Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
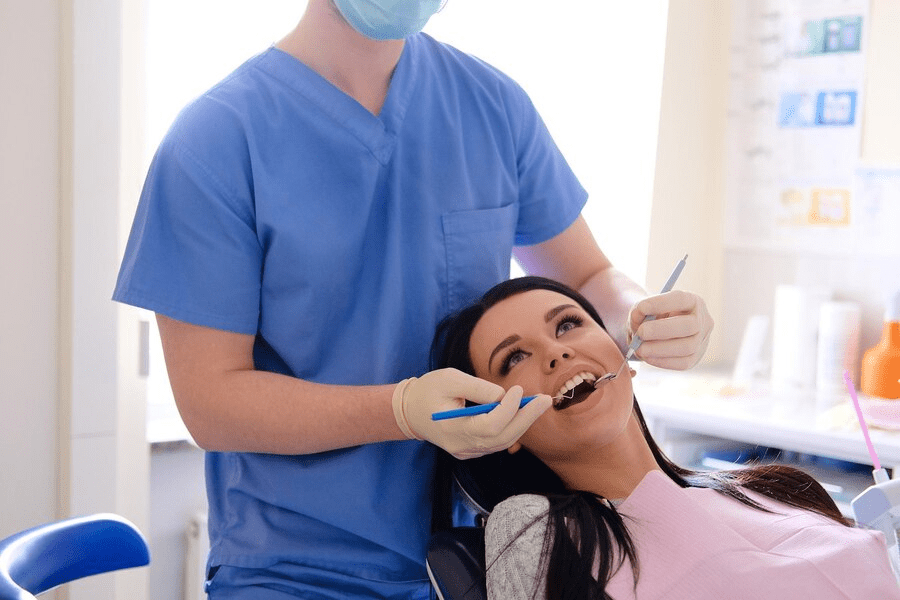
Understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the gum tissues and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious complications including tooth loss and bone damage.
The early stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. As the disease progresses, the gums may recede, exposing the tooth roots and creating pockets where bacteria can thrive. This advanced stage, known as periodontitis, can cause irreversible damage to the gums, bone, and ligaments that support the teeth. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of gum disease early on to prevent further complications and maintain oral health.

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While poor oral hygiene is often the primary cause of gum disease, there are several common risk factors that can increase an individual’s susceptibility to this condition.
One significant risk factor for gum disease is tobacco use. Smoking and chewing tobacco not only stain teeth and cause bad breath, but they also weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including those that affect the gums. Additionally, individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk for gum disease. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal and increase vulnerability to infections, including gum infections. Furthermore, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make women more prone to gum disease. The fluctuation in hormones can lead to increased blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and susceptible to inflammation.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Inadequate brushing and flossing lead to plaque buildup |
| Smoking | Increases the likelihood and severity of gum disease |
| Diabetes | Poorly controlled blood sugar can worsen gum health |
| Genetic Predisposition | Some individuals are more genetically prone to gum disease |
| Hormonal Changes | Hormonal fluctuations, such as during pregnancy, can increase susceptibility |
| Medications | Certain medications can decrease saliva flow or cause gum overgrowth, increasing risk |
| Chronic Stress | May weaken the immune system, making gums more vulnerable |
| Poor Nutrition | Inadequate intake of essential nutrients can impair gum health |
| Age | Risk increases with age as gums naturally recede and teeth become more susceptible |
Other common risk factors for gum disease include a family history of gum disease, certain medications that reduce saliva production, and a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates. Additionally, stress can weaken the immune system and make an individual more susceptible to infections, including gum infections. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups to minimize these risk factors and prevent the onset of gum disease.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is important to identify the early signs and symptoms of gum disease in order to prevent further progression and potential complications.
One common early sign of gum disease is gum inflammation, often referred to as gingivitis. This is characterized by red and swollen gums that may bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Additionally, individuals with gum disease may experience persistent bad breath, even after proper oral hygiene practices. Another early symptom is gum recession, where the gums appear to be pulling away from the teeth, exposing the roots.
If left untreated, gum disease can progress to more advanced stages, leading to significant damage to the gums and the supporting structures of the teeth. This can eventually result in tooth loss and may even impact overall oral health. It is crucial to seek prompt dental care if any of these signs and symptoms are present, as early intervention can help prevent further complications and preserve oral health.
Gum disease, also known as gingivitis or periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that, if left untreated, can progress and cause serious complications. As plaque and tartar build up on the teeth and along the gum line, bacteria begin to multiply and release toxins that irritate the gums. In the early stages, gum disease may present with symptoms such as redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. However, if left unaddressed, gum disease can progress to more severe stages, causing irreversible damage to the gums, tooth loss, and potentially impacting overall health.
One of the key risks associated with untreated gum disease is the development of periodontitis. As the condition progresses, the infection spreads beneath the gum line and creates pockets between the gums and teeth. These pockets become a breeding ground for more bacteria, leading to further inflammation and damage to the surrounding tissues and bones that support the teeth. Over time, this can result in the loosening of teeth and eventual tooth loss. Additionally, the inflammation caused by gum disease can have systemic effects, potentially contributing to other health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory issues.

Prevention and early intervention are crucial in combating the progression of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help remove tartar and plaque, reducing the risk of gum disease. Additionally, practicing proper oral hygiene at home, including brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily, can help remove plaque and bacteria from the gum line. By addressing gum disease in its early stages, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and maintain a healthy smile.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is not only a concern for your oral health but also for your overall well-being. Research has shown a strong link between gum disease and various systemic health conditions.
One of the most well-established connections is between gum disease and heart health. Studies have found that individuals with gum disease have an increased risk of developing heart disease, such as coronary artery disease and stroke. The inflammation caused by gum disease can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and potential cardiovascular complications.
Furthermore, gum disease has been associated with respiratory issues. Bacteria from infected gums can travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory infections, pneumonia, and acute bronchitis. It is especially important for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), to maintain good oral hygiene to minimize the risk of exacerbations.
The link between gum disease and overall health extends beyond the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Research has also shown associations between gum disease and conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease, and certain types of cancer. While the exact mechanisms behind these relationships are still being studied, it is believed that the chronic inflammation caused by gum disease plays a role in the development and progression of these systemic conditions.
Given the growing body of evidence linking gum disease to overall health, it is crucial to prioritize oral hygiene and seek professional dental care regularly. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, including brushing and flossing daily, along with regular dental check-ups, you can reduce the risk of developing gum disease and potentially decrease the likelihood of associated systemic health issues. Your dentist can provide individualized guidance on proper oral care techniques and work with you to develop a preventive plan tailored to your specific needs.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial when it comes to preventing gum disease. Poor oral hygiene habits can lead to a buildup of plaque and bacteria, which can eventually cause inflammation and infection in the gums. By incorporating effective oral hygiene practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease.
One of the most important aspects of proper oral hygiene is regular brushing. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, it is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day, for two minutes each time. This helps to remove plaque and bacteria from the surfaces of your teeth and along the gumline. Additionally, be sure to replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
In addition to regular brushing, it is equally important to floss daily. Flossing helps to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and along the gumline, where a toothbrush cannot reach. By incorporating this simple habit into your routine, you can effectively eliminate hidden plaque and reduce the risk of gum disease.
| Importance of Proper Oral Hygiene in Preventing Gum Disease |
|---|
| 1. Plaque Removal |
| Regular brushing and flossing help remove plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, which if left unchecked, can lead to gum disease. |
| 2. Prevention of Gingivitis |
| Proper oral hygiene prevents the onset of gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease characterized by inflamed gums, bleeding, and tenderness. |
| 3. Reduction of Tartar Buildup |
| Effective oral hygiene practices inhibit the accumulation of tartar (hardened plaque), which contributes to gum inflammation and disease progression. |
| 4. Preservation of Gum Tissue |
| By keeping the gums clean and healthy, proper oral hygiene helps preserve the integrity of gum tissue and prevents its recession or deterioration. |
| 5. Prevention of Periodontitis |
| Consistent oral hygiene routines significantly reduce the risk of periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and systemic health issues. |
| 6. Overall Health Benefits |
| Maintaining good oral hygiene not only prevents gum disease but also contributes to overall health, as oral health is linked to systemic conditions like heart disease and diabetes. |
Alongside brushing and flossing, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also be beneficial in preventing gum disease. Mouthwash can help to kill bacteria and freshen your breath, while also reaching areas that may have been missed during brushing and flossing.
In conclusion, the importance of proper oral hygiene in preventing gum disease cannot be overstated. By establishing a consistent routine of brushing, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease. Remember, preventive measures are key in maintaining optimal oral health and preventing more severe dental problems down the line.
Proper oral hygiene practices are essential for maintaining healthy gums and preventing gum disease. While daily brushing is a fundamental aspect of oral care, it is equally important to use the right techniques to ensure effective cleaning and prevent gum inflammation. Here are some brushing techniques to help you maintain healthy gums.
Firstly, make sure to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles. Hard bristles can cause gum irritation and damage the enamel. When brushing, hold the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle towards the gum line. Use gentle, circular motions to clean every surface of your teeth, including the outer, inner, and chewing surfaces. Pay extra attention to the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate. Additionally, don’t forget to brush your tongue to remove bacteria and freshen your breath. Brushing should be done for at least two minutes, twice a day, to effectively remove plaque and maintain healthy gums. Remember, too much pressure or vigorous brushing can harm your gums and lead to gum recession. Use a light touch and be gentle while cleaning your teeth and gums.

By consistently using these brushing techniques, you can help prevent gum disease and maintain optimal gum health. However, it’s important to note that brushing alone is not sufficient. Regular flossing, mouth rinsing, and professional dental cleanings are also necessary to achieve comprehensive oral hygiene and prevent gum disease. Keep in mind that everyone’s oral health needs are unique, so it is advisable to consult with your dentist for personalized recommendations and guidance on maintaining healthy gums.
Flossing plays a crucial role in preventing and treating gum disease. While brushing helps remove plaque from the surfaces of the teeth, it doesn’t effectively reach the spaces between the teeth and along the gumline. This is where flossing comes in. By using dental floss daily, you can remove plaque and food particles that are trapped in these hard-to-reach areas, reducing the risk of gum disease.
Flossing not only helps prevent gum disease, but it can also be an effective treatment for existing gum disease. When the gums become inflamed due to gum disease, flossing can help remove the bacteria and plaque that contribute to the inflammation. Consistent flossing, along with regular dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene habits, can promote healing and prevent further progression of gum disease. It is important to note that flossing should be done gently and effectively to avoid causing damage to the gums.

The impact of diet and nutrition on gum health is often overlooked, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of our gums. Research has shown that a balanced and nutritious diet can help prevent gum disease and improve oral health. On the other hand, a poor diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system, making the gums more prone to infection and inflammation.
One key nutrient that influences gum health is vitamin C. This powerful antioxidant helps strengthen the connective tissues in the gums and promotes healing. Citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, and leafy greens are all excellent sources of vitamin C. Another important nutrient is calcium, which is essential for maintaining strong teeth and bones. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milks are great sources of calcium. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and sardines can help reduce inflammation in the gums.
It’s important to note that excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods and beverages can have a detrimental effect on gum health. These substances contribute to the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to dental decay and gum disease. It’s recommended to limit the intake of sugary drinks, snacks, and processed foods, and opt for healthier alternatives like fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
In conclusion, maintaining a well-balanced diet that is rich in essential nutrients is instrumental in promoting gum health. By incorporating foods that are high in vitamin C, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, and by reducing the consumption of sugary and acidic foods, we can help prevent gum disease and maintain a healthy smile.
Smoking and tobacco use are well-known risk factors for gum disease. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products can have detrimental effects on oral health, including damage to the gums and the surrounding tissues. Studies have shown that smokers are more likely to develop gum disease compared to non-smokers, and their condition tends to worsen at a faster rate.
One of the reasons for this correlation is that smoking weakens the body’s immune system, making it less able to fight off infections and heal damaged tissues. In addition, tobacco use reduces blood flow to the gums, which hinders the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen, further compromising the health of the oral tissues. Furthermore, smoking and tobacco use can mask the early signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, as nicotine constricts blood vessels and reduces inflammation.
Given the detrimental effects of smoking and tobacco use on gum health, it is crucial for individuals to quit these habits to prevent and treat gum disease. Consulting with a healthcare provider, such as a dentist or primary care physician, can provide guidance and support for those looking to quit smoking. With proper oral hygiene practices and a tobacco-free lifestyle, individuals can significantly improve their gum health and reduce the risk of gum disease progression.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people around the world. It is important to understand the different stages of gum disease in order to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
The first stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the gums. During this stage, the gums may appear red, swollen, and bleed easily. However, there is little to no discomfort at this stage, which often leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to the next stage, known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis is the more severe stage of gum disease. At this stage, the infection extends below the gumline and affects the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. As a result, the gums may recede, creating spaces between the teeth and gums known as periodontal pockets. If not treated in a timely manner, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and other complications.
Understanding the different stages of gum disease is crucial for maintaining oral health. Regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene can help prevent gum disease and detect it in its early stages. In the next section, we will explore the diagnostic procedures used to identify gum disease and the treatment options available. Stay tuned to learn more about how to protect your gums and maintain a healthy smile.
When it comes to diagnosing gum disease, dentists employ various diagnostic procedures to accurately assess the severity and progression of the condition. One commonly used diagnostic tool is the periodontal probe, a small instrument that measures the depth of the pockets between the teeth and gums. These measurements help determine the presence of gum inflammation, recession, and potential bone loss.
In addition, dentists may also use dental X-rays to evaluate the condition of the teeth and gums below the gum line. X-rays can reveal hidden signs of gum disease, such as bone loss or abscess formations. These images provide valuable insights into the extent of the disease and aid in devising an effective treatment plan. By combining the findings from probing and X-rays, dentists can accurately diagnose gum disease and tailor treatments to meet the specific needs of each patient.
When it comes to treating gum disease, non-surgical options are often the first line of defense. These treatments are less invasive and can effectively restore oral health when the disease is caught in its early stages. One common non-surgical treatment option is scaling and root planing.
Scaling involves removing the plaque and tartar buildup from the surfaces of the teeth and along the gumline. This is done using specialized instruments to gently remove the accumulated bacteria. Root planing, on the other hand, smooths out the rough areas on the roots of the teeth, making it harder for bacteria to attach and multiply. This can help prevent further progression of gum disease and promote healing of the gums.
Another non-surgical treatment option for gum disease is the use of antibiotics. Topical antibiotics in the form of gels, mouthwashes, or oral medications can be used to kill the harmful bacteria that contribute to gum disease. These antibiotics are typically prescribed for short-term use to combat infection and reduce inflammation.
In addition to scaling, root planing, and antibiotics, non-surgical treatment may also include the use of antimicrobial rinses to further fight bacterial growth. Regular follow-up appointments with your dentist are crucial to monitor the progress of treatment and ensure that the gum disease is under control.
It is important to note that non-surgical treatment options are most effective in the early stages of gum disease. In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to fully restore oral health. However, with proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits, gum disease can often be prevented or successfully managed without the need for surgery. Stay tuned for our next section where we will delve deeper into surgical treatment options for advanced gum disease.
When gum disease progresses to its advanced stage, non-surgical treatment options may no longer be sufficient to restore oral health. In such cases, surgical interventions provide viable solutions to combat the effects of advanced gum disease. There are several surgical treatment options available, depending on the severity and extent of the gum disease.
One of the most common surgical procedures for advanced gum disease is called flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery. This procedure involves the lifting of the gum tissue to access the roots of the teeth and remove any tartar or bacteria. The gums are then repositioned to reduce the depth of the pockets and promote healing. Flap surgery is often combined with bone grafts or soft tissue grafts to restore the integrity and structure of the affected area. Another surgical option is guided tissue regeneration, which involves the use of specialized membranes to encourage the growth of new bone and gum tissue.
Maintaining healthy gums through ongoing maintenance and prevention strategies is crucial in the fight against gum disease. By implementing these strategies, individuals can reduce the risk of developing gum disease and promote optimal oral health.
Regular dental appointments play a vital role in ongoing maintenance and prevention. Dentists are able to closely monitor the health of the gums and provide professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup. During these visits, dentists can also provide guidance on proper oral hygiene techniques, such as effective brushing and flossing methods. Additionally, dentists can assess any potential risk factors or early signs of gum disease, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
In addition to dental visits, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy gums at home. These include brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and incorporating flossing into daily oral hygiene routines. A balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals is also essential for gum health, as certain nutrients play a key role in supporting gum tissue. By adopting these ongoing maintenance and prevention strategies, individuals can safeguard their gum health and reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
The main cause of gum disease is the buildup of plaque on the teeth and along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums.
Yes, gum disease has been linked to several health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and complications during pregnancy. Taking care of your gum health is important for maintaining overall well-being.
It is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day, preferably after meals. Brushing for two minutes each time using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
Yes, flossing is an essential part of maintaining healthy gums. It helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline, areas that a toothbrush cannot reach effectively.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, can help support healthy gums. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods can also reduce the risk of gum disease. Proper nutrition plays an important role in gum health.
Yes, smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors for gum disease. They can weaken the immune system, impair blood flow to the gums, and hinder the healing process, making it easier for gum disease to develop and progress.
The different stages of gum disease are gingivitis (mild inflammation of the gums), periodontitis (inflammation and infection spreading to the supporting structures of the teeth), and advanced periodontitis (severe damage to the gums, bones, and teeth).
Gum disease is diagnosed through a comprehensive dental examination, which may include checking for signs of inflammation, measuring the depth of gum pockets, and taking X-rays to assess the underlying bone structure.
Yes, non-surgical treatment options for gum disease include professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing (deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar), and antibiotic therapy. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and control the infection.
Surgical treatment for gum disease is typically recommended when non-surgical methods are insufficient to control the infection or when there is significant damage to the gums and supporting structures. Examples of surgical treatments include flap surgery and bone grafting.
To maintain healthy gums after gum disease treatment, it is important to practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing. Follow-up visits with your dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups are also crucial in preventing recurrence of gum disease.