Table of Contents
The Prevalence of Oral Cancer: Statistics and Trends
Oral cancer is a significant global health issue, with statistics revealing an increasing prevalence and worrying trends. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), oral cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. In fact, it is estimated that there were over 450,000 new cases of oral cancer diagnosed in 2020 alone.
When examining the trends, it becomes evident that the prevalence of oral cancer varies across different regions and populations. While the incidence of oral cancer has been declining in some high-income countries, it continues to rise in low- and middle-income countries. This discrepancy can be attributed to various factors, including disparities in access to healthcare, tobacco and alcohol use, and exposure to risk factors such as human papillomavirus (HPV).
Despite advancements in medical technology and treatment options, oral cancer remains a significant health concern. Understanding the prevalence and trends of oral cancer is essential in developing effective prevention and early detection strategies. By targeting vulnerable populations and addressing key risk factors, healthcare professionals can work towards reducing the burden of this disease and improving oral health outcomes globally.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer: Identifying the Vulnerable Populations
Oral cancer is a complex disease with various risk factors that can contribute to its development. Identifying the vulnerable populations who are at a higher risk for oral cancer is crucial in order to implement targeted prevention and intervention strategies.
One key risk factor for oral cancer is age. Studies have consistently shown that older individuals are more susceptible to developing oral cancer compared to younger individuals. According to the American Cancer Society, the risk of developing oral cancer increases significantly after the age of 45. This emphasizes the need for regular dental check-ups and oral cancer screenings, especially among the elderly population.
Another important risk factor for oral cancer is tobacco use. Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as using smokeless tobacco products, significantly increases the risk of developing oral cancer. In fact, the Oral Cancer Foundation states that approximately 90% of oral cancers are linked to tobacco use. This highlights the importance of tobacco cessation programs and educating individuals about the detrimental effects of tobacco on oral health.
| Risk Factor | Description | Vulnerable Populations |
|---|---|---|
| Tobacco Use | Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes | Smokers, long-term tobacco users |
| Alcohol Consumption | Regular heavy drinking | Heavy drinkers |
| HPV Infection | Human papillomavirus infection | Sexually active individuals |
| Sun Exposure | Excessive exposure to sunlight | Outdoor workers, sunbathers |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Lack of regular brushing and dental check-ups | Individuals with limited access to dental care |
| Age | Increasing age | Elderly individuals |
| Gender | Men are more likely to develop oral cancer | Men |
| Diet | Poor nutrition, low fruit and vegetable intake | Individuals with unhealthy dietary habits |
| Family History | Previous history of oral cancer in the family | Individuals with a family history of oral cancer |
| Immunodeficiency | Weakened immune system | Immunocompromised individuals |
Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption has also been strongly associated with an increased risk of oral cancer. Studies have shown that alcohol acts as a carcinogen, damaging the DNA in cells and potentially leading to the development of cancer. The risk of oral cancer rises with the amount and duration of alcohol consumption. It is important to educate individuals about the potential risks of excessive alcohol consumption and promote moderation to reduce the incidence of oral cancer.
In conclusion, identifying the vulnerable populations who are at a higher risk for oral cancer is crucial in order to develop effective prevention and intervention strategies. Age, tobacco use, and excessive alcohol consumption are important risk factors that contribute to the development of oral cancer. By targeting these risk factors and implementing appropriate interventions, we can work towards reducing the burden of oral cancer and promoting better oral health for all.
The Role of Tobacco and Alcohol in Oral Cancer Development
Tobacco and alcohol use have long been recognized as major risk factors for the development of oral cancer. Studies have consistently shown a strong association between these substances and the incidence of oral cancer. According to the World Health Organization, smokers are six times more likely to develop oral cancer than non-smokers, while heavy alcohol drinkers are also at a significantly increased risk.
The harmful effects of tobacco and alcohol on oral health are multi-faceted. Tobacco contains numerous carcinogens that can damage the DNA in the cells of the mouth, leading to the formation of cancerous growths. Additionally, smoking diminishes the body’s immune response, making it more difficult for the body to fight off cancer cells. Alcohol, on the other hand, acts as a solvent, increasing the absorption of harmful substances from tobacco and causing further damage to the cells lining the mouth.
It is important to educate the public about the risks associated with tobacco and alcohol use in order to promote healthier choices and reduce the incidence of oral cancer. Dentists play a vital role in this effort, as they can provide patients with information, advice, and resources to help them quit smoking or reduce their alcohol consumption. By addressing these risk factors, we can take a significant step towards preventing oral cancer and improving overall oral health.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its Link to Oral Cancer
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) has long been associated with cervical cancer, but recent research has shed light on its link to oral cancer as well. HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses, and certain strains, especially HPV-16 and HPV-18, have been identified as high-risk factors for both cervical and oral cancer. In fact, studies have shown that HPV is responsible for an increasing number of oral cancer cases, particularly among younger individuals.
The transmission of HPV to the oral cavity can occur through various means, including intimate contact such as kissing, sexual activity, and even from mother to child during childbirth. The virus can infect the epithelial cells of the mouth and throat, leading to the development of oral tumors over time. Although not all individuals infected with HPV will develop oral cancer, the presence of the virus significantly increases the risk.
Experts believe that the rise in HPV-related oral cancer cases can be attributed to changes in sexual behavior, such as increased prevalence of oral sex, as well as a lack of awareness about the potential risks. It is important to note that HPV-related oral cancer typically occurs at the base of the tongue, tonsils, or back of the throat, making it difficult to detect in its early stages. Regular dental check-ups and screenings can help in early detection, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral health and seeking professional care.
Uncovering the Common Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a serious condition that can often go unnoticed until it reaches an advanced stage. However, by being aware of the common signs and symptoms, individuals can achieve early detection and improve their chances of successful treatment. There are several key indicators that may suggest the presence of oral cancer.
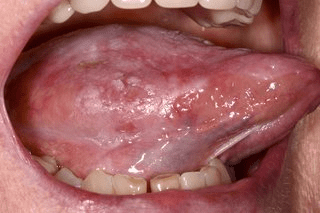
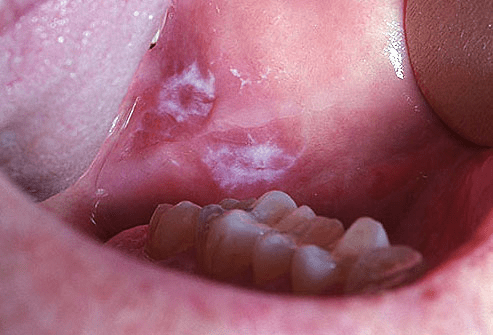
One of the most noticeable signs of oral cancer is the presence of a mouth sore or ulcer that does not heal within a reasonable time frame. These sores may appear as red or white patches or as a lump or thickening in the mouth or throat. Additionally, persistent pain or discomfort in the mouth, face, or neck can also be a warning sign. Other symptoms to be on the lookout for include difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking, unexplained bleeding in the mouth, and loose teeth. While these symptoms do not necessarily indicate the presence of oral cancer alone, it is important to consult with a dental professional if they persist or worsen. Early detection is key to successful treatment and a positive prognosis for oral cancer patients.
| Sign/Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent mouth sore | A sore in the mouth that does not heal within two weeks, often painless initially. It may appear as a white or red patch, or a lump. |
| Persistent mouth pain | Continuous pain or discomfort in the mouth, throat, or neck that doesn’t go away. It may be accompanied by difficulty chewing or swallowing. |
| Changes in voice | Hoarseness or changes in the voice that persist for more than two weeks without an obvious cause, such as a cold or flu. |
| Difficulty swallowing | Difficulty or pain while swallowing, which may indicate a tumor obstructing the throat or esophagus. |
| Numbness | Numbness, tenderness, or a tingling sensation in the mouth, lips, or tongue, which may indicate nerve involvement due to cancer growth. |
| Bleeding | Unexplained bleeding in the mouth, throat, or gums, especially if it’s frequent or severe. |
| Loose teeth | Teeth that become loose without apparent dental cause, such as gum disease or trauma. |
| Persistent bad breath | Chronic halitosis (bad breath) that persists despite oral hygiene measures. |
| Difficulty wearing dentures | Difficulty fitting or wearing dentures, indicating changes in the oral cavity’s structure due to tumor growth. |
| Ear pain | Persistent ear pain, particularly on one side, which may be referred pain from oral cancer affecting nearby nerves. |
References:
– American Cancer Society. (2021). Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancers. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/oral-cavity-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-symptoms.html
– National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. (n.d.). Oral Cancer. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/oral-cancer/more-info
Oral Lesions and their Potential Connection to Oral Cancer
Oral lesions, also known as mouth sores or ulcers, are common occurrences in the oral cavity. While most lesions are harmless and resolve on their own within a week or two, some can be indicative of a more serious condition, such as oral cancer. It is important to understand the potential connection between oral lesions and oral cancer in order to promote early detection and timely intervention.
Research has shown that certain types of oral lesions, such as leukoplakia and erythroplakia, have a higher likelihood of developing into malignant tumors. In fact, these two conditions are considered to be potentially premalignant, meaning that they have the potential to transform into cancer over time. It is estimated that approximately 5-27% of leukoplakic lesions and 50-90% of erythroplakic lesions progress to oral cancer if left untreated.
Detecting and monitoring these lesions is crucial for identifying individuals who are at a higher risk of developing oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in examining these lesions and determining their potential for malignancy. Dentists are well-equipped with the knowledge and expertise to detect and evaluate suspicious oral lesions, ensuring that appropriate diagnostic tests and further management can be promptly initiated.
In the next section of this article, we will delve deeper into the signs and symptoms of oral cancer, shedding light on the various warning signals that necessitate further investigation. Stay tuned as we explore the intricacies of this disease and delve into the significance of early detection and prevention.
Pain and Discomfort: Oral Cancer’s Warning Signals
Pain and discomfort are common warning signals of oral cancer that should not be ignored. While these symptoms can be caused by a variety of other dental and health issues, it is crucial to be aware of their potential connection to oral cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, persistent pain in the mouth, throat, or ear can be an indication of oral cancer. This pain may manifest as a sore or ulcer that does not heal within two weeks, and can also be accompanied by difficulty swallowing or speaking.
It is important to note that pain and discomfort alone are not definitive proof of oral cancer. However, if you experience these symptoms and they persist or worsen over time, it is recommended to seek professional dental and medical evaluation. Early detection and diagnosis are vital in treating oral cancer effectively. Dentists are highly trained to identify potential signs of oral cancer during routine dental examinations, and they can provide appropriate referrals for further testing or treatment if necessary. Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in oral health maintenance and can significantly increase the chances of early cancer detection.
How Changes in Oral Sensation can Indicate Oral Cancer
Changes in oral sensation can be indicative of oral cancer and should not be ignored. Oral sensations such as numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation can be early warning signs of oral cancer. These abnormal sensations may be present on the tongue, lips, or inside the mouth. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other dental or medical conditions, so it is crucial to consult a dentist or healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
The presence of persistent changes in oral sensation may be a cause for concern. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Dental Association, individuals with alterations in taste or a persistent numbness in the mouth were more likely to have oral cancer. Another study published in the Oral Oncology journal found that patients with oral cancers had significantly higher rates of altered oral sensations compared to those without cancer. Therefore, any unusual changes or persisting sensations in the mouth should not be taken lightly and should be evaluated by a dental professional promptly.
Recognizing Swelling and Lumps in the Oral Cavity
Swelling and lumps in the oral cavity can be a cause for concern and should not be ignored. These abnormalities can occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from benign conditions to potentially serious diseases such as oral cancer. It is important to recognize and promptly address these signs, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
One common cause of swelling and lumps in the oral cavity is the presence of oral infections. These infections can occur in the gums, teeth, or other soft tissues of the mouth. If left untreated, they can lead to abscesses or the formation of fluid-filled sacs that can cause pain and discomfort. In some cases, these infections can also spread to other parts of the body, posing a systemic health risk.
Another potential cause of swelling and lumps is the development of oral tumors, both benign and malignant. Benign tumors, such as fibromas or papillomas, are usually harmless but may still require treatment if they cause discomfort or interfere with oral function. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, can be indicative of oral cancer and should be promptly evaluated by a dental professional.
In conclusion, it is crucial to recognize and address any swelling or lumps in the oral cavity. These signs could indicate the presence of infections or tumors, including oral cancer. By seeking timely evaluation and treatment, individuals can greatly increase their chances of successful recovery and long-term oral health.
Oral Cancer’s Effect on Speech and Swallowing
Oral cancer can have significant effects on a person’s ability to speak and swallow. The location and size of the tumor, as well as the stage of the cancer, can all contribute to these difficulties. When cancer affects the tongue, lips, or floor of the mouth, it can impair articulation and make speech unclear. Swallowing can also become challenging as the tumor grows, obstructing the passage of food and liquids.
In some cases, oral cancer’s impact on speech and swallowing may necessitate the use of alternative methods to communicate, such as speech therapy or assistive devices. Speech therapists can work with individuals to improve their ability to form sounds and words, while swallowing therapists can provide techniques to help manage swallowing difficulties. Additionally, dentists and oral surgeons may collaborate with other healthcare professionals to develop treatment plans that can minimize the impact of oral cancer on speech and swallowing function.
It is important for individuals with oral cancer to work closely with their healthcare team to address these challenges and improve their quality of life. Early detection, timely treatment, and rehabilitation programs can play a crucial role in minimizing the impact of oral cancer on speech and swallowing.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue: Red Flags for Oral Cancer
Unexplained weight loss and fatigue can be red flags for oral cancer and should not be overlooked. While these symptoms can be attributed to a variety of factors, it is important to pay attention to their potential connection to oral health. Research has shown that individuals with oral cancer often experience unexplained weight loss, which is defined as a significant decrease in body weight without intentionally dieting. This can be a result of the cancer cells in the oral cavity interfering with normal bodily functions such as eating and digestion.
Furthermore, fatigue is also a common symptom among oral cancer patients. This persistent feeling of tiredness can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it difficult for them to carry out daily activities. It is believed that the tumor growth and metabolic changes associated with oral cancer contribute to this fatigue.
If you or someone you know is experiencing unexplained weight loss and fatigue, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional, preferably a dentist specializing in oral health. These symptoms may not always indicate oral cancer, but it is better to be safe than sorry. Early detection and intervention can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
The Role of Routine Dental Examinations in Early Oral Cancer Detection
Routine dental examinations play a crucial role in the early detection of oral cancer. During these examinations, dentists thoroughly examine the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, gums, cheeks, and throat, for any signs or symptoms of oral cancer. This includes checking for abnormal growths, persistent sores or ulcers, unusual patches of red or white, or any other suspicious changes that may indicate the presence of cancerous or pre-cancerous cells.
According to the American Dental Association, regular dental check-ups are essential as they can help identify oral cancer at its earliest stages when the chances of successful treatment are significantly higher. Dentists are trained to spot abnormalities that may go unnoticed by the untrained eye, allowing for prompt referral to a medical professional for further evaluation and diagnosis. By incorporating routine dental examinations into their oral healthcare regimen, individuals increase their chances of early detection and better outcomes in the management of oral cancer.

The Importance of Regular Self-Examinations for Oral Cancer
Regular self-examinations for oral cancer play a crucial role in early detection and prevention. By performing these simple checks at home, individuals can become more proactive in safeguarding their oral health and identifying any potential red flags. It is recommended to conduct self-examinations monthly, as this frequency allows for timely identification of any changes that may occur.
During a self-examination, individuals should thoroughly inspect their mouth, tongue, gums, and the inside of their cheeks for any abnormalities such as sores, white or red patches, lumps, or other unusual changes. By familiarizing themselves with the normal appearance of their oral cavity, individuals are better equipped to notice any deviations or signs of concern. Regular self-examinations not only encourage early detection but also empower individuals to seek professional dental care promptly, thus increasing the likelihood of successful treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic Tests and Tools for Oral Cancer Screening
Diagnostic tests and tools play a crucial role in the early detection of oral cancer, allowing for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes. Several diagnostic techniques are commonly used by dental professionals to screen for oral cancer, including visual examination, palpation, and adjunctive screening tools.
Visual examination involves carefully inspecting the oral cavity, lips, and surrounding tissues for any abnormalities or suspicious lesions. The dentist examines the color, texture, and size of the lesions and assesses their potential for malignancy. Palpation, on the other hand, involves manually feeling the oral tissues and lymph nodes to detect any unusual lumps, swelling, or tenderness.
To further enhance the accuracy of oral cancer screening, dentists may employ adjunctive screening tools like toluidine blue staining, VELscope, and brush biopsy. Toluidine blue staining is a non-invasive technique that utilizes a dye to identify abnormal cells in the oral mucosa. The VELscope, a handheld device that emits a safe blue light, helps dentists visualize abnormal tissue that may be indicative of oral cancer. Brush biopsy involves gently scraping cells from suspicious lesions for further analysis under a microscope.
By utilizing these diagnostic tests and tools, dental professionals can effectively identify potential signs of oral cancer during routine check-ups, allowing for early intervention and potentially saving lives. It is important to note that these screening methods are not definitive and may require further confirmatory tests, such as biopsy, for a definitive diagnosis. Regular oral cancer screenings are vital, particularly for individuals with known risk factors, to ensure early detection and successful treatment.
Preventive Measures: Promoting Oral Health and Reducing Oral Cancer Risks
Promoting oral health and reducing the risk of oral cancer is of utmost importance in maintaining overall well-being. Implementing preventive measures can significantly contribute to early detection and treatment, ultimately saving lives. Here are some key strategies to promote oral health and reduce the risk of oral cancer.
First and foremost, adopting a thorough oral hygiene routine is crucial. This includes brushing at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups are equally important, as they allow for the identification of any early signs or symptoms of oral cancer. Dentists can perform comprehensive examinations and oral cancer screenings, providing valuable insights and guidance.
In addition to good oral hygiene practices, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption is essential. Numerous studies have shown direct links between tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and oral cancer development. By educating individuals on the harmful effects of these substances and offering support for smoking cessation or alcohol reduction, the risks associated with oral cancer can be significantly minimized.
Furthermore, encouraging a healthy diet that includes ample fruits and vegetables can help reduce the risk of oral cancer. Certain foods, such as broccoli, berries, and leafy greens, contain antioxidants that may protect against cancer-causing toxins. Limiting the intake of processed and sugary foods can also contribute to overall oral health.
Lastly, raising awareness about the human papillomavirus (HPV) and its connection to oral cancer is essential. HPV is a sexually transmitted virus that can be transmitted through oral-genital contact. Promoting safe sexual practices and vaccinations against HPV can play a vital role in preventing the development of oral cancer.
By implementing these preventive measures and maintaining good oral health habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of oral cancer. It is important to remember that prevention is key, and proactive steps taken today can lead to a healthier future.
Note: The list provided below explores a wide range of topics related to oral cancer, shedding light on its prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, and diagnostic tools.
By delving into the evidence-based research available, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex disease. From examining the impact of tobacco and alcohol use to unraveling the connection between human papillomavirus (HPV) and oral cancer, these articles strive to inform and educate readers about the various aspects of this health concern. Furthermore, we will explore the role of routine dental examinations and regular self-examinations in early detection, as well as preventive measures that can be taken to reduce the risks associated with oral cancer. By comprehensively addressing these topics, we hope to contribute to the public’s awareness and understanding of oral cancer, ultimately enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their oral health.
Please note that the information provided in these articles is based on scientific research and reputable sources, ensuring accuracy and reliability. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
What are the risk factors for developing oral cancer?
Risk factors for oral cancer include tobacco and alcohol use, infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), poor oral hygiene, a weakened immune system, and a family history of oral cancer.
What are some common signs and symptoms of oral cancer?
Common signs and symptoms of oral cancer include persistent mouth sores, pain or discomfort in the mouth or throat, difficulty swallowing or speaking, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
How are oral lesions connected to oral cancer?
While not all oral lesions are cancerous, certain types of lesions can be precursors to oral cancer. Regular dental examinations and biopsies can help identify and monitor any suspicious lesions.
Can changes in oral sensation indicate oral cancer?
Yes, changes in oral sensation, such as numbness or tingling in the mouth, tongue, or lips, can be an indication of oral cancer. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any such changes.
How can swelling and lumps in the oral cavity be recognized?
Swelling and lumps in the oral cavity can be recognized through self-examinations and routine dental check-ups. Any persistent or unusual swelling or lumps should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
What effects can oral cancer have on speech and swallowing?
Oral cancer can affect speech and swallowing by causing difficulty in articulating words, hoarseness, persistent coughing, difficulty swallowing, or a feeling of something being stuck in the throat.
Can unexplained weight loss and fatigue be red flags for oral cancer?
Yes, unexplained weight loss and fatigue can be red flags for oral cancer. If you experience these symptoms along with other oral cancer signs, it is important to seek medical attention for proper evaluation.
How important are routine dental examinations for early oral cancer detection?
Routine dental examinations are essential for early oral cancer detection. Dentists are trained to recognize the signs of oral cancer, and regular check-ups can help identify any potential issues in their early stages.
Why is self-examination for oral cancer important?
Self-examination for oral cancer is important because it allows individuals to monitor their own oral health and identify any changes or abnormalities. Early detection through self-examination can lead to better treatment outcomes.
What diagnostic tests and tools are used for oral cancer screening?
Diagnostic tests and tools used for oral cancer screening include visual examination, tissue biopsy, endoscopy, imaging tests (like X-rays or CT scans), and laboratory tests to detect the presence of HPV.
How can oral health be promoted and oral cancer risks be reduced?
Oral health can be promoted and oral cancer risks can be reduced by practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use, maintaining a healthy diet, and getting regular dental check-ups.
Note: This list is not exhaustive, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and information.