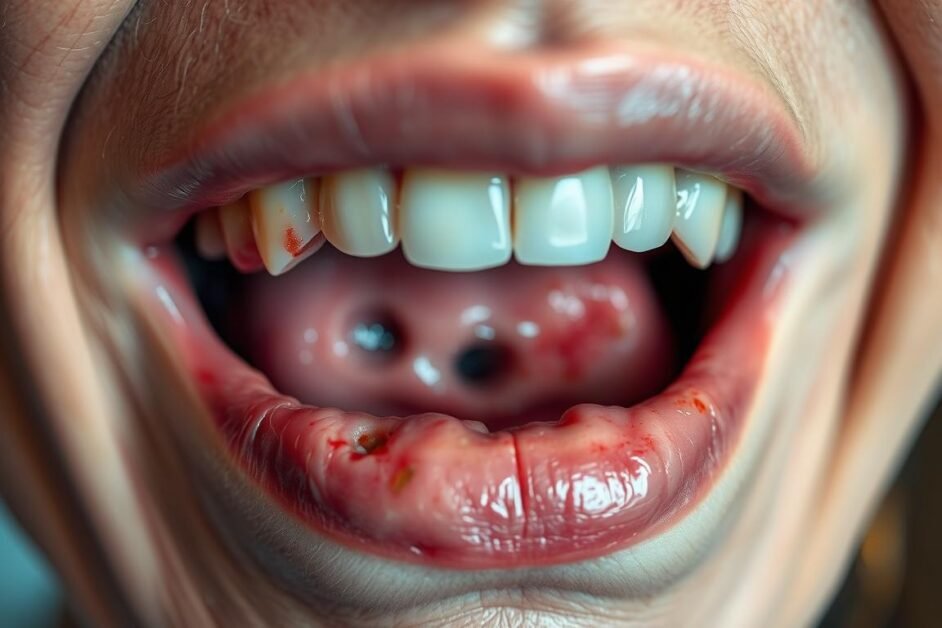
Discover the early signs and treatments of mouth cancer. Learn to spot symptoms like ulcers, lumps, and white spots on gums for prompt action.
Imagine waking up with a sore in your mouth that won’t heal. It stays for weeks, a painful sign that something’s off. For many, this is a harsh reality when facing mouth cancer. With over 54,000 new cases in the U.S. each year, knowing the early signs and symptoms of mouth cancer is crucial.
Mouth cancer can appear anywhere in the mouth, like the gums or tongue. Catching it early is vital for better treatment. Sadly, almost 43% of cases are found late, making treatment harder. Symptoms like sores can last over two weeks in 80% of cases. Regular dental visits are key to spotting these signs early.
This article will help you spot the early signs of mouth cancer. It’s about being proactive for your health. For more on why dental check-ups are important, check out this guide.
Mouth cancer is another name for oral cancer. It happens in the mouth area, including lips, gums, and tongue. It starts in the squamous cells, leading to tumors. Knowing about mouth cancer helps spot early signs and get medical help fast.
Oral cancer is a big health issue, making up 3% of all cancers in the U.S. In 2022, there were about 54,000 new cases. People over 40 and men are more at risk. Tobacco and alcohol use are the main causes, with tobacco and alcohol together being the biggest risk.
Recently, more cases of oral cancer are linked to Human Papillomavirus (HPV), type 16. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type. Regular dental checks help catch cancer early, making treatment easier.

Oral cancer risk factors are key to understanding its development. Tobacco use is a major contributor, leading to more cases of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. This is true for those who have smoked or been exposed to tobacco.
Drinking a lot of alcohol also raises the risk, more than drinking a little. When you smoke and drink a lot, the risk goes up even more. People who do both are about 30 times more likely to get these cancers than those who don’t.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is another big factor, found in about 67% of oropharyngeal cancers. It affects younger people, often those with many sexual partners and no tobacco or alcohol use. Men get these cancers more often than women, likely because they used to smoke and drink more.
Getting older also increases the risk, with people over 55 more likely to get these cancers. But, cancers linked to HPV happen more in those under 50. People who work outside a lot are at higher risk for lip cancers. Eating too few fruits and vegetables also makes you more likely to get oral cancers.
People with weak immune systems, like those with HIV/AIDS, are at higher risk. Genetic conditions like Fanconi anemia also raise the risk, but studies don’t give exact rates.
Knowing the causes of mouth cancer and risk factors helps in preventing it. Being aware can lead to healthier choices and better screening.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Tobacco Use | Includes smoking and other forms of tobacco. | Strongly increases risk of oral cancers. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Heavy drinking elevates risk significantly. | Greater risk when combined with tobacco use. |
| HPV Infection | Found in a majority of oropharyngeal cancers. | Increasing incidence in younger, non-drinkers. |
| Age | Higher risk for individuals over 55. | HPV-related cancers more common in younger adults. |
| Diet | Low consumption of fruits and vegetables. | Linked to increased oral cancer risk. |
| Immune Suppression | Higher risk for those with weakened immune systems. | Increased vulnerability to various cancers. |
| Environmental Exposure | Prolonged sun exposure for outdoor workers. | Increased risk for lip cancer. |
Knowing the early signs of mouth cancer is key to getting timely treatment. Spotting these signs early can prevent serious health issues. Being aware of oral cancer symptoms helps you take care of your health.
Potential early signs of mouth cancer include:
If symptoms last more than two weeks, see a doctor. Look out for a flat, painless white or red spot, or a small sore in the mouth.
Finding oral cancer early is crucial. It greatly improves treatment chances. Regular dental visits help catch signs of oral cancer early.
Being aware of mouth cancer signs leads to quick action. This is key for better survival rates.
| Symptom | Significance |
|---|---|
| Persistent sores | May indicate ongoing oral health issues |
| White or red patches | Can be an early sign of precancerous changes |
| Lumps or growths | May signify tumor development |
| Mouth pain | Can signal infection or malignancy |
| Difficulties in swallowing | Could suggest advanced disease |
Being proactive about oral health is crucial. Awareness leads to early diagnosis and better treatment options.
Mouth cancer shows different signs that are important to spot early. You might see white patches or leukoplakia, which mean abnormal cells are growing. Also, look out for red patches called erythroplakia. These are more likely to turn into cancer than white patches.
Lumps and sores that don’t go away are also warning signs. They should last no more than two weeks. If they stick around, it could mean cancer.
Ulcers are another sign of cancer inside the cheek. These sores don’t heal and might look crusted. If any mouth patch starts bleeding on its own, see a doctor right away. It could be a sign of cancer.
Knowing what mouth cancer looks like is key to catching it early. If oral patches change, like they hurt more, bleed, or grow, get checked by a doctor fast.
Spotting mouth cancer symptoms early is key to a good treatment and recovery. Oral cancer signs can differ from person to person. Yet, some visual signs and feelings are often a sign of the disease.
It’s important to watch for visual signs that might mean mouth cancer. Common symptoms include:
These changes can be early warnings. Regular self-checks can help spot these signs early. This leads to quicker visits to healthcare professionals.
Oral cancer symptoms aren’t just visual. Many people also feel discomfort, such as:
Feeling these symptoms might mean there’s a problem. It’s important to see a doctor if these feelings last. Recognizing these symptoms can greatly improve treatment results.
It’s crucial for both dentists and patients to know the signs of oral cancer. Spotting mouth cancer symptoms early is key. Look out for sore throats, numbness in the mouth, and changes in how teeth fit together.
Regular dental visits are important. They let dentists check for these signs early on.
Other signs include ulcers that won’t heal and red or white patches in the mouth. Also, lumps and swellings in the head or neck are warning signs. Trouble swallowing could mean oral cancer is getting worse.
Even without a national screening program, dentists can spot problems. They use visual exams and fluorescence checks during visits. Knowing these symptoms helps you take care of your health. It also shows why regular dental visits are important.
Stay alert and proactive. For more on oral cancer signs, make sure to get your dental check-ups.
Knowing the early signs of mouth cancer is key for catching it early. Pictures help show symptoms like lesions, white patches, and sores that won’t go away. Looking at first signs of mouth cancer pictures helps people know what to look for. This way, they can spot oral cancer early and get medical help fast.
Here are some common early signs to look for:
Looking at first signs of mouth cancer pictures from trusted sources can help. Early detection is crucial and can greatly improve survival rates. With about 54,540 new cases of oral cancer each year in the U.S., knowing what to look for is vital.
Spotting oral cancer early is key to successful treatment. Many symptoms show up in the mouth, hinting at a problem. Catching these signs early helps get the right care, leading to better health.
Lesions or ulcers in the mouth can signal oral cancer. People might notice lumps or sores that don’t heal in two weeks. These signs need quick attention, as they might be early signs of cancer.
Regular dental visits are crucial. They help catch these symptoms early, thanks to dental professionals.
White or red patches in the mouth are also warning signs. A white patch is called leukoplakia, and a red one is erythroplakia. These can be signs of conditions that might turn into cancer.
It’s important to watch for these changes. Talking to a dentist can help catch problems early. This can greatly improve treatment chances.
Gum cancer is a type of mouth cancer. It can show up in several ways. It’s important to watch your mouth for any signs of gum cancer early on. Look out for:
If you notice any of these symptoms, talk to a doctor right away. Catching gum cancer early can help a lot. Regular dental visits are key to spotting problems early.
Not all gum changes mean gum cancer. But, taking care of your mouth is very important. If you see any of these signs, get help fast.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Swelling | Inflammation or enlargement of the gums that persists over time. |
| Persistent sores | Non-healing ulcers or sores that may be painful and concerning. |
| Bleeding gums | Unexplained bleeding that occurs without any traumatic cause. |
| Changes in texture | Rough patches or abnormal growths on the gum surface. |
| Pain | Unusual discomfort during normal chewing or speaking actions. |
Knowing about these symptoms can help catch gum cancer early. Take care of your gum health as part of your overall health plan.
Mouth cancer sores can look like common canker sores. They are painful and irritating. Canker sores usually heal in a week or two without treatment.
It’s important to watch how long these sores last. If they don’t go away after two weeks, you should see a doctor.
Persistent sores could mean a serious problem, like oral cancer. Oral cancer sores don’t heal and may not hurt as much as canker sores. Knowing when to get help is key. Oral cancer can get worse if not treated early.
Here are some symptoms that need quick attention:
Regular dental check-ups are important. Your dentist can do oral cancer screenings during these visits. If you’re looking for mouthwash to help with sores, check out recommended brands for oral healing.
Knowing the signs is key. If you see any of these symptoms and they last, see a doctor. Early action can prevent bigger problems.
Taking steps to prevent mouth cancer can greatly lower your risk. Every year, about 53,000 Americans are diagnosed with oral cancer. Being aware and taking action is key to oral cancer prevention.
Staying away from tobacco and drinking less alcohol are important steps. Heavy drinking and smoking together can increase your risk by 30 times. Women should limit their alcohol to one drink a day, and men to two.
Eating a diet full of fruits and veggies is also good for your mouth. Regular dental visits help catch problems early. You should see a dentist every 6 to 12 months.
Getting vaccinated against HPV can also help. This is important for people aged 9 to 26. It can lower the risk of HPV-related cancers. Also, practicing safe sex and having fewer partners can reduce HPV exposure.
Wearing sunscreen and lip balm with SPF 30 is crucial for protecting your skin and lips from cancer. These steps can help keep your mouth healthy and lower the risk of serious problems later.

For more tips on keeping your mouth safe, check out this resource.
| Preventative Measure | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Avoiding tobacco | Reduces overall cancer risk |
| Limiting alcohol intake | Decreases chances of mouth cancer |
| Regular dental check-ups | Enables early detection |
| Healthy diet | Supports oral health and reduces obesity risk |
| HPV vaccination | Protects against HPV-related cancers |
Managing mouth cancer requires a variety of treatments. These depend on the cancer’s stage, location, and the patient’s health. It’s important for patients and their families to understand these options. Treatments include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and new methods like immunotherapy.
Surgery is often the first step in treating mouth cancer. It involves removing the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. This helps prevent the cancer from coming back. If the cancer is more advanced, the doctor might need to rebuild the area with tissue from another part of the body.
For cancers that have spread, the doctor might remove lymph nodes. This is done through a procedure called neck dissection.
Radiation therapy is another common treatment. It uses beams of energy to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy is used in more serious cases, often with radiation. This combination is called chemoradiotherapy.
Targeted therapies can be very effective for some patients. These include drugs like cetuximab. Immunotherapy drugs, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, are also options. They work best when the tumor has a certain protein.
After treatment, regular check-ups are crucial. This is because cancer can come back, usually within two years. Eating a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables can help prevent this.
For more information on staying healthy during treatment, check out this resource on braces preparation.
Dealing with mouth cancer can be tough. Patients face physical, emotional, and mental challenges. Up to 70% of mouth cancer patients feel a lot of emotional pain during treatment.
It’s important to find support. Talking to doctors and joining local support groups can help a lot. These resources can make living with mouth cancer easier.
Support groups and educational resources are key. They let patients share their stories and learn how to deal with symptoms. Many say talking to others who understand has helped them a lot.
After treatment, it’s key to tackle nutritional and mental health issues. Some patients have trouble eating and swallowing. This can make them feel isolated.
Getting help with speech, diet, and emotional support is crucial. It helps patients cope with the tough parts of oral cancer recovery.
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, happens in different parts of the mouth. This includes the lips, gums, tongue, and inner cheeks. It starts from squamous cells and can cause abnormal growths.
Early signs include sores that don’t heal, lumps, and white or red patches. Spotting these signs early is key for treatment.
It can look like white patches (leukoplakia), red patches (erythroplakia), sores, and lumps. Knowing these looks helps in early detection.
Symptoms include white or red patches, sores, pain, trouble swallowing, and speaking discomfort. These signs are important to watch for.
Look for swelling, sores, bleeding gums, and gum texture changes. Keeping an eye on gum health is crucial.
See a doctor if sores last over two weeks, bleed, or don’t heal. This could be a sign of mouth cancer or another serious issue.
Risks include tobacco use, heavy drinking, HPV, a diet lacking fruits and veggies, and mouth inflammation. These factors increase the risk.
Treatments include surgery to remove tumors. Radiation and chemotherapy might be needed, based on the cancer’s stage and location. New treatments like immunotherapy are also being looked into.
Avoid tobacco and too much alcohol. Eat lots of fruits and veggies. Keep your mouth clean and see your dentist regularly.
You can find support groups, mental health counseling, and educational resources. These help with the emotional and psychological challenges of a diagnosis.