Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
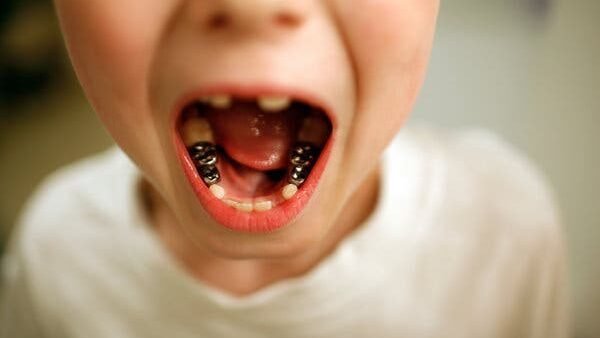
Losing a Tooth Too Early. Understand the implications of losing a tooth too early and how to address it for dental health.
Premature tooth loss can be attributed to various factors that affect the health and stability of teeth. One of the common causes is poor oral hygiene practices, leading to the buildup of plaque and eventually tooth decay. This decay can progress to the point where the tooth becomes irreparably damaged and necessitates extraction. Additionally, gum disease, such as periodontitis, can contribute to premature tooth loss by weakening the supporting structures around the teeth, making them more susceptible to falling out or needing extraction.
Trauma to the mouth or teeth, whether from sports injuries, accidents, or other external forces, is another significant cause of premature tooth loss. The impact or force applied to the teeth can result in fractures, cracks, or complete avulsion, causing the affected tooth to be lost prematurely. Additionally, certain systemic conditions like diabetes, osteoporosis, or genetic disorders can also play a role in the early loss of teeth by affecting the overall health and strength of the teeth and surrounding structures.
Tooth loss, especially when it occurs prematurely, can have a significant impact on oral health. When a tooth is lost early in life, it can lead to a variety of issues such as misalignment of remaining teeth, shifting of the bite, and changes in jaw structure. These changes can create difficulty in maintaining proper oral hygiene, increasing the risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and further tooth loss. Additionally, the gap left by a missing tooth can cause neighboring teeth to become unstable and susceptible to damage.

Moreover, beyond the physical implications, the emotional toll of tooth loss should not be underestimated. Aesthetically, missing teeth can affect one’s self-confidence and self-esteem, potentially leading to social anxiety and avoiding social interactions. As such, addressing tooth loss promptly is crucial not only for preserving oral health but also for maintaining overall well-being and quality of life.
Premature tooth loss can have significant ramifications on speech and eating abilities. Speech articulation may be hindered by missing teeth, leading to difficulties in forming certain sounds and pronunciation. The absence of teeth can alter airflow patterns during speech production, resulting in speech impediments that may impact communication and self-esteem.
Moreover, the function of teeth in chewing and breaking down food is essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption. Missing teeth can impair one’s ability to chew food effectively, potentially leading to inadequate mastication and digestion. This can further result in gastrointestinal issues and malnutrition if not addressed promptly through appropriate dental interventions. It is crucial to recognize the impact of tooth loss on both speech and eating functions to highlight the importance of early intervention and comprehensive dental care.
Tooth loss, especially in children, can have significant psychological effects beyond just the physical impact on oral health. Children may experience feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, or low self-esteem due to missing teeth, which can affect their social interactions and overall well-being. Furthermore, the aesthetic changes resulting from premature tooth loss can contribute to body image issues and potentially lead to anxiety or depression in some cases.
Research suggests that children who experience premature tooth loss may also face challenges related to their speech development and pronunciation. Missing teeth can alter the alignment of the remaining teeth and affect the proper articulation of sounds, leading to speech impediments or difficulties in communication. These challenges can further exacerbate the psychological impact of tooth loss on children, emphasizing the importance of addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of missing teeth in pediatric dental care.
Dental professionals offer various treatment options for individuals with missing teeth, catering to the specific needs and preferences of each patient. One common option is dental implants, which are durable and natural-looking replacements that function similarly to natural teeth. Through a surgical procedure, titanium posts are securely inserted into the jawbone, providing a stable foundation for attaching prosthetic teeth.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Dental Implants | Surgically implanted artificial tooth roots made of titanium that fuse with the jawbone to support replacement teeth. |
| Fixed Dental Bridges | Artificial teeth (pontics) held in place by dental crowns attached to adjacent natural teeth or dental implants. |
| Removable Partial Dentures | Removable prosthetic teeth attached to a plastic base that fits over the gums and is supported by neighboring teeth. |
| Removable Complete Dentures | Full set of artificial teeth that can be taken out and put back in place by the wearer. |
| Maryland Bridge | A conservative option where artificial teeth are bonded to adjacent teeth using a metal or ceramic framework. |
| Cantilever Bridge | Similar to traditional bridges but supported on only one side by adjacent natural teeth or dental implants. |
Another effective treatment for missing teeth is the use of dental bridges, which consist of artificial teeth that are anchored to the surrounding natural teeth or dental implants. This option is suitable for those who may not be good candidates for implants or prefer a non-surgical approach. Dental bridges not only restore the appearance of the smile but also help maintain proper alignment and prevent shifting of remaining teeth in the mouth.
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, play a crucial role in a child’s oral development. Despite being temporary, these teeth serve as placeholders for the permanent teeth to come. They help guide the permanent teeth into their proper positions, ensuring proper alignment and bite function in the future. Neglecting the importance of baby teeth can lead to potential misalignment issues and other dental complications down the road. It is essential to care for and maintain baby teeth to support optimal oral health throughout childhood and into adulthood.
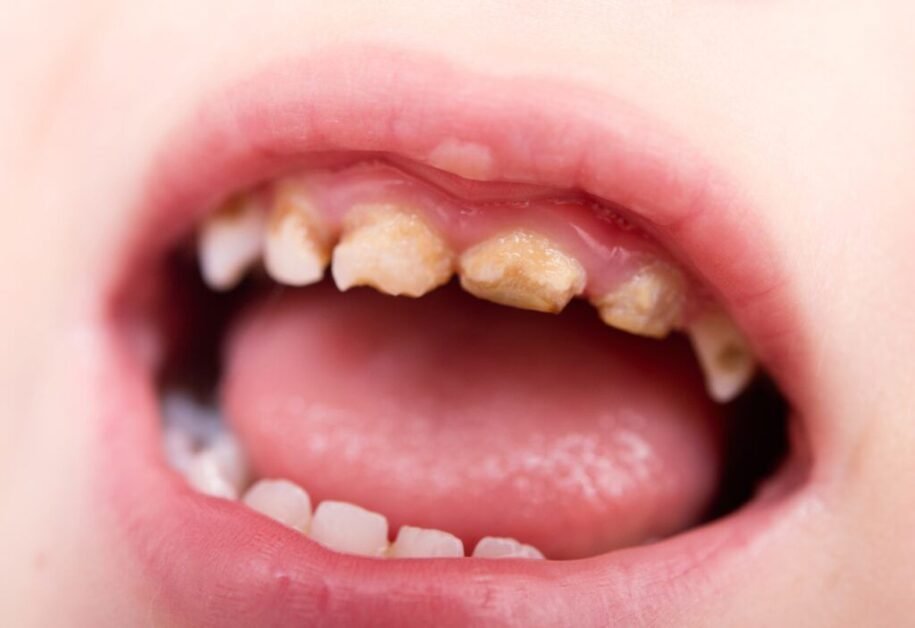
Furthermore, baby teeth are essential for proper speech development and nutrition. These teeth aid in articulating sounds and words correctly, laying the foundation for clear and effective communication. Additionally, baby teeth enable children to chew food thoroughly, promoting proper digestion and nutrient absorption. Losing baby teeth prematurely can hinder speech development and impede a child’s ability to eat a balanced diet, potentially affecting their overall growth and well-being. As such, parents and caregivers should prioritize the care and preservation of baby teeth to ensure the healthy development of their child’s oral and overall health.
Early tooth loss in children can manifest through various signs that parents and guardians should be vigilant about. One common indicator is the premature shedding of baby teeth, especially if the loss occurs before the expected age range. This may be accompanied by issues such as pain or discomfort in the gums, bleeding, or swelling around the affected tooth. Additionally, noticeable gaps or spaces between teeth that were previously not present could indicate an impending loss.
Another sign of early tooth loss is the presence of decay or cavities that have progressed to a severe extent, leading to weakening of the tooth structure and eventual loss. Discoloration of teeth, particularly dark spots or areas on the enamel, can also signal underlying problems that may result in premature tooth loss if left untreated. It is crucial for parents to monitor their child’s oral health closely and seek prompt evaluation by a dental professional if any of these signs are observed.
Preventative measures play a crucial role in maintaining optimal oral health and preventing premature tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups are essential to identify any potential issues early on and address them before they escalate. Additionally, practicing good oral hygiene at home, including brushing teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly, can help prevent decay and gum disease that may lead to tooth loss.
| Preventative Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Dental Check-ups | Routine visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and examinations to detect early signs of dental issues. |
| Good Oral Hygiene | Brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash to remove plaque. |
| Balanced Diet | Eating a nutritious diet rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins essential for healthy teeth and gums. |
| Avoiding Tobacco | Refraining from smoking or chewing tobacco, which can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth decay leading to loss. |
| Mouthguards | Wearing custom-fitted mouthguards during sports or activities to prevent trauma to the teeth and gums. |
| Fluoride Treatment | Utilizing fluoride toothpaste, mouth rinses, or professional fluoride treatments to strengthen tooth enamel. |
| Sealants | Applying dental sealants to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent decay and the need for premature extractions. |
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin C is vital for supporting healthy teeth and gums. Limiting sugary and acidic foods and beverages can also help prevent erosion and cavities, which are common culprits of tooth loss. Furthermore, wearing mouthguards during sports activities and avoiding habits like nail-biting and using teeth as tools can protect teeth from trauma and damage, reducing the risk of premature loss.
Premature tooth loss, if left unaddressed, can lead to a myriad of complications that can significantly impact oral health. One of the primary concerns associated with losing teeth too early is the potential shifting of adjacent teeth into the gap left by the missing tooth. This movement can result in misalignment of the remaining teeth, causing bite issues, difficulty chewing or speaking, and even further tooth loss as the misaligned teeth become more susceptible to decay and gum disease. Moreover, the loss of teeth can lead to bone resorption in the jaw, which may compromise the stability and strength of the surrounding teeth and ultimately affect facial structure.
In addition to the physical implications, losing teeth prematurely can also take a toll on an individual’s psychological well-being. Studies have shown that missing teeth can impact a person’s self-esteem, confidence, and social interactions, leading to feelings of embarrassment or self-consciousness about their appearance. Furthermore, the functional limitations resulting from tooth loss can hinder one’s ability to enjoy a varied diet, potentially affecting their overall nutritional intake and general health. Addressing premature tooth loss promptly through appropriate treatment options is crucial in mitigating these complications and preserving both oral health and overall quality of life.
Premature tooth loss can be influenced by various common risk factors. Poor oral hygiene practices, such as irregular brushing and flossing, can lead to gum disease and tooth decay, ultimately resulting in tooth loss. Additionally, a diet high in sugary foods and beverages can contribute to the erosion of tooth enamel, weakening the teeth and increasing the likelihood of premature loss.
Furthermore, habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of tooth loss. These habits not only impact oral health directly but can also impede the body’s ability to heal and repair damaged tissues in the mouth. Addressing these common risk factors through education, early intervention, and lifestyle modifications is crucial in preventing premature tooth loss and maintaining optimal oral health.
Orthodontic considerations are vital following premature tooth loss, especially in pediatric patients. The absence of teeth can lead to misalignment issues as neighboring teeth may gradually shift or tilt into the empty space. This can disrupt the natural alignment of the dental arches, potentially causing bite problems and aesthetic concerns. Early intervention by an orthodontic specialist is crucial to address these issues promptly and prevent further complications.
Orthodontic treatment options such as braces or clear aligners may be recommended to correct misalignments resulting from premature tooth loss. These interventions aim to realign the teeth, restore proper occlusion, and improve overall oral function and appearance. Regular orthodontic evaluations are essential to monitor the progress of treatment and ensure optimal outcomes, particularly in young patients whose dental development is still ongoing.
Tooth loss, especially when experienced prematurely, can lead to a host of potential long-term consequences that extend beyond the immediate impact on oral health. One significant issue that arises from early tooth loss is the potential for adjacent teeth to shift or tilt into the empty space, causing misalignment and bite problems. This shift can also lead to changes in the jaw structure over time, potentially affecting the individual’s facial appearance and overall oral function. Additionally, the lack of stimulation from the missing tooth can result in bone loss in the jawbone, which may compromise the stability of neighboring teeth and impact future dental implant options.
Furthermore, the consequences of premature tooth loss can extend to psychological and social aspects, as individuals may experience a loss of self-esteem or confidence due to changes in their smile or speech patterns. This can have a ripple effect on interpersonal relationships and overall quality of life. Additionally, compromised chewing ability and digestion issues may arise from missing teeth, impacting one’s nutritional intake and overall health in the long term. Addressing premature tooth loss promptly and effectively through appropriate treatment is crucial in mitigating these potential long-term consequences and preserving optimal oral health and overall well-being.
Genetics play a crucial role in the development of our teeth, influencing the size, shape, structure, and even susceptibility to certain dental conditions. The blueprint encoded in our genes dictates the formation of our primary and permanent teeth, guiding the intricate process of tooth development starting from the embryonic stage. Variations in genes can lead to diverse outcomes in tooth morphology, eruption patterns, and even enamel thickness, highlighting the significant impact genetics wield on oral health.
Research into the genetic basis of tooth development has unveiled essential insights into the hereditary factors contributing to conditions like missing teeth, malformed dentition, and dental anomalies. By understanding how genetic variations influence tooth development, dental professionals can better tailor treatment plans to address individual patient needs and anticipate potential dental challenges. Collaborating advancements in genetics and dentistry offer a promising avenue for personalized oral healthcare, paving the way for precise interventions and preventive strategies tailored to an individual’s genetic predispositions.
After experiencing tooth loss, maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial to prevent further dental issues and maintain overall oral health. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent bacterial build-up and protect the gums from infections. Flossing daily is also essential to remove food particles and plaque from between teeth, reducing the risk of gum disease.
In addition to regular oral hygiene practices, it is important to schedule regular dental check-ups with a professional to monitor any changes in the mouth and address any concerns promptly. Professional cleanings and exams can help detect early signs of decay or gum disease, ensuring timely treatment to prevent complications. Implementing these habits post-tooth loss can help preserve the remaining teeth and gums, promoting better oral health in the long run.
When considering consulting with a dental professional for missing teeth, it is crucial to seek care from a qualified dentist who specializes in restorative dentistry. A dental professional can assess the extent of tooth loss, evaluate oral health status, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on individual needs. Through a comprehensive examination, including X-rays and oral health history review, the dentist can develop a personalized treatment plan to address missing teeth effectively.
Furthermore, consulting with a dental professional allows for early intervention to prevent potential complications associated with tooth loss. Dental professionals can provide valuable guidance on maintaining optimal oral hygiene after tooth loss, reducing the risk of gum disease, bone loss, and adjacent teeth shifting. By seeking timely advice and treatment from a dental professional, patients can improve their overall oral health and restore function and aesthetics, contributing to a better quality of life.
Genetics can influence the strength of enamel, tooth size, and the alignment of teeth, which can all impact the likelihood of premature tooth loss.
Yes, maintaining good oral hygiene habits, avoiding tobacco use, wearing mouthguards during sports activities, and regular dental check-ups can help prevent premature tooth loss.
Untreated premature tooth loss can lead to shifting of remaining teeth, changes in bite alignment, jawbone deterioration, and even an increased risk of developing gum disease.
Baby teeth play a crucial role in guiding the eruption of permanent teeth and maintaining proper spacing in the mouth. Premature loss of baby teeth can lead to alignment issues and potential premature loss of permanent teeth.
Orthodontic treatment may be necessary to help realign teeth and correct bite issues that may arise from premature tooth loss.
Common risk factors include poor oral hygiene, gum disease, smoking, genetics, trauma to the mouth, and certain medical conditions like diabetes.
Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, can help prevent infection, decay, and further tooth loss after losing a tooth prematurely.
It is important to consult with a dental professional if you experience any signs of early tooth loss, such as loose teeth, gum recession, or persistent tooth pain, to discuss treatment options and preventative measures.