Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

What’s Causing Your Toothache? Common Causes and Treatment Options. Find out the common causes of toothache and effective treatment options.
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental issue that can cause discomfort and pain for individuals. It occurs when the protective layer of enamel on the teeth wears away, exposing the sensitive dentin underneath. There are several causes of tooth sensitivity, including tooth decay, gum disease, teeth grinding, and even certain dental procedures.
One of the main reasons for tooth sensitivity is dental erosion, which is the gradual breakdown of tooth enamel due to acid exposure. This can be caused by consuming highly acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, and sports drinks. In addition, brushing your teeth too vigorously or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can also contribute to enamel erosion.

Another common cause of tooth sensitivity is receding gums. As the gums recede, the tooth roots are exposed, which are more sensitive than the enamel. This can be a result of gum disease, aging, or brushing too aggressively.
Treatment options for tooth sensitivity vary depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, using desensitizing toothpaste or mouthwash can provide relief by reducing sensitivity. Dentists may also recommend applying fluoride gel or varnish to strengthen the enamel and decrease sensitivity. In more severe cases, dental procedures such as dental bonding or a gum graft may be necessary to address the root cause of the sensitivity.
It is important to consult with a dentist if you experience tooth sensitivity, as they can determine the underlying cause and provide the most appropriate treatment. Taking steps to prevent tooth sensitivity, such as practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding acidic foods and drinks, and using a soft-bristled toothbrush, can also help maintain a healthy and pain-free smile.
Dental decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a common dental problem that can cause significant toothaches. It occurs when the tooth enamel, the protective outer layer of the tooth, is damaged by acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. This damage leads to the formation of small, visible holes on the surface of the tooth, which can eventually progress to deeper layers if left untreated.
Causes of dental decay can vary, but the main culprits are poor oral hygiene and a diet high in sugars and carbohydrates. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on the teeth, it produces acids that attack the enamel. Over time, this acid attack weakens the enamel and leads to decay. Additionally, consuming sugary and starchy foods provides fuel for the bacteria, allowing them to produce more acids and further contribute to tooth decay.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and produce acids that attack tooth enamel. |
| Plaque | Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria and food particles that forms on teeth. |
| Tartar | Plaque hardens into tartar when not removed through proper oral hygiene practices. |
| Acidic Foods | Consuming acidic foods and beverages can erode tooth enamel, leading to decay. |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, increasing decay risk. |
| Dry Mouth | Reduced saliva flow due to medication or medical conditions can promote tooth decay. |
| Genetics | Genetic factors can influence the strength of tooth enamel and susceptibility to decay. |
| Dental Anatomy | Misaligned teeth or deep crevices can trap food particles and bacteria, promoting decay. |
Addressing dental decay involves a multi-faceted approach. Prevention is key, and maintaining a proper oral hygiene routine is crucial. This includes brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also important to identify and address any early signs of decay.
In cases where dental decay has progressed, treatment options may include dental fillings, which involve removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the cavity with a tooth-colored material. In more advanced cases, dental crowns or root canal treatment may be necessary to save the tooth. Seeking prompt dental care is vital to prevent further damage and alleviate toothaches associated with dental decay.
Dental decay can have a significant impact on oral health, causing toothaches and potential complications if left untreated. It is important to understand the causes and treatment options available to address this major culprit behind toothaches and maintain optimal dental health. By prioritizing preventive measures and seeking timely dental care, individuals can take control of their oral health and prevent the discomfort and potential complications associated with dental decay.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental condition that can have serious implications for oral health. It is important to understand the link between gum health and toothaches in order to prevent and treat this condition effectively.
Gum disease begins with the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, this plaque can spread below the gumline and cause inflammation and infection in the gums. As the disease progresses, it can lead to the breakdown of the tissues and supporting structures that hold the teeth in place.
One of the major consequences of gum disease is toothaches. As the infection spreads and the gums recede, the sensitive roots of the teeth become exposed. This can result in pain and discomfort, especially when eating or drinking hot or cold substances. Additionally, gum disease can lead to the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, which can trap food particles and bacteria, further aggravating the condition.

Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are crucial for preventing gum disease and addressing toothaches caused by this condition. Proper brushing and flossing techniques, along with the use of antibacterial mouthwashes, can help control plaque buildup and reduce the risk of gum disease. In more severe cases, professional treatments such as deep cleaning, root planing, and surgical interventions may be necessary to restore gum health and alleviate toothaches.
In conclusion, gum disease is closely tied to toothaches, as the infection and inflammation in the gums can lead to tooth sensitivity and pain. By understanding the link between gum health and toothaches, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent and treat gum disease, preserving their oral health and overall well-being.
Cracked or fractured teeth can be both painful and potentially damaging to your overall dental health. Identifying the causes behind these issues is crucial in finding effective solutions for treatment. Understanding the common triggers for cracked or fractured teeth can help you prevent such issues from arising.
One common cause of cracked or fractured teeth is dental trauma or injury, such as a hard blow to the mouth during sports or accidents. Accidents can cause the tooth to chip, crack, or even break. Another cause is teeth grinding or clenching (known as bruxism), which can put excessive pressure on the teeth and lead to fractures over time. It’s worth noting that certain habits, like biting on hard objects or opening packages with your teeth, can also contribute to the risk of cracks or fractures.
When it comes to finding effective solutions for cracked or fractured teeth, the primary goal is to preserve the tooth’s structure and prevent further damage. Depending on the severity, treatment options may vary from bonding or dental veneers for minor cracks to dental crowns or root canals for more severe cases. In some instances, extraction may be necessary if the tooth cannot be saved. It’s essential to consult with a qualified dentist who can assess the situation and recommend the best course of action based on your specific circumstances. Regular dental check-ups can help identify and address any signs of cracked or fractured teeth early on, preventing more significant issues down the line.
Dental abscesses are a hidden danger that can cause severe toothaches and lead to more serious oral health issues if left untreated. An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms around the tooth, usually as a result of an infection. It can occur either in the tooth’s root or in the gum tissue surrounding it.
The primary cause of a dental abscess is dental decay. When a cavity is left untreated, bacteria can penetrate the tooth’s enamel and dentin, reaching the pulp where the nerves and blood vessels are located. This leads to an infection that can eventually progress into an abscess. In addition to dental decay, other factors such as a cracked tooth, trauma to the tooth, or gum disease can also contribute to the development of an abscess. It is crucial to address a dental abscess promptly as it can lead to more serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body if left untreated.
Malocclusion, or misalignment of the teeth, is a common dental issue that can lead to tooth pain. When the teeth are not properly aligned, they can put excessive pressure on certain teeth or areas of the mouth, causing discomfort and pain. This misalignment can occur due to various reasons, such as genetics, oral habits like thumb sucking or tongue thrusting, or even trauma to the mouth.
One of the primary causes of tooth pain due to malocclusion is the unequal distribution of biting forces. When the teeth are not properly aligned, some teeth may bear more pressure than others during chewing and biting. This can lead to excessive wear and tear on certain teeth, causing sensitivity and discomfort. Additionally, misaligned teeth can also interfere with proper oral hygiene practices, making it difficult to thoroughly clean certain areas of the mouth. This can result in tooth decay and gum disease, leading to further pain and discomfort.
Furthermore, malocclusion can also affect the alignment of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jawbone to the skull. When the teeth are not aligned correctly, the jaw may not close in its proper position, putting strain on the TMJ. This can result in jaw pain, headaches, and even difficulty in opening or closing the mouth.
In conclusion, malocclusion is not just an aesthetic concern but can also lead to tooth pain and other oral health issues. If you suspect that your teeth are misaligned and are experiencing tooth pain, it is essential to seek the advice of a dental professional. They can evaluate your bite and recommend appropriate treatment options to alleviate pain, improve oral health, and enhance your overall dental well-being.
Bruxism, also known as teeth grinding, is a common condition that affects both adults and children. It is characterized by the involuntary grinding, clenching, or gnashing of teeth, often during sleep or periods of stress. While occasional teeth grinding may not cause any significant harm, chronic bruxism can have detrimental effects on dental health, specifically on tooth sensitivity.
One of the most noticeable effects of bruxism is increased tooth sensitivity. The constant grinding of teeth can wear down the protective layer of enamel, exposing the underlying dentin. Dentin contains microscopic tubules that connect to the nerve endings in the pulp of the tooth, making them more susceptible to external stimuli such as hot, cold, or acidic foods and drinks. This can result in sharp, shooting pain or discomfort when consuming certain foods or exposing the teeth to extreme temperatures.
Additionally, the excessive forces exerted during teeth grinding can cause microfractures in the enamel, further compromising the tooth’s protective barrier. These microfractures not only increase sensitivity but also create an entry point for bacteria, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Therefore, addressing bruxism is crucial to prevent further damage to the teeth and maintain optimal dental health.
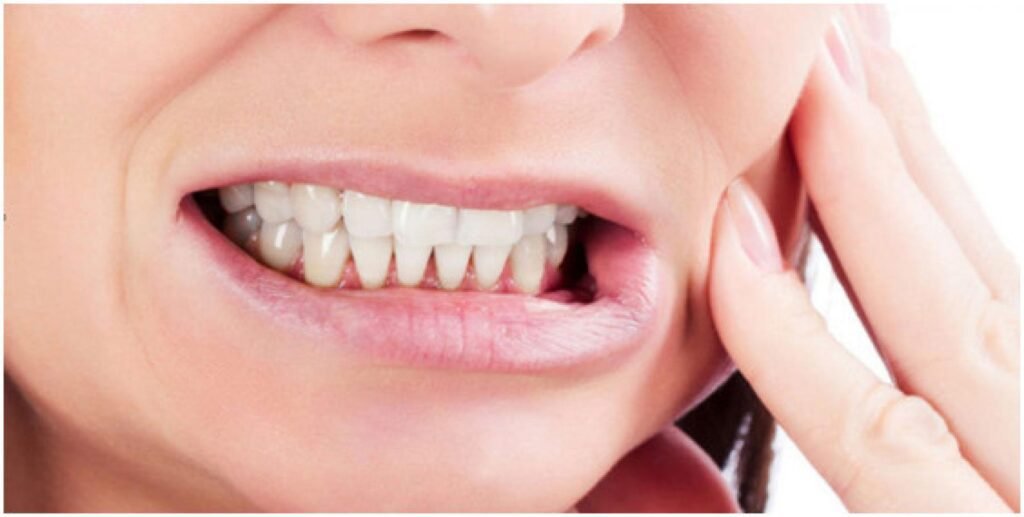
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ), although lesser-known, can actually be a significant cause of toothaches. This disorder affects the joints that connect the jawbone to the skull, leading to various painful symptoms, including tooth pain. TMJ can result from a variety of factors, including jaw misalignment, teeth grinding, stress, and arthritis.
One of the primary ways TMJ can cause toothaches is through referred pain. When the jaw joint is inflamed or misaligned, the pain can radiate to other parts of the head, including the teeth. This can make it challenging to pinpoint the exact source of the pain and may lead individuals to seek dental treatment for what they believe is a tooth-related issue.
Additionally, TMJ can lead to teeth grinding or clenching, medically known as bruxism. This excessive force on the teeth can cause tooth sensitivity, enamel wear, and ultimately toothaches. It is crucial for individuals experiencing toothaches to consider the possibility of TMJ and seek the appropriate assessment and treatment from a dental professional who specializes in these disorders.
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, can be a surprising source of tooth pain. Many people may not initially associate their toothache with a sinus infection, as the pain is often felt in the upper teeth, mimicking a dental issue. However, the connection between sinus issues and tooth pain is not to be overlooked.
When a person has a sinus infection, the sinuses become congested and inflamed. This inflammation can put pressure on the surrounding areas, including the roots of the upper teeth. As a result, the affected teeth may become sensitive or even painful. This is known as referred pain, where the source of the pain is felt in a different location.
Furthermore, sinus infections can also lead to a condition called sinusitis toothache. In this case, the infection spreads from the sinuses to the roots of the upper teeth, causing widespread tooth pain. It is essential to recognize this connection between sinus issues and tooth pain to ensure the proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
As we can see, sinus infections can have a surprising connection to tooth pain. Understanding this link is crucial in accurately identifying and addressing the underlying cause of toothache. In the next sections, we will further explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for sinus infections and how they relate to tooth pain. Stay tuned for more valuable insights into this unexpected connection and its impact on oral health.
Trauma and injury can have significant consequences on dental health, potentially leading to toothaches and various other problems. Accidents, sports injuries, falls, or even biting down on a hard object can cause damage to the teeth, gums, or jaw. Depending on the severity, trauma and injury can result in tooth fractures, dislodged teeth, gum lacerations, or even jaw fractures. These conditions not only cause acute pain and discomfort but also have long-term implications for oral health.
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to address dental consequences resulting from trauma and injury. In cases of tooth fractures, dental bonding, dental crowns, or veneers may be recommended to restore the damaged tooth’s structure and protect it from further damage. For dislodged teeth, immediate repositioning and stabilization are necessary to increase the chances of successful reinsertion. In more severe cases, oral surgery may be required to repair the fractured jaw or reposition the dislocated jaw joint. It is crucial to seek dental assistance promptly after any traumatic dental injury to minimize the risk of complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
| Type of Trauma/Injury | Dental Consequences | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Avulsion (Tooth Knocked Out) | Loss of tooth, potential damage to surrounding tissues | Immediate re-implantation, tooth preservation techniques, dental implants, bridges, or dentures |
| Fractured Tooth | Pain, sensitivity, risk of infection | Dental bonding, crown placement, root canal therapy, extraction if severe |
| Luxation (Tooth Displacement) | Displacement of tooth from its socket, damage to surrounding tissues | Repositioning of the tooth, splinting, root canal therapy, monitoring for any complications |
| Dental Trauma from Accidents | Fractures, dislodgment, avulsion, soft tissue injuries | Immediate dental evaluation, treatment based on the specific injury, follow-up care |
| Trauma from Sports Injuries | Fractures, avulsion, soft tissue injuries | Wearing protective gear (mouthguards), regular dental check-ups, prompt treatment for any injuries |
Impacted Wisdom Teeth: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for Toothache Relief
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, typically erupt between the ages of 17 and 25. However, for many individuals, these teeth do not have enough space to fully emerge or align properly with the rest of the teeth. When this occurs, wisdom teeth become impacted, resulting in various dental issues.
The primary cause of impacted wisdom teeth is insufficient space in the mouth. This lack of space can be attributed to the size of the jaw or the presence of other teeth obstructing their eruption. As a result, the impacted wisdom teeth can push against adjacent teeth, leading to pain, swelling, and inflammation in the affected area. Additionally, impacted wisdom teeth can also contribute to the development of dental caries, gum disease, and even cysts or tumors.
Common symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth include pain or tenderness around the back of the mouth, swelling, redness or bleeding of the gums, jaw stiffness, and persistent bad breath. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a dental professional who can properly diagnose and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
The treatment for impacted wisdom teeth usually involves extraction. Early removal of impacted wisdom teeth is often recommended to prevent potential complications and to alleviate discomfort. The extraction procedure may vary depending on the position and condition of the impacted teeth. In some cases, a simple extraction can be performed, while more complex cases may require surgical intervention.
In conclusion, impacted wisdom teeth can cause a range of issues, including toothaches. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt dental advice is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment for toothache relief. If you are experiencing any discomfort or suspect that your wisdom teeth may be impacted, consult a dental professional for a thorough examination and personalized treatment plan.
Dental procedures can be essential for maintaining oral health and addressing various dental issues. However, it is important to note that certain treatments can result in toothaches, albeit temporarily, as part of the healing process. While this discomfort may cause concern for patients, it is crucial to understand the reasons behind these toothaches and how they can be managed effectively.
One common dental procedure that may cause temporary toothaches is a dental filling. Fillings are used to repair cavities caused by dental decay. During the filling process, the decayed portion of the tooth is removed, and the cavity is filled with a material, such as composite resin or amalgam. While this procedure is relatively straightforward, it can result in tooth sensitivity or mild discomfort after the anesthesia wears off. This sensitivity occurs because the tooth and surrounding tissues may need time to adapt to the new filling. The discomfort usually subsides within a few days, but it is important to inform your dentist if the pain persists or worsens. They can provide appropriate guidance and ensure there are no underlying issues.
Another dental procedure that may result in temporary toothaches is a root canal treatment. This procedure is necessary for treating infected or inflamed dental pulp, which is the soft tissue inside the tooth. During a root canal, the infected pulp is removed, and the canals of the tooth are carefully cleaned and shaped before being filled with a biocompatible material. While a root canal is often pain-relieving, patients may experience some post-treatment discomfort. This can be attributed to the healing process and inflammation in the surrounding tissues. Most patients find that any discomfort can be managed effectively with over-the-counter pain medications, as recommended by their dentist.
Understanding that toothaches following certain dental procedures are typically temporary can help alleviate concerns for patients. It is crucial to communicate openly with your dentist about any discomfort experienced after a dental procedure, as they can provide appropriate guidance and ensure a smooth recovery. By being proactive in managing these temporary toothaches, patients can focus on the long-term benefits that these dental procedures provide in maintaining oral health and addressing dental issues effectively.
Tooth sensitivity can be a bothersome condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are various causes for this issue, one factor that often goes unnoticed is dental erosion caused by acidic foods and drinks. Acidic substances can erode the protective layer of enamel on our teeth, leaving the underlying dentin layer exposed and vulnerable to sensitivity.
The effects of acidic foods and drinks on tooth sensitivity can be significant. Foods and beverages such as citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and certain types of vinegar can have a low pH level, which means they are highly acidic. When consumed frequently or in large amounts, these substances can gradually wear away the tooth enamel, leading to increased tooth sensitivity. Additionally, acidic foods and drinks can also irritate the nerves within the teeth, causing discomfort and pain.
Preventing dental erosion caused by acidic foods and drinks is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Limiting the consumption of highly acidic substances, practicing proper oral hygiene, and using fluoride toothpaste or mouth rinses can help protect the enamel and reduce tooth sensitivity. Regular dental check-ups are also essential, as dentists can provide professional advice and recommend suitable treatments to address any erosion already present. By being mindful of our dietary choices and taking proactive measures to protect our teeth, we can overcome the effects of dental erosion and enjoy a pain-free and healthy smile.
A dental abscess is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment. It occurs when a pocket of pus forms in the tooth or gum, usually as a result of a bacterial infection. This can cause severe pain, swelling, and in some cases, even fever. Ignoring a dental abscess can lead to complications, such as the infection spreading to other parts of the body. That is why it is crucial to understand the seriousness of a dental abscess and take the necessary steps for treatment.
When it comes to treating a dental abscess, the first step is to drain the pus and clean the affected area. This is usually done through a procedure called an incision and drainage, where a small incision is made to release the trapped pus. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to help clear the infection. In some cases, a root canal or tooth extraction may be necessary to remove the source of the infection. It is important to see a dentist as soon as possible if you suspect you have a dental abscess, as timely treatment can prevent further complications and alleviate the pain associated with this condition.
When it comes to toothaches, one of the most serious and potentially dangerous causes is a dental abscess. A dental abscess is a painful infection that occurs within the tooth, in the gum, or in the bone surrounding the tooth. It is often caused by untreated bacterial infection that travels deep into the tooth’s pulp.
What makes a dental abscess so concerning is that if left untreated, it can lead to severe complications. The infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the jaw, neck, or even the brain, putting the individual’s overall health at risk. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a dental abscess, such as severe, throbbing tooth pain, sensitivity to hot or cold, and swollen gums, is crucial in seeking prompt treatment. Depending on the severity of the abscess, the dentist may perform a root canal, prescribe antibiotics, or in more severe cases, extract the tooth. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent further complications and ensure a healthy, pain-free mouth.
Common symptoms of tooth sensitivity include pain or discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods or beverages, sensitivity to sweet or sour foods, and pain when brushing or flossing.
Yes, dental decay is a major culprit behind toothaches. When the enamel on your teeth is damaged by decay, it exposes the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, leading to pain and sensitivity.
Yes, gum disease can contribute to toothaches. Gum disease causes inflammation and infection in the gums, which can lead to tooth pain and sensitivity.
Cracked or fractured teeth can be caused by trauma, such as a blow to the face, biting down on a hard object, or even tooth grinding. These cracks can lead to toothaches.
A dental abscess is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if left untreated. It is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection, and it can lead to severe toothache, swelling, and even spread to other parts of the body.
Yes, misaligned teeth, also known as malocclusion, can cause tooth pain. When teeth do not align properly, it can put excessive pressure on certain teeth, leading to pain and discomfort.
Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, can wear down the enamel of your teeth and cause tooth sensitivity. The constant grinding motion can also lead to tooth pain and jaw discomfort.
Yes, TMJ can contribute to toothaches. TMJ disorder affects the temporomandibular joint, which connects the jaw to the skull. When this joint is not functioning properly, it can cause tooth pain.
Yes, sinus infections can cause tooth pain. The roots of the upper teeth are close to the sinuses, so when the sinuses become inflamed or infected, it can lead to toothache in the upper teeth.
Trauma or injury, such as a direct blow to the mouth, can cause toothaches. The impact can damage the teeth, leading to pain and sensitivity.
Impacted wisdom teeth are molars that do not have enough space to fully emerge or develop normally. This can cause pain, swelling, and infection, leading to toothaches.
Yes, certain dental procedures can result in temporary toothaches. For example, after a filling or crown placement, it is common to experience sensitivity or mild discomfort in the tooth.
Dental erosion occurs when the enamel on the teeth is worn away by acidic foods and drinks. This can lead to tooth sensitivity as the sensitive inner layers of the tooth become exposed.
Treatment for a dental abscess typically involves draining the pus and eliminating the infection. This may require a root canal, extraction of the affected tooth, or the use of antibiotics.
Note: The FAQs provided in this response are based on the given article headings and are not a direct representation of the actual content.