Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Mouth Sores. Learn about the causes, prevention, and treatment options for common mouth sores.
Oral lesions can be caused by a variety of factors, with some of the most common culprits being trauma or injury to the mouth’s soft tissues. Accidental bites, sharp food particles, or irritation from orthodontic appliances can all lead to the development of oral sores. Infections, whether bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature, can also contribute to the formation of lesions within the oral cavity. Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can create an environment ripe for the proliferation of harmful bacteria that may trigger oral lesions. Additionally, systemic conditions like autoimmune diseases or nutritional deficiencies can manifest as oral ulcers, highlighting the interconnectedness of overall health with oral health.

Furthermore, certain lifestyle habits can exacerbate the risk of developing oral lesions. Tobacco use, whether through smoking or chewing, is a significant contributor to oral health issues, including the formation of oral lesions. Alcohol consumption, particularly excessive or frequent intake, can also irritate the oral mucosa and increase susceptibility to oral sores. Moreover, stress and anxiety have been linked to the development and aggravation of oral lesions, underscoring the importance of managing one’s mental well-being in conjunction with maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Identifying and addressing these common causes of oral lesions is crucial in preventing their occurrence and promoting optimal oral health.
Mouth sores, also known as oral ulcers, can present in various forms, each with its own distinct characteristics. The most common types of mouth sores include canker sores, cold sores, leukoplakia, and candidiasis. Canker sores are small, painful ulcers that typically appear inside the mouth, often on the inner cheeks or lips. They are not contagious and usually heal on their own within 1-2 weeks. Cold sores, on the other hand, are caused by the herpes simplex virus and are contagious. They appear as fluid-filled blisters on the lips or around the mouth and can be recurrent.
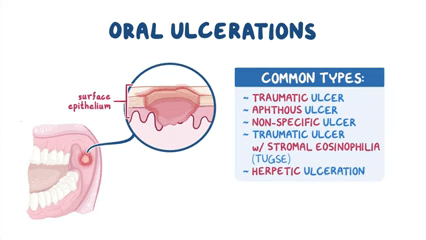
Leukoplakia manifests as white or gray patches inside the mouth, which can be precancerous and may require medical attention. Candidiasis, also known as oral thrush, is a fungal infection characterized by creamy white lesions on the tongue and inner cheeks. It is more common in infants, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems. Understanding the distinguishing features of each type of mouth sore is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment interventions.
Oral ulcers, commonly known as canker sores, present with various symptoms that can cause discomfort and affect daily activities such as eating and speaking. The primary symptom of oral ulcers is the presence of round or oval-shaped sores inside the mouth, often with a red border and a white or yellow center. These ulcers can develop on the inner cheeks, gums, tongue, or roof of the mouth. Individuals may experience pain or a burning sensation at the site of the ulcer, especially when consuming acidic or spicy foods.
| Symptoms of Oral Ulcers | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Pain or Discomfort | Oral ulcers often cause localized pain or discomfort, especially when eating, drinking, or speaking. |
| 2. Redness or Inflammation | The affected area may appear red, swollen, or inflamed, indicating irritation or infection. |
| 3. White or Yellow Center | Ulcers may have a white or yellow center, surrounded by a red border, resembling a crater or blister. |
| 4. Difficulty Eating | Painful ulcers can make eating or chewing difficult, leading to changes in diet or appetite. |
| 5. Sensitivity to Spicy or Acidic Foods | Ulcers can become more painful when exposed to spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods. |
| 6. Soreness or Burning Sensation | A sore or burning sensation may be felt in the affected area, especially when touched or irritated. |
| 7. Recurrence | Oral ulcers may recur periodically, with varying frequency and severity. |
In addition to the physical appearance of the sores, individuals with oral ulcers may also experience sensitivity in the affected area. This sensitivity can range from mild discomfort to sharp pain, making it challenging to eat or drink certain foods. Some individuals may also notice a tingling or burning sensation before the ulcer appears, serving as an early warning sign of an impending lesion. In severe cases, oral ulcers can lead to difficulty in speaking or swallowing, further impacting an individual’s quality of life.
Oral lesions can be discomforting and concerning, requiring appropriate treatment to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. One common treatment option for oral ulcers is the use of topical corticosteroids, which can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with the lesions. These medications are available in various forms such as creams, gels, or mouth rinses and are typically prescribed by healthcare providers based on the severity of the lesions.
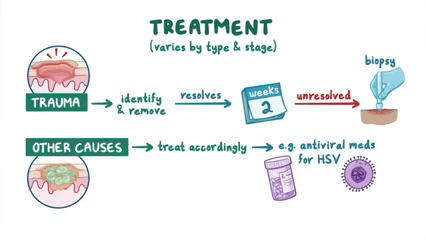
In addition to corticosteroids, over-the-counter topical anesthetics can also be used to numb the affected area and provide temporary relief from pain. These products contain numbing agents such as benzocaine or lidocaine, which can help patients manage discomfort while the lesions heal. It is important to follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals or written on the product packaging to ensure safe and effective use of these topical anesthetics.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing the development of painful mouth sores. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help keep your mouth free from harmful bacteria that may lead to oral lesions. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water and avoiding tobacco products can also contribute to a healthy oral environment.
Furthermore, being mindful of your diet can play a significant role in preventing mouth sores. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and iron, can support a strong immune system and promote overall oral health. Limiting the intake of acidic and spicy foods, as well as sugary snacks and beverages, can help reduce the likelihood of developing oral ulcers. Remember, a healthy mouth starts with good oral care habits and a nutritious diet.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is paramount in preventing oral lesions. Brushing your teeth twice a day, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily can significantly reduce the risk of developing mouth sores. Proper oral hygiene practices help remove bacteria and food particles that can irritate the delicate tissues in the mouth, decreasing the likelihood of lesions forming.
| Importance of Oral Hygiene | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Removal of Plaque and Bacteria | Regular brushing and flossing help remove plaque and bacteria from the mouth, reducing the risk of oral lesions. |
| 2. Prevention of Gum Disease | Proper oral hygiene prevents gum disease, which can contribute to the development of oral lesions. |
| 3. Reduction of Oral Irritation | Keeping the mouth clean and free of irritants reduces the likelihood of developing oral lesions caused by irritation. |
| 4. Promotion of Healing | Good oral hygiene supports the body’s natural healing process, aiding in the recovery of existing oral lesions. |
| 5. Prevention of Infections | Oral lesions provide entry points for bacteria and viruses, which can lead to infections; maintaining oral hygiene reduces this risk. |
| 6. Detection of Lesions | Regular oral hygiene practices allow individuals to identify changes or abnormalities in the mouth, prompting timely evaluation and treatment of lesions. |
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings play a crucial role in oral health maintenance. Professional cleanings can remove plaque and tartar buildup that may contribute to oral lesions. Additionally, dentists can identify early signs of potential issues during routine exams, allowing for prompt intervention and prevention of more severe oral health conditions.
Mouth sores are a common occurrence for many individuals, often resolving on their own within a week or two. However, there are certain instances where seeking medical attention is essential. If a mouth sore persists for more than two weeks without showing signs of improvement, it is advisable to consult a dentist or healthcare provider. Prolonged sores could be indicative of a more serious underlying condition that requires professional evaluation and treatment.
Additionally, if the mouth sore is unusually large, painful, recurrent, or accompanied by severe symptoms such as fever, difficulty swallowing, or swollen lymph nodes, prompt medical attention is warranted. These signs may indicate a more severe form of oral lesion or an underlying health issue that needs to be addressed by a healthcare professional for appropriate management. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent complications and ensure optimal oral health.
Untreated oral ulcers can lead to several complications if not addressed promptly. One of the primary risks associated with ignoring oral ulcers is the potential for infection. When the delicate tissue in the mouth is compromised by an ulcer, it becomes more susceptible to bacterial invasion, which can result in localized or systemic infections. These infections may exacerbate the ulcer, leading to prolonged healing times and increased discomfort for the individual.
Moreover, leaving oral ulcers untreated can also heighten the risk of developing chronic oral conditions. Recurrent mouth sores can indicate an underlying health issue or trigger factors that need to be identified and managed. Ignoring these ulcers may perpetuate the cycle of recurring lesions, causing undue stress and discomfort for the patient. Additionally, certain types of oral ulcers can be symptomatic of more serious systemic conditions, necessitating timely intervention to prevent further health complications.
Canker sores, clinically known as aphthous ulcers, are small, shallow lesions that develop on the soft tissues inside the mouth, such as the cheeks, lips, or tongue. These painful sores are typically round or oval with a white or yellow center and a red border. Canker sores are not contagious and are believed to be triggered by factors like stress, tissue injury from braces or rough brushing, hormonal changes, or certain foods like citrus fruits or spicy dishes. They generally heal on their own within one to two weeks without scarring.
In contrast, cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and are highly contagious. Cold sores appear as clusters of small blisters, often on the lips but can also occur around the mouth or nostrils. These blisters burst, crust over, and then heal within about two to four weeks. Cold sores can be recurrent, as the herpes virus remains dormant in the body and can be reactivated by triggers like stress, illness, sunlight exposure, or hormonal fluctuations. Managing cold sores involves antiviral medications, topical creams, and avoiding direct contact with the sores to prevent spreading the virus.
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining good oral health and preventing the occurrence of mouth sores. Certain nutrients are essential for healthy gums and tissues in the mouth. For instance, Vitamin C supports collagen production, which is crucial for gum health, while Vitamin B complex helps in preventing inflammation and canker sores. Moreover, a diet rich in antioxidants such as Vitamin E and beta-carotene can help reduce the risk of oral lesions by combating free radicals that damage oral tissues. On the other hand, consuming excessive sugary and acidic foods can contribute to the development of cavities and mouth ulcers, as they create an environment conducive to bacterial growth and inflammation in the oral cavity.
In addition to nutrients, hydration is key for overall oral health. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain saliva production, which plays a vital role in washing away food particles and bacteria in the mouth. Saliva also contains minerals that contribute to the remineralization of tooth enamel, thus preventing the formation of cavities. Therefore, staying hydrated by drinking water throughout the day can boost saliva production and support oral health, reducing the likelihood of developing oral lesions. It is essential to be mindful of what we consume, as our dietary choices have a direct impact on the health of our mouths.
Stress is a common factor that can exacerbate oral lesions in individuals, particularly those prone to conditions such as canker sores or oral ulcers. The connection between stress and oral health is well-documented, with research indicating that high-stress levels can lead to a weakened immune system, making individuals more susceptible to developing oral lesions. Additionally, stress can trigger inflammatory responses in the body, which may manifest in the form of painful mouth sores.
Furthermore, prolonged periods of stress can also contribute to habits like teeth grinding or clenching, known as bruxism, which can further aggravate oral lesions. Bruxism can exert excessive pressure on the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues, leading to irritation and potential injury, ultimately worsening existing oral ulcers. Moreover, the physical manifestation of stress through habits like nail-biting or cheek chewing can also introduce harmful bacteria into the oral cavity, increasing the likelihood of developing or worsening mouth sores.
Oral lesions can be influenced by a variety of factors, one of which is genetics. Researchers have found that a person’s genetic makeup can play a role in their predisposition to developing mouth sores. Certain genetic variations may make individuals more susceptible to oral ulcers, while others may offer protection against them. Understanding the genetic component of oral lesions is essential in providing personalized care and treatment for individuals who are prone to developing these conditions.
Studies have shown that specific genes related to immune function and inflammation may affect an individual’s likelihood of experiencing recurrent mouth sores. Genetic predisposition to conditions such as autoimmune diseases can also increase the risk of developing oral ulcers. By unraveling the genetic factors involved in oral lesions, healthcare professionals can better tailor preventive measures and treatment plans to address the unique needs of patients with a genetic predisposition to mouth sores.
Oral lesions in children can be a cause of concern for parents, as they may not always be able to communicate their discomfort effectively. It is important for parents to be observant and proactive in ensuring their child’s oral health. Common oral lesions in children include canker sores, cold sores, and ulcers. These lesions can be triggered by various factors such as infections, injuries, or underlying health conditions. Parents should monitor their child’s oral hygiene practices and diet to help prevent the development of oral lesions.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and management of oral lesions in children. If a parent notices any unusual lesions or sores in their child’s mouth that do not heal within a week or seem to be worsening, it is advisable to seek prompt medical attention from a pediatric dentist or healthcare provider. Timely intervention can prevent potential complications and ensure the child’s oral health is maintained effectively.
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body. Research has shown a correlation between certain autoimmune diseases and the development of oral lesions or mouth sores. In individuals with autoimmune conditions like lupus, Crohn’s disease, or pemphigus vulgaris, the body’s immune response can target the tissues in the mouth, leading to painful ulcers and sores. Understanding the link between autoimmune diseases and oral lesions is crucial in managing both the systemic health of the patient and their oral wellbeing.
Patients with autoimmune diseases experiencing oral lesions may require a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals like dentists, rheumatologists, and immunologists. Proper diagnosis and management of the underlying autoimmune condition are essential in addressing the oral manifestations effectively. Moreover, monitoring oral health regularly and seeking prompt treatment for any oral lesions can help in preventing complications and improving the overall quality of life for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
For individuals seeking alternative remedies to alleviate oral ulcers, there are several natural options that may provide relief. Aloe vera, known for its soothing properties, can be applied topically to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and pain associated with oral ulcers. Additionally, gargling with salt water several times a day can help promote healing and prevent infection in the mouth.
Another alternative remedy for oral ulcers is honey, which possesses antimicrobial properties that can aid in the healing process. Applying honey directly to the ulcer or incorporating it into warm water for a soothing mouth rinse may help reduce discomfort and promote faster recovery. Furthermore, chamomile tea, with its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, can be used as a mouth rinse to help alleviate pain and promote healing of oral ulcers.
Yes, there are several alternative remedies that can help alleviate oral ulcers. These include using aloe vera gel, applying honey directly to the ulcer, rinsing with salt water, using licorice root extract, and taking vitamin B supplements.
Yes, essential oils such as tea tree oil and lavender oil have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help with oral ulcers. However, it is important to dilute the essential oils properly before use and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Some people find relief from oral ulcers through acupuncture, as it can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. However, it is important to consult with a licensed acupuncturist to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Probiotics can help restore the balance of good bacteria in the mouth, which may help prevent oral ulcers from recurring. Consuming probiotic-rich foods or taking probiotic supplements can support overall oral health.
Yes, herbal supplements such as echinacea, myrrh, and chamomile have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that may help alleviate oral ulcers. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any herbal supplements.