Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
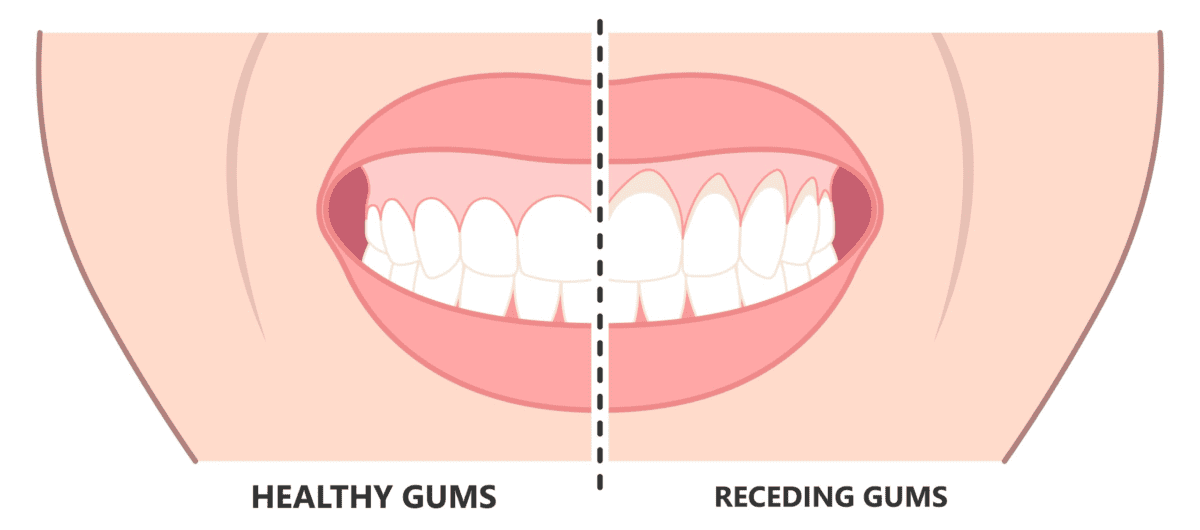
Find out the truth about gum recession and whether receding gums can grow back.
Gum recession is a common dental condition that occurs when the gums surrounding the teeth gradually pull back or wear away, exposing more of the tooth roots. While it may seem like a minor issue, gum recession can have serious implications for oral health if left untreated. Understanding the causes of gum recession is crucial in order to prevent and address this condition effectively.
One of the primary causes of gum recession is poor oral hygiene. Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can irritate the gums and eventually cause them to recede. Additionally, aggressive brushing techniques and using a toothbrush with hard bristles can contribute to gum recession. It is essential to adopt proper oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and daily flossing, to minimize the risk of gum recession.

Furthermore, certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to gum recession. These include tobacco use, which can hinder blood flow to the gums and increase the likelihood of gum deterioration. Additionally, bruxism, or teeth grinding, can exert excessive pressure on the gums and lead to recession. Regular dental check-ups can help detect any signs of gum recession early on and enable timely intervention. By addressing the causes of gum recession, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy gums and prevent further complications in the future.
Gum recession is a common dental condition that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth starts to pull away or recede, exposing the tooth root. It is important to recognize the early signs of gum recession in order to prevent further damage and protect your oral health.
One of the earliest signs of gum recession is tooth sensitivity. You may notice that your teeth become more sensitive to hot or cold temperatures, as well as to sweet or acidic foods. This sensitivity occurs because the tooth roots, which are normally protected by the gums, become exposed and vulnerable.
Another sign of gum recession is the appearance of longer teeth. As the gum tissue recedes, the teeth can appear longer than usual, giving your smile an uneven or aged look. Additionally, you may notice a notch or groove forming near the gumline of certain teeth. This indentation is known as a tooth abrasion and is caused by the friction of brushing against the exposed tooth root.
If you notice any of these early signs of gum recession, it is important to schedule a visit with your dentist. Early intervention is key in preventing further damage and treating gum recession effectively. Remember, maintaining healthy gums is essential for a beautiful smile and optimal oral health.
Gum recession is a common dental issue that occurs when the gum tissues surrounding the teeth begin to pull away or recede. This can lead to exposure of the tooth roots, which can increase the risk of tooth decay, sensitivity, and even tooth loss. That’s why early intervention for gum recession is crucial in maintaining optimal oral health.
One of the main reasons why early intervention is important is that it allows for more conservative treatment options. When gum recession is detected and addressed in its early stages, non-surgical interventions such as deep cleaning, scaling, and root planing can often be effective in halting the progression of the condition. These procedures help to remove plaque and tartar buildup, reduce inflammation, and promote gum tissue regeneration. By seeking treatment early on, patients can avoid invasive surgical procedures that may be required in advanced stages of gum recession. Additionally, early intervention can prevent further complications, such as infections or bone loss, which can lead to more extensive and costly treatments down the line.
In conclusion, early intervention for gum recession is of utmost importance in preserving the health and integrity of the gums and teeth. By seeking dental care at the first signs of gum recession, patients can significantly improve their chances of successful treatment and prevent further damage to their oral health. If you suspect you may be experiencing gum recession, don’t hesitate to seek the advice of a dental professional who can provide a thorough examination and recommend appropriate treatment options. Remember, taking proactive steps towards early intervention can save you from potential dental complications in the future.
Gum recession is a common dental condition that directly affects oral health. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth gradually wears away, exposing the tooth roots. While this may seem like a minor issue, gum recession can actually have serious implications for overall oral health.
One of the key links between gum recession and oral health is the increased risk of tooth decay. When the gum tissue recedes, the tooth roots become exposed, making them more vulnerable to decay. Additionally, the loss of gum tissue can lead to pockets or gaps between the teeth and gums, creating an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. These bacteria can cause gum infections and contribute to the development of periodontal disease, a more advanced form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Gum Recession | The process where the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. |
| Causes | – Poor oral hygiene – Aggressive tooth brushing – Genetics – Smoking – Hormonal changes – Periodontal disease |
| Effects on Oral Health | – Increased sensitivity – Tooth decay – Tooth loss – Aesthetically unpleasing appearance |
| Importance of Addressing Recession | Prevents further oral health complications – Preserves tooth structure and function |
| Prevention and Treatment | – Regular dental check-ups and cleanings – Proper oral hygiene practices – Soft-bristled toothbrushes – Gum graft surgery for severe cases |
Ensuring optimal oral health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. By understanding the link between gum recession and oral health, individuals can take the necessary steps to prevent and address this condition.
Gum recession can have a significant impact on the appearance of your smile. As the gums recede, more of the tooth structure becomes exposed, leading to longer-looking teeth and an uneven gumline. This can make your smile appear less attractive and may even affect your self-confidence.
Additionally, as the gum tissue pulls back, it can reveal the roots of the teeth. Unlike the smooth and pearly white enamel that covers the crown of the tooth, the roots are yellowish and more prone to staining. This can further detract from the aesthetic appeal of your smile and make it more difficult to maintain a bright and white appearance.

Moreover, gum recession can also create gaps or spaces between the teeth, known as diastemas. These gaps can be unsightly and disrupt the harmonious alignment of the dental arch. They may also affect the function of your bite and make it more challenging to clean between the teeth effectively.
In summary, gum recession can have a negative impact on the appearance of your smile. It can lead to longer-looking teeth, an uneven gumline, exposed roots, and gaps between the teeth. Addressing gum recession promptly and seeking appropriate treatment can help restore both the health and the aesthetics of your smile.
Gum recession, a common dental condition, can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics. While poor oral hygiene and gum disease are often cited as primary causes of gum recession, studies have shown that genetics can also play a significant role in this condition. Research has indicated that certain individuals may be more predisposed to developing gum recession due to inherited traits and variations in their genetic makeup.
One study published in the Journal of Periodontology found that genetic factors accounted for 30-50% of the risk of developing gum recession. This suggests that individuals with a family history of gum recession may be more likely to experience this condition themselves. Understanding the role of genetics in gum recession is crucial in providing personalized treatment and preventive care. By identifying individuals with a higher risk due to genetic factors, dentists can develop targeted interventions and provide proactive oral health guidance to help prevent or minimize the progression of gum recession.
Gum recession is a common dental problem that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing the roots of the teeth. Unfortunately, there are many myths and misconceptions surrounding gum recession that can lead to misunderstandings and misinformation. In this section, we will address some of the most common myths about gum recession and provide accurate information to help you better understand this condition.
Myth #1: Gum recession is caused by brushing too hard.
Fact: While aggressive brushing can contribute to gum recession, it is not the sole cause. Other factors, such as gum disease, hormonal changes, tobacco use, and genetic predisposition, can also play a role in the development of gum recession. It is important to brush your teeth gently and use a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent further damage to the gums. Regular dental check-ups can help identify any underlying causes and provide appropriate treatment.
Myth #2: Gum recession is only a cosmetic issue.
Fact: Although gum recession can affect the appearance of your smile, it is not purely cosmetic. Receding gums can leave the roots of your teeth exposed, making them more susceptible to decay and damage. Additionally, gum recession can lead to tooth sensitivity and increase the risk of tooth loss. It is crucial to address gum recession promptly to prevent further oral health complications. Seeking professional dental care and practicing good oral hygiene habits are key to maintaining healthy gums and preventing gum recession.
Tooth sensitivity can have a significant impact on daily quality of life, making it difficult to enjoy hot or cold beverages, eat certain foods, or even brush and floss properly. While there are various factors that contribute to tooth sensitivity, gum recession is a common culprit. When the gum tissue surrounding the teeth begins to wear away and expose the sensitive roots, it can lead to increased tooth sensitivity. This occurs because the roots contain microscopic tubules that connect to the nerve endings of the teeth, allowing for sensations such as temperature and pressure. As these tubules become exposed, stimuli can easily reach the nerves, resulting in discomfort or pain.
Gum recession not only affects tooth sensitivity, but it can also lead to other dental problems. With the roots of the teeth exposed, there is an increased risk of developing cavities, as the roots do not have the same protective layer of enamel that covers the crowns of the teeth. Additionally, gum recession can contribute to gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. When the gum tissue recedes, it creates pockets around the teeth where bacteria can accumulate and cause inflammation. This can lead to further gum recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss if left untreated. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the early signs of gum recession and seek prompt intervention to minimize the impact on tooth sensitivity and overall oral health.
Gum recession is a common dental condition where the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots. While it may seem like a minor cosmetic concern, gum recession is actually strongly linked to a more serious oral health issue – periodontal disease. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth, including the gums, ligaments, and bone.
When the gum tissue recedes, it creates pockets between the teeth and gums, which become ideal breeding grounds for harmful bacteria. These bacteria can easily accumulate in the pockets and cause infection, leading to chronic inflammation and destruction of the supporting structures around the teeth. If left untreated, periodontal disease can eventually result in tooth loss.
| Gum Recession | Periodontal Disease |
|---|---|
| The gradual loss of gum tissue along the gum line, exposing the roots of teeth. | A bacterial infection that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth, leading to inflammation, bone loss, and eventual tooth loss if left untreated. |
| Common causes include aggressive brushing, genetics, poor oral hygiene, smoking, and gum disease. | Gingivitis, an early stage of periodontal disease, is often marked by swollen, red gums that bleed easily. If not addressed, it can progress to periodontitis, where the supporting bone and fibers that hold teeth in place are damaged. |
| Symptoms may include tooth sensitivity, elongation of teeth, visible roots, and increased risk of cavities at the gum line. | Gum recession is both a symptom and a potential consequence of periodontal disease. As the gums recede, pockets can form between the gums and teeth, creating ideal environments for bacteria to thrive and exacerbate periodontal disease. |
| Treatment options vary depending on the severity and underlying cause and may include scaling and root planing, gum grafting, and lifestyle changes. | Prevention involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, avoiding tobacco products, and addressing risk factors such as teeth grinding or misaligned teeth. |
| Left untreated, severe gum recession can lead to tooth mobility, sensitivity, and eventual tooth loss. | Periodontal disease not only affects oral health but is also linked to systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. |
| It’s essential to address gum recession promptly to prevent further damage and maintain overall oral health. | Collaborative efforts between patients and dental professionals are crucial in managing gum recession and preventing its association with periodontal disease. |
Research has shown a clear connection between gum recession and periodontal disease. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that individuals with at least one recessed gum area were more likely to have periodontal disease. Another study conducted at the University of Maryland School of Dentistry revealed that severe gum recession was significantly associated with increased levels of periodontal pathogens.
It is important to understand that gum recession should not be ignored, as it can be an early sign of underlying periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups and early intervention are crucial in preventing the progression of gum recession and the development of periodontal disease.
Non-surgical treatment options for gum recession involve a range of procedures that can help restore gum tissue and prevent further recession without the need for surgery. These treatments are typically recommended in the early stages of gum recession when the condition is still reversible and has not progressed to a more severe stage.
One non-surgical treatment option is scaling and root planing, which involves deep cleaning of the teeth and roots to remove plaque and tartar buildup. This procedure can help reduce inflammation and promote gum reattachment to the tooth surface. Another option is the use of topical antibiotics, such as antimicrobial mouth rinses or gels, which can help control bacterial infection and promote healing of the gum tissue.
In addition, your dentist may recommend certain lifestyle changes to help improve gum health, such as quitting smoking, maintaining good oral hygiene practices, and avoiding foods and beverages that are known to contribute to gum inflammation. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also crucial in keeping gum recession at bay.
By exploring these non-surgical treatment options and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals with gum recession can take proactive steps towards improving their gum health and preserving their smiles. It is important to consult with a dental professional who can provide personalized recommendations based on the severity of your condition and overall oral health.
Surgical treatment can offer several benefits for individuals experiencing gum recession. One of the primary advantages is the ability to restore lost gum tissue and cover exposed roots, providing protection and improving the aesthetic appearance of the smile. Through procedures like gum grafting, surgeons can harvest healthy tissue from another area of the mouth, such as the roof of the mouth, and transplant it to the receding area. This helps to rebuild the gum line and prevent further recession, reducing the risk of tooth sensitivity and decay.
However, it is essential to consider the limitations of surgical treatment for gum recession. First and foremost, surgery is a more invasive option compared to non-surgical methods, and it may involve a longer recovery period. It is also important to note that surgical procedures may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with underlying medical conditions or compromised immune systems. Additionally, the success of surgical treatment depends on several factors, including the individual’s oral hygiene habits, overall health, and the skill of the surgeon. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a dental professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for gum recession.
After undergoing treatment for receding gums, it is important to follow a proper post-treatment care routine to ensure optimal healing and long-term oral health. This care routine will help to minimize discomfort, reduce the risk of complications, and promote the regeneration of gum tissue. Here are some key steps to include in your post-treatment care for receding gums.
First and foremost, maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial. Brushing your teeth gently twice a day with a soft-bristle toothbrush and a fluoride toothpaste will help to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and the gumline. It is important to avoid brushing too aggressively, as this can further irritate the gum tissue. Additionally, flossing daily will help to clean between the teeth and remove any debris that may have accumulated.
To further support healing and reduce discomfort, rinsing with a warm saltwater solution can be beneficial. Mix half a teaspoon of salt with eight ounces of warm water and gently swish it around in your mouth for about 30 seconds. This can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Following these post-treatment care tips will help to ensure a successful recovery from gum recession treatment. However, it is essential to consult with your dentist or periodontist for personalized advice and instructions based on your specific situation and treatment. They will be able to provide you with the best guidance to promote healing and maintain optimal oral health.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential for preventing gum recession and promoting overall dental health. By following a few best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum recession and keep your gums healthy.
Firstly, it is crucial to brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brushing should be done using gentle, circular motions to effectively remove plaque without damaging the gums. It is recommended to replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
Additionally, flossing daily is an essential part of a good oral hygiene routine. Flossing helps remove plaque and bacteria from between the teeth and along the gumline, areas that cannot be reached by a toothbrush alone. Use a gentle sawing motion to slide the floss between each tooth, being careful not to snap it against the gums. Regular flossing can help prevent gum recession by removing plaque buildup that can lead to gum disease.
By incorporating these simple practices into your daily routine, you can effectively prevent gum recession and maintain optimal oral hygiene. However, it is important to remember that regular professional dental cleanings and check-ups are also vital for early detection and treatment of any potential dental issues. Your dentist will be able to provide personalized guidance and recommend additional preventive measures based on your specific needs.
Regular professional dental cleanings play a crucial role in preventing gum recession and maintaining optimal oral health. These cleanings, performed by dental hygienists or dentists, offer a level of deep cleaning that cannot be achieved through regular brushing and flossing alone. During a professional cleaning, the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can contribute to gum recession, is skillfully removed.
Plaque is a sticky film containing bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. When plaque is not adequately removed, it hardens into tartar, which irritates and inflames the gums. This inflammation can ultimately lead to gum recession. Professional dental cleanings effectively remove both plaque and tartar, reducing the risk of gum recession and helping to maintain healthy gums. Additionally, these cleanings provide an opportunity for early detection of any signs of gum disease or other oral health issues, allowing for prompt interventions and preventative measures.
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health, and there are certain lifestyle factors that can significantly contribute to gum recession. Poor oral hygiene is perhaps the most common cause of gum recession. Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque, which can gradually erode the gum tissue surrounding the teeth. Additionally, using a toothbrush with hard bristles or brushing too aggressively can also damage the delicate gum tissue, eventually leading to recession.
Another lifestyle factor that can contribute to gum recession is tobacco use. Smoking or chewing tobacco not only stains the teeth, but it also reduces the flow of blood to the gums. This reduced blood flow weakens the gum tissue, making it more susceptible to recession. Furthermore, smoking can impair the body’s ability to heal and fight off infections, increasing the risk of gum disease, which is closely linked to gum recession.
In conclusion, taking care of your gums is essential for maintaining good oral health, and several lifestyle factors can contribute to gum recession. Practicing proper oral hygiene and avoiding tobacco use are crucial steps in preventing gum recession and maintaining healthy gums. By being mindful of these lifestyle factors, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum recession and enjoy a healthier, more confident smile.
Taking proactive steps to maintain healthy gums is crucial for long-term gum recession prevention. By incorporating these simple tips into your oral care routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum recession and promote optimal oral health.
1. Practice proper oral hygiene: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste is essential. Additionally, regular flossing helps remove plaque and bacteria from hard-to-reach areas, preventing gum disease and recession.
2. Use a gentle technique: Avoid using excessive force when brushing your teeth, as aggressive brushing can damage your gum tissue and lead to recession. Instead, use a gentle circular or back-and-forth motion to effectively clean your teeth without causing harm.
3. Maintain a balanced diet: A nutritious diet not only benefits your overall health but also plays a significant role in promoting gum health. Ensure your diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products to provide the essential nutrients needed for strong and healthy gums.
4. Quit tobacco use: Smoking and using other tobacco products drastically increase the risk of gum disease and recession. If you are a tobacco user, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your oral health and overall well-being.
Remember, prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to gum recession. By following these tips and seeking regular dental check-ups, you can maintain healthy gums and keep the risk of gum recession at bay.
The common causes of gum recession include aggressive brushing, poor oral hygiene, gum disease, hormonal changes, tobacco use, grinding or clenching of teeth, and genetics.
Early signs of gum recession include tooth sensitivity, longer-looking teeth, visible roots, swollen or red gums, bleeding gums, and bad breath.
Early intervention is important for gum recession because it can help prevent further damage to the gums and teeth, and it increases the chances of successful treatment.
Gum recession can make your teeth look longer, change the shape of your smile, and expose the roots of your teeth, affecting the overall appearance of your smile.
While genetics can play a role in gum recession, it is not solely caused by genetics. Poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and certain lifestyle factors can also contribute to gum recession.
Yes, common misconceptions about gum recession include the belief that it only affects older adults, that it is irreversible, and that it doesn’t require treatment if there is no pain.
Gum recession exposes the roots of the teeth, which can lead to increased tooth sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, as well as sweet or acidic foods and beverages.
Gum recession can be a sign or result of periodontal disease. If left untreated, gum recession can further worsen the progression of periodontal disease.
Yes, non-surgical treatment options for gum recession include scaling and root planing, professional teeth cleanings, antibiotic therapy, and the use of oral hygiene aids.
Surgical treatment for gum recession, such as gum grafting, can help restore gum tissue and cover exposed roots. However, it may have limitations depending on the severity of the recession and individual factors.
After treatment for gum recession, it is important to follow the dentist’s instructions, maintain good oral hygiene, avoid smoking or tobacco use, and attend regular dental check-ups.
Best practices for preventing gum recession include maintaining good oral hygiene, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, practicing gentle brushing techniques, and avoiding tobacco use.
Professional dental cleanings can remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are major contributors to gum disease and gum recession. Regular cleanings can help prevent gum recession.
Yes, lifestyle factors such as smoking, poor nutrition, grinding or clenching of teeth, and stress can contribute to gum recession. It is important to address these factors for long-term gum recession prevention.