Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
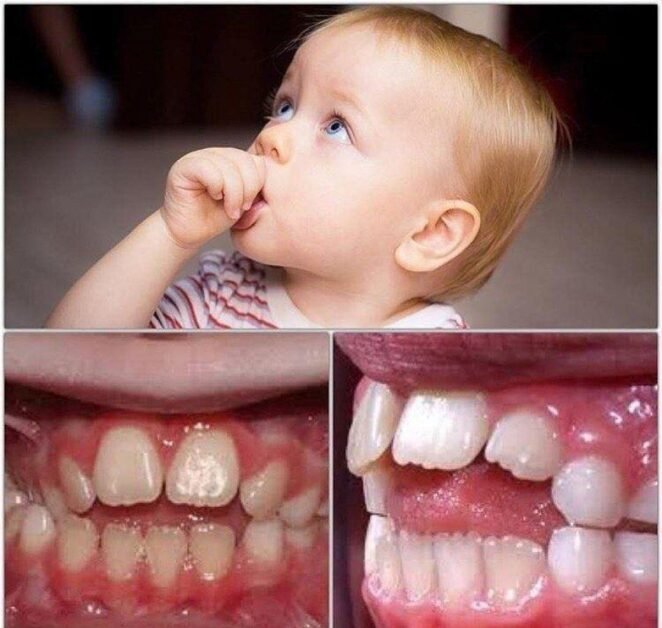
Discover how thumb sucking affects your child's smile and how to break the habit.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children, but its impact on dental health should not be overlooked. In fact, prolonged and vigorous thumb sucking can lead to a variety of dental issues that may require orthodontic intervention. One of the primary concerns is the misalignment and positioning of the teeth.
When a child sucks their thumb, the constant pressure and suction exerted on the teeth can cause them to shift out of their natural alignment. This can result in a malocclusion, or a bad bite, with potential consequences such as crowded or crooked teeth, an overbite, or an open bite. These dental problems not only affect the appearance of the smile but can also lead to difficulties with biting, chewing, and proper speech development.
Additionally, thumb sucking can also affect the development of the jawbone and facial muscles. The repetitive motion of thumb sucking can alter the natural growth and development of the bones and muscles in the mouth, leading to changes in the shape and size of the dental arches. In some cases, this can result in a narrow upper jaw, a crossbite, or an underbite. These skeletal abnormalities may require orthodontic treatment and can impact the overall facial aesthetics and function.
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to understand the potential consequences of thumb sucking on dental health. Early recognition and intervention are key in preventing long-term issues. By addressing thumb sucking habits at an appropriate age and seeking guidance from a dental professional, parents can help mitigate the impact on their child’s dental development. Stay tuned for the upcoming sections of this article to better understand the mechanics of thumb sucking and effective strategies for breaking this habit.

Thumb sucking is a common habit in young children and infants, often providing comfort and reassurance. However, it is important to understand the mechanics of thumb sucking and its effects on teeth. When a child sucks their thumb, it exerts pressure on the teeth and surrounding structures. Over time, this sustained pressure can lead to changes in dental alignment and positioning.
One of the primary effects of thumb sucking on teeth is the misalignment of the dental arches. The continuous pressure from the thumb can cause the upper teeth to become protruded and the lower teeth to shift inward, resulting in a misaligned bite. This can lead to difficulties in chewing, speech problems, and potential jaw joint issues later in life. Additionally, prolonged thumb sucking can cause the roof of the mouth to become narrower, which can also contribute to dental and orthodontic issues.
It is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the potential consequences of thumb sucking on dental health and to take appropriate measures to address the habit. Early intervention and encouragement of alternative comforting techniques can help prevent long-term dental issues. Consulting with a dentist or orthodontist experienced in pediatric dentistry is crucial in developing a personalized plan to break the thumb sucking habit and support optimal dental development.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children, but there are several misconceptions regarding its impact on dental health. One common misconception is that thumb sucking is harmless and will not affect the alignment or positioning of teeth. However, prolonged thumb sucking can indeed cause dental issues. The constant pressure and suction from thumb sucking can push the teeth out of alignment, leading to malocclusion and bite problems. This can result in difficulty chewing, speech issues, and even self-esteem concerns as the child grows older.
Another misconception is that thumb sucking will naturally stop on its own and does not require intervention. While it is true that many children will naturally outgrow thumb sucking as they develop other coping mechanisms, there are cases where the habit persists well into childhood. In these cases, intervention may be necessary to prevent long-term dental problems. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to monitor their child’s thumb sucking habits and intervene if the habit persists beyond the age of four or five. Early intervention can help prevent the need for more extensive orthodontic treatment in the future.
| Misconception | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Thumb sucking doesn’t affect dental health. | Thumb sucking can cause dental issues like misalignment, overbite, or palate problems, especially if the habit persists beyond infancy. |
| Only infants suck their thumbs. | Thumb sucking can persist beyond infancy and into childhood. Prolonged thumb sucking increases the risk of dental problems and can affect oral development. |
| It’s harmless if the child stops sucking their thumb by age 3. | While stopping thumb sucking early can mitigate dental issues, prolonged sucking beyond age 3 can still lead to dental problems and may necessitate orthodontic treatment. |
| A pacifier is a better alternative to thumb sucking. | While pacifiers may be easier to control, extended pacifier use can also lead to dental issues similar to thumb sucking. Parents should monitor and wean children off pacifiers appropriately. |
| It’s not a big deal if the child sucks their thumb occasionally. | Even occasional thumb sucking can affect dental development over time, especially if it becomes a habit during periods of stress or boredom. Parents should gently discourage the behavior. |
| Thumb sucking is solely a behavioral issue. | While thumb sucking often begins as a soothing behavior, it can also have physiological causes, like teething discomfort or hunger. Addressing underlying causes can help reduce the habit. |
| Once permanent teeth come in, thumb sucking won’t affect them. | Thumb sucking can still impact permanent teeth, leading to issues like misalignment or bite problems, even after the primary teeth have fallen out. Parents should address the habit early. |
Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children and is often considered harmless. However, prolonged and intense thumb sucking can lead to various dental issues that may require professional intervention. As a dentist specializing in pediatric dentistry, I have observed several signs that indicate dental problems caused by thumb sucking.
One of the most noticeable signs is the misalignment of the teeth. Prolonged thumb sucking can apply continuous pressure on the teeth, leading to the misalignment of the front teeth, commonly known as an open bite. This occurs when the upper and lower front teeth don’t meet when the mouth is closed. Additionally, thumb sucking can also cause the upper teeth to be pushed forward and the lower teeth to be pushed backward, resulting in a crossbite. These misalignments can affect not only the appearance of the smile but also the functionality of the teeth.
Another sign to look out for is a change in the shape of the palate. The constant presence of the thumb in the mouth can exert pressure on the roof of the mouth, causing it to become narrower and higher. This condition, known as a high narrow palate, can lead to issues such as speech difficulties, breathing problems, and even obstructive sleep apnea. It is important to identify these signs early on to prevent further complications and ensure the proper development of the child’s dental and oral structures.
In conclusion, identifying the signs of dental issues caused by thumb sucking is crucial for early intervention and prevention of long-term problems. Misaligned teeth and changes in the shape of the palate are common indicators of the detrimental effects of prolonged thumb sucking. By recognizing these signs, parents can seek professional dental care and take appropriate measures to break the thumb sucking habit, ensuring the optimal dental health and development of their child.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children, which can have a significant impact on the alignment and positioning of their teeth. When a child sucks their thumb, it exerts continuous pressure on the developing teeth and oral structures. Over time, this pressure can cause the teeth to shift from their proper alignment, leading to potential dental issues.
One of the main ways thumb sucking affects tooth alignment is by pushing the front teeth forward and causing an overbite. The constant pressure from the thumb can result in the upper front teeth protruding outward, creating an improper bite relationship between the upper and lower jaws. This can also cause the upper jaw to become narrow and the lower jaw to become set back, contributing further to the misalignment. The longer the thumb sucking habit persists, the more likely it is for these misalignments to become permanent.
In addition to overbite, thumb sucking can also lead to an open bite, a condition where the front teeth do not touch when the back teeth are closed together. This can affect proper chewing, speech, and the overall functioning of the jaws. The prolonged thumb sucking habit can also cause other orthodontic issues such as crossbite, crowded teeth, and disruptions in facial growth and development.
It is important to address thumb sucking early on to minimize the potential impact on tooth alignment. Parents should consult with a pediatric dentist or an orthodontist who can provide guidance on effective strategies to break the thumb sucking habit. Timely intervention and appropriate orthodontic treatment, if necessary, can help ensure the proper alignment and positioning of the teeth as the child grows older.

Thumb sucking is a common habit among infants and young children, and it plays a significant role in dental development and growth. The action of sucking provides comfort and soothing for children, but it can have implications on their oral health in the long run.
One of the primary effects of thumb sucking on dental development is the potential misalignment of the teeth. The constant pressure exerted by the thumb on the developing teeth can cause them to shift or tilt, leading to malocclusion or bite problems. Over time, this can result in an improper alignment of the upper and lower jaws, affecting not only the appearance but also the functionality of the teeth. Furthermore, prolonged thumb sucking can also influence the positioning of the tongue and affect the development of the palate, potentially leading to issues like open bite or crossbite.
Research has also shown that the intensity and duration of thumb sucking can have a direct impact on dental growth. Children who engage in aggressive or prolonged sucking are more likely to experience changes in the shape and structure of their developing jawbones. These alterations can disrupt the natural growth process and may require orthodontic intervention later on.
Parents need to be aware of the potential consequences of thumb sucking on their child’s dental development. Early intervention through gentle guidance and encouragement can help children break the habit before it causes significant damage. Pediatric dentists are well-equipped to provide appropriate guidance and strategies to parents, ensuring that their child’s dental health remains on track during this critical phase of development.
Breaking the Thumb Sucking Habit: Effective Strategies for Parents
Thumb sucking is a common habit among children, and while it may seem harmless, it can have long-term effects on their dental health. As parents, it is essential to help our children break the thumb sucking habit to prevent any potential dental issues in the future.
One effective strategy is to create awareness and educate your child about the negative consequences of thumb sucking. Explain to them that prolonged thumb sucking can lead to misalignment of their teeth and jaw, which may require extensive orthodontic treatment later on. Use age-appropriate language and visuals to help them understand the impact on their oral health. Additionally, encourage open conversations and actively listen to your child’s concerns and fears. This will create a supportive environment and foster their willingness to break the habit.
Another effective strategy is to distract your child whenever they engage in thumb sucking. Offer alternative activities or objects that can help keep their hands occupied and away from their mouth. For instance, provide them with a stress ball, fidget spinner, or small toy to hold and play with. This will redirect their attention away from thumb sucking. Additionally, praise and reward your child’s efforts and progress. Positive reinforcement, such as small treats or verbal affirmations, can motivate them and make quitting thumb sucking a more enjoyable experience. Remember, consistency is key in breaking the habit, so continue to provide guidance and support throughout the process.
By implementing these effective strategies, parents can play a crucial role in helping their children break the thumb sucking habit and maintain good dental health. Remember, each child is unique, and it may take time for them to overcome this habit. Patience, persistence, and understanding will go a long way in ensuring their success.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive Reinforcement | Encourage and praise your child when they refrain from thumb sucking. Offer rewards or incentives for successfully avoiding the habit. |
| Distraction Techniques | Provide alternative activities or toys to keep your child’s hands and mouth busy, reducing the likelihood of thumb sucking. |
| Gentle Reminder | Gently remind your child to stop thumb sucking whenever you notice the behavior, but avoid scolding or shaming them as it may exacerbate the habit. |
| Use of Thumb Guards | Consider using thumb guards or gloves designed to make thumb sucking less satisfying or accessible for your child. |
| Identifying Triggers | Determine triggers or situations that prompt thumb sucking, such as stress or boredom, and address them proactively through communication and alternative coping mechanisms. |
| Positive Peer Influence | Encourage positive peer influence by involving your child in activities where they interact with non-thumb sucking peers, which may motivate them to emulate their behavior. |
| Dental Consultation | Consult a pediatric dentist to assess any dental implications of thumb sucking and obtain professional advice on how to manage and mitigate its effects on dental health. |
| Patience and Persistence | Understand that breaking the thumb sucking habit takes time and patience. Be consistent in your approach and provide ongoing support and encouragement to your child. |
| Modeling Behavior | Set a positive example by demonstrating healthy oral habits and avoiding behaviors like nail biting or thumb sucking yourself. |
| Hypnotherapy or Behavioral Therapy | In severe cases, consider seeking professional help from therapists or hypnotherapists who specialize in behavioral modification techniques to address thumb sucking. |
Early intervention plays a crucial role in preventing dental problems in children. As a dentist, I have observed that addressing oral health issues at an early stage can have significant long-term benefits for the overall health and well-being of a child. By identifying and treating dental problems in their infancy, we can minimize the potential complications that may arise later in life.
Research has shown that early dental intervention can help in the proper development and alignment of teeth, reduce the risk of tooth decay, and prevent the need for more extensive and expensive treatments in the future. Regular dental check-ups starting from a young age allow for early detection of any potential issues, such as malocclusions or cavities, which can then be addressed promptly.
Furthermore, early intervention provides an opportunity for dentists to educate parents and caregivers about proper oral hygiene practices and the importance of a nutritious diet. By instilling good dental habits early on, such as regular brushing, flossing, and limiting sugary foods and drinks, parents can set their children on the path to a lifetime of healthy teeth and gums.
Overall, recognizing and acting upon the importance of early intervention in preventing dental problems is key to ensuring optimal oral health for children. By seeking professional dental care at a young age, parents can give their children the best chance of avoiding future dental issues and enjoying a radiant smile for years to come.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among children, but it can have a negative impact on their dental health. Fortunately, there are dental appliances and techniques available to help children stop thumb sucking and break this habit. These tools and strategies aim to discourage thumb sucking and promote healthier oral habits.
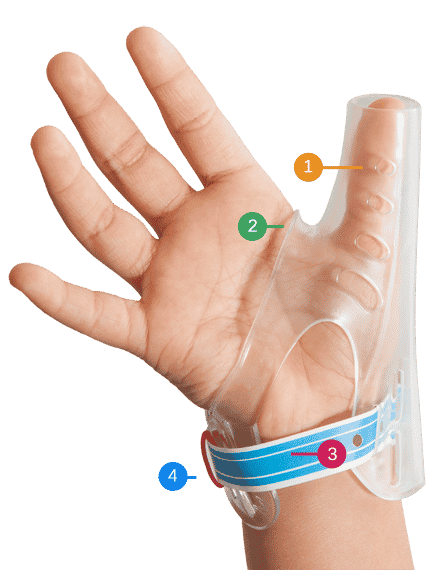
One commonly used dental appliance is a thumb guard. This device is designed to prevent the thumb from entering the mouth, making it physically impossible for children to suck their thumbs. Thumb guards are typically made of soft, flexible materials that are comfortable to wear. They allow the child to freely move their fingers, while still inhibiting thumb sucking. By consistently wearing a thumb guard, children are more likely to become aware of their thumb-sucking habit and gradually reduce their dependence on it. However, it is essential to consult with a dentist or orthodontist to determine if a thumb guard is suitable for your child’s specific needs.
Another technique to help children stop thumb sucking is positive reinforcement. This approach involves praising and rewarding children when they refrain from thumb sucking. Parents can use a reward system, such as a sticker chart or small incentives, to motivate their child. It is crucial to emphasize the importance of good oral habits and explain the potential consequences of thumb sucking on dental health. By creating a supportive and encouraging environment, children are more likely to feel motivated to break the thumb-sucking habit.
It is important to note that dental appliances and techniques may not work instantly for every child. Breaking the thumb-sucking habit requires patience, consistency, and understanding. Therefore, it is advised to consult with a dentist or orthodontist who specializes in pediatric dentistry to develop a personalized approach based on your child’s unique needs.
Behavioral approaches can be an effective way to encourage your child to quit thumb sucking. By implementing positive reinforcement and providing alternative coping mechanisms, you can help your child break the habit and promote healthy dental development.
One approach is to establish a rewards system. Create a chart to track your child’s progress and offer small incentives for each day or week they successfully refrain from thumb sucking. For example, you could reward them with stickers, tokens, or small treats. This method encourages positive behavior and can motivate your child to keep trying.
Another strategy is to help your child find alternative ways to comfort themselves. Thumb sucking is often a soothing mechanism, so providing alternative soothing tools or techniques can help them transition away from this habit. Encourage them to use a stress ball, squeeze toy, or soft blanket instead, as these can provide similar comfort without putting pressure on their teeth.
It’s important to approach these techniques with patience and understanding. Breaking the thumb sucking habit may take time and effort, but with consistency and support, your child can overcome this habit and maintain good oral health.
Positive reinforcement plays a crucial role in breaking the thumb sucking habit in children. By focusing on reinforcing and rewarding desirable behaviors, parents can effectively encourage their child to quit the habit.
One effective strategy is to praise and reward the child when they refrain from thumb sucking for a designated period of time. This can be done through a sticker chart or a reward system, where the child earns a small prize after reaching certain milestones. By positively reinforcing their efforts, children are motivated to continue their progress and gradually overcome their thumb sucking habit.
It is important for parents to be consistent and patient throughout this process. Positive reinforcement should be used consistently and applied whenever the child exhibits self-control and avoids thumb sucking. With time, the child will develop a sense of accomplishment and the motivation to break the habit entirely.
Remember, positive reinforcement should be used alongside open communication and understanding. Parents should offer support and reassurance, reminding their child of their progress and emphasizing the benefits of quitting thumb sucking. By creating a positive and encouraging environment, parents can effectively help their child kick the habit and promote good oral health.
Creating a thumb-sucking-free environment at both home and school is crucial for helping children break the habit and promoting optimal oral health.
At home, parents play a significant role in creating an environment that discourages thumb sucking. It is essential to provide positive reinforcement and encouragement to help children understand the importance of breaking the habit. Setting clear rules and limits, such as designating certain times and places where thumb sucking is not allowed, can be effective. Additionally, parents can engage their child in activities that keep their hands occupied, such as puzzles or arts and crafts, to redirect their attention away from thumb sucking.
Similarly, schools have an important role to play in creating a thumb-sucking-free environment. Educating teachers and staff about the dental effects of thumb sucking and its impact on overall well-being can help them identify and address the issue promptly. Encouraging open communication with parents regarding their child’s thumb-sucking habits can enable schools to provide the necessary support and reinforcement. Furthermore, teachers can help children develop alternative ways to soothe themselves, such as using stress balls or other sensory toys, rather than resorting to thumb sucking. By collaborating with parents and taking a proactive approach, schools can contribute to breaking the thumb-sucking habit and promoting dental health among their students.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among young children that can have emotional and psychological implications. While it may initially provide a sense of comfort and security, prolonged thumb sucking can lead to emotional dependencies and self-esteem issues as children grow older. Children may be teased or ostracized by their peers, causing feelings of shame or embarrassment.
Additionally, thumb sucking can serve as a coping mechanism for children who are experiencing stress or anxiety. It provides a sense of comfort and a way to self-soothe during challenging or overwhelming situations. In some cases, thumb sucking may even become a habit that persists into adulthood, further impacting emotional well-being.
Understanding the emotional and psychological factors behind thumb sucking is crucial for parents and caregivers. By recognizing the potential impact of this habit, they can provide the necessary support and guidance to help children overcome their emotional dependencies and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Through open communication, encouragement, and alternative strategies for stress relief, parents can play a vital role in helping their child manage their emotions in a healthier manner.
Thumb sucking is a common habit among young children and is often a source of concern for parents and caregivers. To address the underlying causes of thumb sucking for long-term success, it is essential to understand the factors that contribute to this behavior.
One of the primary reasons for thumb sucking is the need for comfort and security. Babies and young children often use their thumbs as a means of self-soothing, especially in stressful or unfamiliar situations. Additionally, thumb sucking may also be a sign of boredom or fatigue. By identifying the emotional triggers that lead to thumb sucking, parents can address these underlying causes and provide alternative methods of comfort and security.
It is also important to consider the physical and environmental factors that can contribute to thumb sucking. For instance, prolonged breastfeeding or the use of pacifiers can reinforce the habit of thumb sucking. Similarly, being in a thumb-sucking-friendly environment, where the child sees others engaging in the behavior, can further perpetuate the habit. By recognizing and addressing these factors, parents can create a supportive environment that encourages the child to develop alternative coping mechanisms.
Dentists and orthodontists play a crucial role in managing thumb sucking habits in children. They possess the expertise and knowledge to assess the impact of thumb sucking on dental health and provide appropriate interventions. When a child exhibits persistent thumb sucking, it is recommended to consult a dental professional for a comprehensive evaluation.
These specialists can identify any dental issues that may have arisen from thumb sucking, such as malocclusion, tooth misalignment, and jaw problems. By conducting a thorough examination and utilizing diagnostic tools, dentists and orthodontists can determine the extent of the damage and develop an individualized treatment plan. They may utilize dental appliances, such as habit-breaking devices or orthodontic appliances, to help stop the thumb sucking habit. Additionally, they can provide guidance and support to parents on effective strategies to encourage their child to quit thumb sucking.
Working collaboratively with dentists and orthodontists, parents can ensure that their child’s dental health is not compromised by thumb sucking habits. By seeking professional guidance, they can take proactive steps in preventing long-term dental issues and promoting a healthy oral environment for their child’s overall well-being.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are crucial in mitigating the effects of thumb sucking on dental health. Thumb sucking can cause misalignment and malocclusion of teeth, leading to a host of dental problems. By prioritizing oral hygiene practices and scheduling routine dental examinations, parents can actively combat the negative consequences of thumb sucking.
Proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoridated toothpaste and flossing daily, can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease, which can be exacerbated by thumb sucking. It is crucial to educate children and parents about the importance of consistent oral care routines. Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in monitoring the impact of thumb sucking on the development of teeth and jaws. Dentists can identify early signs of dental problems, such as tooth misalignment or bite issues, and provide appropriate interventions to prevent further complications. Additionally, dental professionals can offer guidance on oral habits and provide strategies to help children break their thumb sucking habit effectively.
By emphasizing the significance of maintaining good oral hygiene and advocating for regular dental check-ups, parents can actively counteract the detrimental effects of thumb sucking on dental health. Taking proactive measures in oral care and seeking professional guidance are key to ensuring the long-term oral health and well-being of children.
Thumb sucking can lead to misalignment of teeth, an open bite, and speech problems.
One misconception is that thumb sucking is harmless and will naturally stop on its own. However, it can have long-term effects on dental health if not addressed.
Parents should look for signs such as protruding front teeth, an open bite, speech difficulties, or changes in the roof of the mouth.
Thumb sucking can push the teeth forward or cause them to tilt, resulting in an improper bite and misaligned teeth.
Thumb sucking can disrupt normal dental development and growth, leading to orthodontic issues and potential speech problems.
Strategies may include positive reinforcement, offering alternative comfort objects, or seeking professional help if needed.
Early intervention can help minimize the long-term effects of thumb sucking on dental health and promote proper oral development.
Yes, there are dental appliances such as thumb guards or habit-breaking appliances that can be used to discourage thumb sucking.
Parents can try techniques such as distraction, positive reinforcement, or setting realistic goals to help their child quit thumb sucking.
Positive reinforcement, such as praising and rewarding a child for not thumb sucking, can motivate them to quit the habit.
Parents can remove triggers, establish routines, and communicate with teachers to create a supportive environment for quitting thumb sucking.
Yes, thumb sucking can be a way for children to cope with stress, anxiety, or boredom, so addressing these underlying factors is important.
It is crucial for parents to identify and address any emotional or psychological factors that may be contributing to the thumb sucking habit.
Dentists and orthodontists can provide guidance, treatment options, and monitor the progress of a child’s efforts to quit thumb sucking.
Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene practices can help detect and prevent any dental issues caused by thumb sucking, promoting overall oral health.