Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
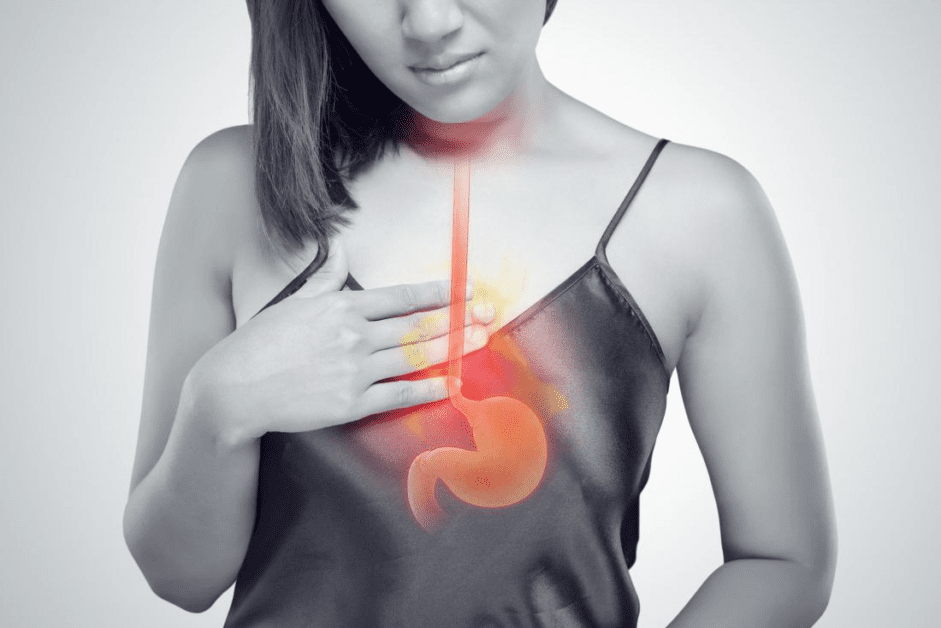
Understand the impact of acid reflux on oral health and effective prevention strategies.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can have significant effects on dental health. The repeated exposure of tooth enamel to stomach acid can result in tooth erosion, making the teeth more prone to cavities and sensitivity. Additionally, acid reflux can contribute to the development of gum disease, further compromising oral health.
One of the most common effects of acid reflux on dental health is tooth erosion. The stomach acid that flows back into the mouth can wear away the protective enamel coating on the teeth. Over time, this can lead to tooth sensitivity, as well as an increased risk of cavities. The erosion may also cause changes in the shape, size, and appearance of the teeth.

Another concerning effect of acid reflux on dental health is the link to gum disease. The acid can irritate and inflame the gums, making them more susceptible to infection. This can result in gum disease, characterized by symptoms such as gum inflammation, bleeding, and bad breath. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and even affect overall health.
It is crucial for individuals with acid reflux to be aware of these dental health consequences and take steps to protect their teeth and gums. By implementing proper oral hygiene practices, seeking professional dental care, and managing acid reflux symptoms, it is possible to minimize the effects on oral health.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a chronic condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This happens when the lower esophageal sphincter, a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus, fails to close properly. Understanding the causes of acid reflux is crucial in managing and preventing its detrimental effects on oral health.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of acid reflux. Obesity, smoking, pregnancy, and certain medications can increase the risk of experiencing acid reflux. Additionally, certain foods and beverages, such as fatty and fried foods, caffeine, alcohol, and citrus fruits, have been identified as common triggers for acid reflux. Understanding these causes can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices and take proactive measures to minimize the risk of acid reflux episodes.
Stomach acid, or gastric acid, plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. This powerful acid is produced by the cells lining the stomach and is responsible for breaking down food and killing harmful bacteria that may enter the oral cavity. The acidity level of stomach acid, which typically ranges from 1.5 to 3.5 on the pH scale, helps in the digestion process and aids in the absorption of essential nutrients.
In addition to its role in digestion, stomach acid serves as a natural defense mechanism against oral infections. It works as a barrier, preventing the growth of bacteria and fungi that can lead to dental diseases. However, an imbalance in the production or regulation of stomach acid can have detrimental effects on oral health. Excessive stomach acid can lead to conditions such as acid reflux, which can significantly impact the teeth and surrounding oral tissues. Understanding the role of stomach acid in oral health is crucial in identifying and managing these potential issues.

Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can cause various symptoms that affect the mouth. One common symptom is persistent bad breath, which is often caused by the regurgitation of stomach acid into the mouth. The acidic nature of the stomach acid can lead to an unpleasant odor and taste, affecting a person’s confidence and causing social discomfort.
Additionally, acid reflux can cause dental erosion, which is the gradual wearing away of tooth enamel. The frequent exposure to stomach acid weakens the protective layer of enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to cavities, sensitivity, and discoloration. It is important to note that dental erosion caused by acid reflux cannot be reversed, and the damaged enamel cannot grow back. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and manage acid reflux to prevent further damage to the teeth and maintain good oral health.
Tooth erosion is a common dental issue that can occur as a result of acid reflux. Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation and other discomforts. When this acidic reflux reaches the mouth, it can have damaging effects on the teeth.
The enamel, which is the protective outer layer of the teeth, is weakened by the acidic content. Over time, repeated exposure to stomach acid can cause the enamel to erode. This erosion leads to sensitive teeth, tooth discoloration, and an increased risk of tooth decay. Additionally, the loss of enamel can expose the underlying dentin, making the teeth more prone to cracks and chips. It is important to address acid reflux and its effects on dental health to prevent further damage and preserve the integrity of the teeth.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing various symptoms and complications. One of the lesser-known but significant effects of acid reflux is its impact on gum health. Research has shown a clear link between acid reflux and gum disease, highlighting the importance of managing this condition for maintaining optimal oral health.
The connection between acid reflux and gum disease stems from the acidic nature of stomach acid. When acid reflux occurs, the acidic stomach contents can reflux into the oral cavity, exposing the gums to excess acidity. This acid exposure can lead to gum inflammation, irritation, and ultimately gum disease if left untreated. The acidic environment created by acid reflux can also disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the mouth, further contributing to the development of gum disease.

Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It starts with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth and along the gumline. If not properly removed through good oral hygiene practices, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to gum inflammation and infection. In the case of acid reflux, the added acid exposure can exacerbate this process, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Acid reflux can wreak havoc on your teeth, causing significant damage if left untreated. However, there are steps you can take to protect your teeth from acid reflux damage. The first and most important step is to address the underlying cause of your acid reflux. Whether it’s through lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, or medical interventions, working with a healthcare professional to manage your acid reflux can make a world of difference in protecting your teeth.
In addition to managing the root cause of acid reflux, there are some practical measures you can take to safeguard your teeth from the harmful effects of stomach acid. One of the main strategies is to rinse your mouth thoroughly with water after experiencing an acid reflux episode. This helps to dilute and rinse away any residual acid that may have reached your mouth, minimizing its contact with your teeth. It’s important to note that brushing your teeth immediately after an episode of acid reflux is not recommended, as the abrasive action of tooth brushing can further erode your enamel, which may already be weakened by the acid.
As a dentist, I am often asked about ways to prevent dental problems associated with acid reflux. Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition in which the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a host of uncomfortable symptoms. However, it is important to note that acid reflux can also have a detrimental impact on your dental health.
One of the first steps in preventing acid reflux-related dental problems is to manage the underlying condition itself. Taking steps to reduce the frequency and severity of acid reflux episodes can significantly minimize the damage to your teeth. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help to alleviate acid reflux symptoms. Additionally, avoiding trigger foods such as fatty or acidic foods, caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco can also help in preventing acid reflux episodes. It is advisable to seek medical advice and explore appropriate treatment options that can address the root cause of acid reflux.
Another important aspect in preventing dental problems related to acid reflux is to protect your teeth from the damaging effects of stomach acid. Acid reflux episodes can lead to tooth erosion, which involves the wearing away of tooth enamel. This can result in increased tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and even tooth loss over time. To protect your teeth, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with water or fluoride mouthwash after an acid reflux episode. This helps to neutralize the acid and remove any residue that may be lingering in your mouth. Additionally, using a soft toothbrush and toothpaste with fluoride can help to strengthen your tooth enamel and prevent further erosion. Regular visits to your dentist for check-ups and cleanings are also crucial in detecting and addressing any acid reflux-related dental issues at an early stage.
By taking proactive measures to manage acid reflux and protect your teeth, you can significantly reduce the risk of dental problems associated with this condition. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to maintaining your oral health. So, if you suffer from acid reflux, it is important to consult with your healthcare professional or dentist for personalized advice and guidance on how to prevent acid reflux-related dental problems.
References:
1. Raghavendra S, et al. The association between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS): A meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270(3):831-839.
2. Bartlett D, et al. The dental implications of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aust Dent J. 2009;54(2): 190-193.
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for reducing acid reflux and protecting your teeth. Making certain dietary changes can help alleviate symptoms and promote oral health. Firstly, it is important to avoid foods and beverages that are known triggers for acid reflux, such as spicy and fatty foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and carbonated drinks. These items can exacerbate acid production in the stomach and increase the likelihood of reflux. Opting for a diet that is low in acid content can also be beneficial. This includes consuming fewer acidic fruits, like lemons and oranges, and choosing alkaline foods to balance the pH levels in your body.
Additionally, incorporating fiber-rich foods, like vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can aid in digestion and reduce the severity of acid reflux. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements and prevents constipation, which can contribute to acid reflux. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is also essential. Not only does it help keep the mouth hydrated and promote saliva production, but it can also aid in the digestion process and dilute stomach acid.
| Food/Drink | Description |
|---|---|
| Vegetables | Incorporate non-citrus vegetables into your diet. |
| Lean Proteins | Choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu. |
| Oatmeal | Oatmeal is a low-acid food that can soothe the stomach. |
| Ginger | Ginger can help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux. |
| Non-Citrus Fruits | Opt for fruits like bananas, melons, and apples. |
| Almonds | Almonds can neutralize stomach acid. |
| Egg Whites | Egg whites are a low-acid protein source. |
| Whole Grains | Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa are less acidic. |
| Water | Stay hydrated with water to help dilute stomach acid. |
| Herbal Tea | Chamomile, licorice, and marshmallow root teas can soothe acid reflux. |
| Yogurt | Opt for plain yogurt without added sugars. |
| Avoid Citrus | Citrus fruits and juices can trigger acid reflux. |
| Tomatoes | Tomatoes are acidic and can worsen symptoms. |
| Spicy Foods | Spicy foods can irritate the stomach lining. |
| Carbonated Drinks | Carbonated beverages can exacerbate acid reflux. |
| Coffee | Coffee can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acid to rise. |
| Mint | Mint can relax the muscles that close the esophagus, worsening reflux. |
| Alcohol | Alcohol can increase stomach acid production. |
| Chocolate | Chocolate contains substances that can relax the esophageal sphincter. |
| Fried Foods | High-fat foods can trigger acid reflux. |
In summary, following a healthy and well-balanced diet is essential for reducing acid reflux and protecting your teeth. By avoiding trigger foods and consuming foods that support proper digestion, you can minimize the occurrence of acid reflux and maintain optimal oral health. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a dentist or gastroenterologist, can provide personalized dietary recommendations for managing acid reflux.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial in managing the effects of acid reflux on dental health. Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a range of unpleasant symptoms. The acid from the stomach can also make its way into the mouth, leading to various dental complications.
One of the main concerns for individuals with acid reflux is tooth erosion. The acidic nature of stomach acid can wear away the enamel on the teeth, leaving them vulnerable to decay and sensitivity. This erosion can result in the thinning and weakening of the enamel, which cannot be reverse. Therefore, practicing good oral hygiene is essential to minimize further damage.

To protect your teeth from acid reflux-related dental problems, it is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush. Additionally, flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. It is also advised to use a mouthwash that contains fluoride to further strengthen the tooth enamel. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial in monitoring any acid reflux-induced changes to your oral health and preventing more severe dental issues. By incorporating these oral hygiene practices into your routine, you can better manage the effects of acid reflux on your dental health and maintain a healthy and beautiful smile.
Antacids and medications play a crucial role in managing acid reflux and preventing its damaging effects on dental health. These medications work by neutralizing excess stomach acid or reducing its production, thus relieving the symptoms of acid reflux and protecting the teeth from erosion.
Antacids, such as calcium carbonate and aluminum hydroxide, work by directly neutralizing the acid in the stomach, providing immediate relief from heartburn and acid reflux symptoms. These over-the-counter medications are often recommended for mild cases of acid reflux and can be taken as needed.
For more severe or persistent acid reflux, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly prescribed by doctors. PPIs reduce the production of stomach acid by blocking the enzyme responsible for its secretion. This not only alleviates the symptoms of acid reflux but also prevents the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, reducing the risk of dental erosion.
It is important to note that while antacids and medications can provide relief from acid reflux, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and duration, as prolonged use of certain medications can have potential side effects. Consulting with a dentist or physician can help determine the most suitable medication and dosage for managing acid reflux effectively.
Saliva, often considered the unsung hero of oral health, plays a crucial role in minimizing acid reflux damage. This natural bodily fluid acts as a protective barrier, helping to neutralize stomach acid and prevent it from wreaking havoc on our teeth. Saliva contains bicarbonate, a natural buffer that helps to neutralize the acidic environment in the mouth, creating a more alkaline pH. This pH balance is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums, as prolonged exposure to acid can contribute to tooth erosion and other dental issues.
In addition to its buffering capacity, saliva also aids in the remineralization process, helping to repair and strengthen tooth enamel that may have been damaged by acid reflux. The key here lies in the minerals present in saliva, such as calcium and phosphate, which are essential for maintaining enamel integrity. By promoting the deposition of these minerals onto the tooth surface, saliva assists in the re-hardening of weakened enamel, reducing the risk of tooth erosion and sensitivity. Therefore, ensuring adequate saliva flow is crucial in minimizing the detrimental effects of acid reflux on oral health.
However, it’s important to note that individuals who suffer from chronic acid reflux may experience reduced saliva production, leading to decreased protection against acid damage. In such cases, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, as they may recommend strategies to stimulate saliva flow or prescribe medications to manage acid reflux symptoms effectively. By addressing the root cause of the issue and maintaining a healthy balance of saliva in the mouth, individuals can provide their teeth with the best defense against acid reflux damage.
Dental restorations, such as fillings, crowns, and bridges, are designed to repair and restore damaged teeth. However, individuals who suffer from acid reflux may experience negative effects on their dental restorations. Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing an array of symptoms and complications.
| Aspect of Dental Restoration | Effect of Acid Reflux |
|---|---|
| Dental Fillings | Acid reflux can erode the margins of dental fillings, leading to leakage and eventual failure of the restoration. |
| Dental Crowns | Acidic reflux can corrode the materials used in dental crowns, causing them to weaken or degrade over time. |
| Dental Veneers | Acid reflux may etch the surface of dental veneers, compromising their appearance and structural integrity. |
| Dental Implants | Acid erosion can affect the surrounding bone tissue and compromise the stability of dental implants. |
| Composite Bonding | Acidic substances can degrade the bonding agent used in composite bonding, leading to bond failure and detachment. |
| Dental Sealants | Acid reflux can wear down dental sealants, reducing their effectiveness in protecting against decay. |
The acidity of stomach acid is incredibly powerful and can erode dental restorations over time. Restorations that are made of materials like porcelain or composite resin may be particularly vulnerable to the corrosive effects of acid reflux. The constant exposure to stomach acid can cause these restorations to weaken, discolor, or even break. Additionally, the acid reflux itself can lead to increased plaque formation, which can further compromise the longevity of dental restorations. Therefore, individuals with acid reflux should be aware of the potential impact on their dental restorations and take steps to minimize the damage.
Identifying and managing acid reflux triggers is an essential part of controlling the symptoms and preventing further damage to the oral health. By understanding what triggers your acid reflux episodes, you can take proactive measures to reduce their occurrence and minimize the impact on your teeth and gums.
One of the primary steps in identifying acid reflux triggers is keeping a food diary. Write down everything you consume and note any symptoms you experience afterward. Certain foods and beverages are known to exacerbate acid reflux, such as citrus fruits, spicy foods, fatty or fried foods, caffeine, and alcohol. By identifying which foods trigger your symptoms, you can make informed choices about what to avoid or consume in moderation.

Additionally, lifestyle factors can play a role in acid reflux episodes. Stress, smoking, and certain medications can all contribute to increased acid production and relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, leading to reflux. Identifying and managing these triggers may involve stress management techniques, quitting smoking, or speaking with your healthcare provider about alternative medications that may be less likely to worsen acid reflux symptoms.
By pinpointing and managing the triggers of your acid reflux, you can take proactive steps to protect your dental health. It is essential to work in partnership with your dental and medical professionals to create an individualized management plan that considers your unique situation and needs. With careful attention to triggers and effective management strategies, you can minimize the impact of acid reflux on your oral health and overall well-being.
Collaborating with dental and medical professionals is crucial for the effective treatment of acid reflux. When it comes to managing acid reflux and its impact on dental health, dentists and medical professionals can work together to ensure comprehensive care.
Dentists play a key role in identifying and diagnosing the dental effects of acid reflux. Through thorough examination and evaluation, dentists can identify signs of tooth erosion, gum disease, and other oral health issues that may be caused or exacerbated by acid reflux. By working alongside medical professionals, dentists can provide valuable insights and information that can contribute to an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Medical professionals, such as gastroenterologists, can provide specialized insight into the underlying causes of acid reflux and offer treatment options to manage the condition. With their expertise, they can prescribe medications or recommend lifestyle changes that can alleviate symptoms and reduce the impact of acid reflux on dental health.
Collaboration between dental and medical professionals ensures a holistic approach to acid reflux treatment, addressing both the dental and medical aspects of the condition. By working together, these professionals can develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account each patient’s unique needs and circumstances. This collaboration enhances patient care and increases the likelihood of successful management of acid reflux and its impact on oral health.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a chronic condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. While it is commonly associated with heartburn and digestive issues, the long-term effects of untreated acid reflux can have a significant impact on oral health.
One of the primary concerns is tooth erosion. The acid from the stomach can wear away the protective enamel on the teeth, leading to sensitivity, yellowing, and even tooth loss. Additionally, acid reflux can contribute to the development of cavities as the acid creates an acidic environment that is conducive to bacterial growth. These dental issues can have a detrimental effect on an individual’s overall oral health and quality of life.
Common symptoms of acid reflux that affect the mouth include bad breath, a sour or bitter taste in the mouth, dry mouth, and a burning sensation in the throat.
Acid reflux can lead to tooth erosion because the stomach acid that comes up into the mouth can erode the enamel, which is the protective outer layer of the teeth.
Yes, there is a link between acid reflux and gum disease. The acid from the stomach can irritate and inflame the gums, making them more susceptible to gum disease.
To protect your teeth from acid reflux damage, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene, avoid foods and drinks that trigger acid reflux, and seek treatment for acid reflux from a medical professional.
Yes, there are dietary tips to reduce acid reflux and protect your teeth. These include avoiding acidic foods and drinks, eating smaller meals more frequently, and avoiding eating or drinking anything for at least two hours before bedtime.
Oral hygiene is important in acid reflux management because it helps remove the acid and bacteria from the mouth, reducing the risk of tooth erosion and gum disease.
Yes, antacids and medications can help manage acid reflux by reducing the amount of acid in the stomach. However, it is important to consult with a medical professional before taking any medications.
Saliva plays a role in minimizing acid reflux damage by neutralizing the acid in the mouth and helping to wash it away. Chewing sugar-free gum can also stimulate saliva production.
Acid reflux can affect dental restorations by causing them to deteriorate or become damaged over time. The acid can weaken the materials used in restorations, such as fillings or crowns.
To identify and manage acid reflux triggers, it is helpful to keep a food diary and note any symptoms that occur after eating or drinking certain foods or beverages. Avoiding these triggers can help manage acid reflux.
Yes, collaborating with dental and medical professionals is important for effective acid reflux treatment. They can work together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan and address any oral health issues caused by acid reflux.
The long-term effects of untreated acid reflux on oral health can include tooth erosion, gum disease, dental decay, and damage to dental restorations. It is important to seek treatment for acid reflux to prevent these effects.