Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Understand the causes, treatment, and prevention of bleeding gums for better oral health.
Maintaining healthy gums is an essential aspect of overall oral health. Understanding gum health involves recognizing the factors that can contribute to gum problems and taking proactive steps to prevent them. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It can range from mild gingivitis, characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums, to more severe forms of periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
One of the primary causes of gum disease is the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Other factors that can contribute to gum problems include poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain medical conditions, hormonal changes, and certain medications. It is important to be aware of these factors and take steps to maintain good gum health. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings, along with a thorough at-home oral care routine, can greatly reduce the risk of gum disease and help keep your gums healthy. In the next sections, we will explore the importance of oral hygiene and the common symptoms of gum problems in more detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of gum health.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall health and well-being. When it comes to oral health, prevention is key. By practicing regular oral hygiene habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease, tooth decay, and other dental problems.
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day is the foundation of a good oral hygiene routine. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to effectively remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums. Don’t forget to gently brush your tongue as well, as it can harbor harmful bacteria.
In addition to brushing, flossing daily is crucial for removing plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline. This helps prevent the buildup of plaque, which can lead to gum inflammation and gum disease. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
By prioritizing oral hygiene and making it a daily habit, you can proactively protect your oral health and prevent dental issues. Remember, a healthy smile goes beyond aesthetics – it plays a significant role in your overall well-being. So, take the time to care for your oral health, and it will pay off in the long run.
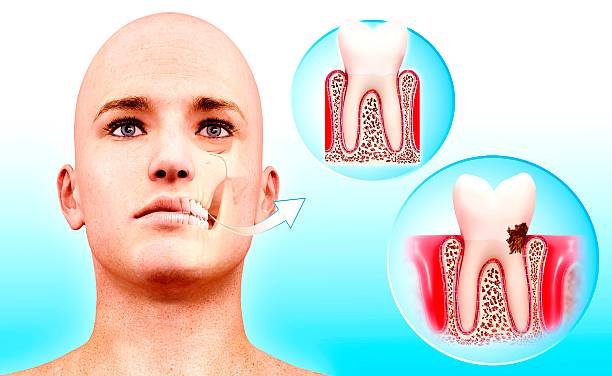
Gum problems can manifest through a variety of noticeable symptoms. One of the most common symptoms is gum bleeding, which can occur during brushing, flossing, or even spontaneously. Bleeding gums may also be accompanied by swelling and tenderness in the gum tissues. Another common symptom of gum problems is bad breath or a persistent unpleasant taste in the mouth. This can stem from the buildup of bacteria and plaque along the gumline. Additionally, gum problems can lead to receding gums, where the gum tissue begins to pull away from the teeth, exposing the sensitive tooth roots. This can cause tooth sensitivity and discomfort while eating or drinking.
In some cases, individuals may also experience changes in the appearance of their gums. This includes gums that appear redder or darker than usual, as well as gums that feel spongy or puffy to the touch. It is important to note that these symptoms may vary in severity depending on the underlying cause of the gum problem. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek professional dental care to accurately diagnose and address the issue before it worsens.
Bleeding gums can be an alarming and uncomfortable symptom, but it is important to understand that it is often a sign of an underlying issue. There are several potential causes for bleeding gums that should be identified and addressed in order to maintain optimal oral health. One common cause is inadequate oral hygiene, which can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar along the gumline. This can irritate the gums and cause them to bleed, especially when brushing or flossing.
Another potential cause of bleeding gums is periodontal disease, which is an infection of the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth. Periodontal disease can develop when plaque and tartar are not properly removed, allowing harmful bacteria to grow and invade the gums. As the infection progresses, the gums can become inflamed, swollen, and prone to bleeding. Other dental conditions, such as gingivitis or abscessed teeth, can also contribute to bleeding gums.
It is important to note that certain lifestyle factors can contribute to gum bleeding as well. Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can weaken the immune system and reduce the body’s ability to fight off infection, including gum disease. Additionally, certain medications, such as blood thinners or antiplatelet drugs, can increase the risk of bleeding gums. Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can also make the gums more susceptible to bleeding.
Identifying the root cause of bleeding gums is crucial in order to develop an appropriate treatment plan. If you are experiencing bleeding gums, it is advisable to seek professional dental care. A thorough examination by a dentist or periodontist can help determine the underlying cause and guide the appropriate treatment approach. With proper identification and management of the causes, bleeding gums can be effectively addressed to promote optimal gum health.
Here’s a table summarizing the causes of bleeding gums along with brief descriptions and credible sources:
| Causes of Bleeding Gums | Description | Credible Source |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque along the gumline, causing inflammation known as gingivitis. Gingivitis is characterized by swollen, tender gums that may bleed easily during brushing or flossing. | American Dental Association (ADA): Link |
| Gingivitis | Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, resulting from plaque buildup along the gumline due to poor oral hygiene. Symptoms include red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, leading to tooth loss and other oral health complications. | Mayo Clinic: Link |
| Periodontal Disease | Advanced gum disease, known as periodontitis, occurs when gingivitis is left untreated, leading to infection and inflammation of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Periodontitis can cause gum recession, tooth mobility, and eventual tooth loss if not managed promptly by a dental professional. | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Link |
| Trauma or Injury | Trauma or injury to the gums, such as accidental biting, vigorous brushing, or oral piercings, can cause gum tissue to become irritated, inflamed, and prone to bleeding. Proper oral care and avoiding habits that may injure the gums can help prevent trauma-related bleeding. | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR): Link |
| Medications | Some medications, such as blood thinners, anticoagulants, or certain chemotherapy drugs, may increase the risk of bleeding gums as a side effect. Individuals taking these medications should inform their dentist to ensure appropriate management of oral health and minimize bleeding complications. | American Academy of Periodontology (AAP): Link |
| Hormonal Changes | Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can affect gum health and increase the likelihood of bleeding gums. Fluctuations in hormone levels may lead to increased gum sensitivity and susceptibility to inflammation and bleeding. | American Pregnancy Association: Link |
Bleeding gums can be a sign of various dental conditions that require attention and treatment. One common condition associated with bleeding gums is gingivitis, which is the inflammation of the gums caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria. When plaque is not properly removed from the teeth and gumline, it can cause the gums to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding.
Another dental condition that may contribute to bleeding gums is periodontitis. This is a more advanced stage of gum disease where the infection has spread to the tissues and bones that support the teeth. As the infection progresses, the gums can recede, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive. These bacteria can further damage the gums and bone, leading to bleeding and even tooth loss if left untreated.
It is important to note that bleeding gums should not be ignored, as they can be indicative of underlying dental conditions. Seeking prompt dental care and professional treatment is crucial in addressing the root cause of the bleeding gums and preventing further damage to your oral health.
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in maintaining overall gum health. One such factor is poor oral hygiene practices, including inadequate brushing and flossing. When plaque and bacteria accumulate on the teeth and gumline, inflammation can occur, leading to bleeding gums. To prevent this, it is crucial to maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine and use proper brushing and flossing techniques recommended by dental professionals.
Another lifestyle factor that can contribute to gum bleeding is smoking or tobacco use. Studies have shown that smoking weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to infection and inflammation. In addition, smoking can hinder the body’s natural healing process, making it harder for gums to recover from damage. Quitting tobacco use not only improves overall health but can also have a positive impact on gum health and reduce the risk of bleeding gums.
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal gum health. The food we consume provides essential nutrients that support the overall health of our gums. A balanced diet, rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, helps strengthen the immune system and promotes healthy gum tissue.
Insufficient intake of essential nutrients can lead to gum problems and increase the risk of gum disease. For example, vitamin C deficiency can weaken the connective tissues in the gums and make them more susceptible to infections. Deficiency in vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus can also impact gum health, as these nutrients are necessary for strong teeth and bones.
Additionally, a diet high in sugar and processed foods can contribute to gum inflammation and dental caries. These unhealthy food choices not only lack the necessary nutrients but also provide an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive in the mouth.
It’s important to prioritize a nutrient-rich diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. By doing so, we can provide our gums with the proper nourishment they need to stay healthy and ward off potential gum problems. However, it’s also essential to remember that a balanced diet should work alongside regular oral hygiene practices and professional dental care for optimal gum health.
Hormonal changes can have a significant impact on the health of our gums. Many women may experience gum problems during certain stages of their lives, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. These hormonal fluctuations can lead to an increased risk of gum inflammation and bleeding.
During puberty, the surge of hormones can affect the blood flow in the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to bleeding. Similarly, pregnant women often experience a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. This is due to the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, which can exaggerate the body’s response to plaque and bacteria in the mouth.
As women approach menopause, hormonal changes can also affect the health of their gums. Decreased estrogen levels can lead to a decrease in gum tissue, making them more susceptible to infection and bleeding. It is important for women during these hormonal changes to pay extra attention to their oral hygiene and visit their dentist regularly to maintain gum health. Hormonal changes are just one of the many factors that can contribute to gum problems, and understanding their effect can help individuals take necessary precautions to protect their oral health.
Medications and Bleeding Gums: What You Need to Know
Certain medications can have an impact on the health of your gums, leading to symptoms such as bleeding, inflammation, and sensitivity. It’s important to be aware of these potential side effects and to consult with your dentist or healthcare provider if you notice any changes in your gum health.
One category of medications that can contribute to bleeding gums is anticoagulants, also known as blood thinners. These medications are commonly prescribed to individuals at risk of blood clots or those with certain heart conditions. While they are crucial for preventing serious health complications, they can increase the risk of bleeding, including bleeding gums. If you are taking anticoagulants, it’s essential to let your dentist know, as they may need to adjust certain aspects of your dental treatment to minimize bleeding and ensure your safety.
When it comes to treating bleeding gums, there are several professional options available to help address the issue effectively. One of the most common approaches is scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning. This procedure involves removing plaque and tartar below the gum line and smoothing the roots of the teeth to promote gum reattachment and reduce inflammation. Scaling and root planing can help control bleeding gums and prevent further damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
In some cases, more advanced treatments may be necessary. For instance, if the gum disease is severe and has progressed to a more advanced stage, your dentist may recommend gum surgery. There are different types of gum surgery available, such as gum grafting, pocket reduction surgery, and laser therapy. These procedures aim to repair or regenerate gum tissue, reduce pocket depths, and promote gum healing. Your dentist will assess your specific condition and recommend the most suitable treatment option based on your needs.
Gum bleeding can be a concerning issue, but there are several home remedies that can help provide relief. One effective remedy is rinsing your mouth with a saltwater solution. Salt has natural antimicrobial properties that can help reduce inflammation and fight against bacteria in the mouth. Simply dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and rinse your mouth thoroughly. Repeat this process a few times a day for optimal results.
Another home remedy that can aid in relieving gum bleeding is the application of a cold compress. Cold temperatures can help reduce swelling and numb the affected area, providing temporary relief. Take a clean cloth or towel, wrap some ice cubes in it, and apply it gently to the affected area. Keep it in place for a few minutes and repeat as needed. It is important to note that while these remedies may offer temporary relief, they are not a substitute for professional dental care. If gum bleeding persists or worsens, it is crucial to seek professional dental advice and treatment.
Proper brushing and flossing are essential for maintaining optimal gum health. These daily oral hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing gum problems and promoting overall oral well-being. By incorporating effective brushing and flossing techniques into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum bleeding and other related issues.
When it comes to brushing, it is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a fluoride-based toothpaste. Brushing should be done at least twice a day, using gentle circular motions to effectively remove plaque and debris from all surfaces of the teeth. It is recommended to spend at least two minutes on each brushing session, ensuring that all areas of the mouth are thoroughly cleaned.
In addition to brushing, flossing is equally important for maintaining healthy gums. Dental floss helps to remove food particles and plaque buildup from between the teeth and along the gumline. Regular flossing, preferably once a day, can prevent gum inflammation and reduce the risk of bleeding. It is crucial to be gentle while flossing, carefully maneuvering the floss between the teeth without causing any damage to the gums.
Effective brushing and flossing are the foundation of good oral hygiene and are essential for preventing gum bleeding. However, it is important to remember that these practices should be complemented by regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and a healthy lifestyle to ensure optimal gum health.
When it comes to maintaining gum health, one of the key aspects is choosing the right dental products. With a wide range of options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to decide which products are best suited for promoting gum health. However, making informed choices can play a significant role in preventing gum problems and maintaining a healthy mouth.
First and foremost, it is essential to opt for toothpaste that is specifically formulated for gum health. These toothpastes usually contain active ingredients that target gum inflammation, reduce bleeding, and prevent tartar buildup. Look for toothpaste with ingredients such as fluoride, triclosan, or stannous fluoride, as they have been proven to be effective in improving gum health.
In addition to toothpaste, choosing the right toothbrush is equally important. Opt for a toothbrush with soft bristles, as it is gentle on the gums and helps to prevent damage or irritation. An electric toothbrush with a rotating or oscillating head can be particularly beneficial in removing plaque and promoting gum health.
Furthermore, incorporating interdental cleaning tools into your oral hygiene routine is highly recommended. These tools, such as dental floss or interdental brushes, help to clean the areas between your teeth where a regular toothbrush cannot reach. This aids in removing plaque and reducing the risk of gum disease.
When selecting mouthwash, it is advisable to choose an alcohol-free version. Alcohol-based mouthwash can be drying to the gums and oral tissues, potentially causing irritation. Look for mouthwash that is specifically designed to promote gum health and contains antibacterial properties to help reduce plaque and gingivitis.
Remember, consulting with your dentist or dental hygienist can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific dental needs. They can assess the condition of your gums and guide you in selecting the most suitable dental products to maintain optimal gum health. By making informed decisions and using the right dental products, you can take an active role in preventing gum problems and promoting a healthy mouth.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in preventing gum bleeding and promoting a healthy mouth. Here are some tips to help you keep your gums in optimal condition.
1. Brush and floss regularly: Brushing twice a day and flossing once daily is crucial for removing plaque and food particles that can irritate the gums. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, and be gentle when brushing to prevent gum damage.
2. Use the right technique: Angle your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle towards the gum line and use small, circular motions to clean the teeth and gums. Don’t forget to clean the back of your mouth and your tongue as well.
It’s important to note that these tips provide a general guide to preventing gum bleeding, but they may not apply to everyone. If you are experiencing persistent gum bleeding or other concerning symptoms, it is best to seek professional dental care for a comprehensive evaluation. Remember, your dentist is your partner in maintaining good oral health.
Maintaining good gum health is not only crucial for a healthy mouth but also for overall well-being. The link between gum health and overall well-being has been extensively documented by various scientific studies. In fact, research has shown that there is a bidirectional relationship between gum disease and systemic health conditions.
One of the key connections between gum health and overall well-being is inflammation. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is characterized by inflammation of the gums. When left untreated, this inflammation can spread to other parts of the body, leading to chronic inflammation that is associated with a range of systemic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, respiratory issues, and even certain types of cancers. Additionally, these conditions can also exacerbate gum disease, resulting in a vicious cycle of poor oral health and deteriorating overall health.
Furthermore, the mouth serves as a gateway to the body, and any infection or inflammation in the gums can potentially enter the bloodstream and affect other organs and systems. This is particularly concerning for individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic health conditions.
Given the clear links between gum health and overall well-being, it is essential to prioritize regular dental check-ups, maintain a good oral hygiene routine, and seek prompt treatment for any gum-related issues. By doing so, not only can you ensure a healthy smile, but also contribute to the overall wellness of your body.
If you are experiencing bleeding gums, it is important to know when it is necessary to seek professional dental care. While occasional gum bleeding can be common, persistent bleeding can be a sign of an underlying dental issue that requires attention from a dental professional.
One key factor to consider is the frequency and severity of the bleeding. If you notice that your gums bleed consistently, even with gentle brushing and flossing, it may be a sign of periodontal disease or gingivitis. Additionally, if the bleeding is accompanied by other symptoms such as redness, swelling, or tenderness in the gums, it is crucial to schedule an appointment with your dentist. They can assess your oral health and provide appropriate treatment to address the underlying cause of the bleeding.
Another important consideration is if the bleeding gums are affecting your daily life. If you find that you are avoiding certain foods or activities because of the discomfort or embarrassment caused by bleeding gums, it is a clear indication that professional dental care is needed. Your dentist can help alleviate the symptoms and provide guidance on how to manage the condition effectively.
Remember, these guidelines are meant to serve as a general reference, and it is always best to consult with a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. In the next section, we will explore the various options available for treating bleeding gums.
Proper brushing and flossing help remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are major contributors to gum disease. By maintaining good oral hygiene, you can reduce the risk of bleeding gums.
Yes, poor nutrition can contribute to gum problems and bleeding gums. A lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C and vitamin K, can weaken the gums and make them more susceptible to bleeding.
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause, can cause an increase in blood flow to the gums. This can make them more sensitive and prone to bleeding, especially if proper oral hygiene is not maintained.
Yes, certain medications, such as blood thinners or antiplatelet drugs, can increase the risk of bleeding gums. It is important to inform your dentist about any medications you are taking to ensure proper care and management of your oral health.
Professional treatment options for bleeding gums may include deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotic therapy, gum surgery, or other interventions depending on the severity of the gum condition.
While home remedies may provide temporary relief, it is important to consult a dental professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. However, practicing good oral hygiene, using a saltwater rinse, or applying a cold compress to the affected area may help alleviate symptoms.
Look for dental products that are specifically designed for gum health, such as toothpaste and mouthwash containing antibacterial ingredients. It is also advisable to consult with your dentist for recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
Gum health is closely linked to overall well-being. Untreated gum problems can contribute to systemic inflammation, increasing the risk of various health conditions, including heart disease and diabetes.
If you notice persistent or excessive bleeding gums, it is important to seek professional dental care. Additionally, if you experience other symptoms such as swollen gums, bad breath, or loose teeth, it is advisable to schedule a dental appointment for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment.