Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
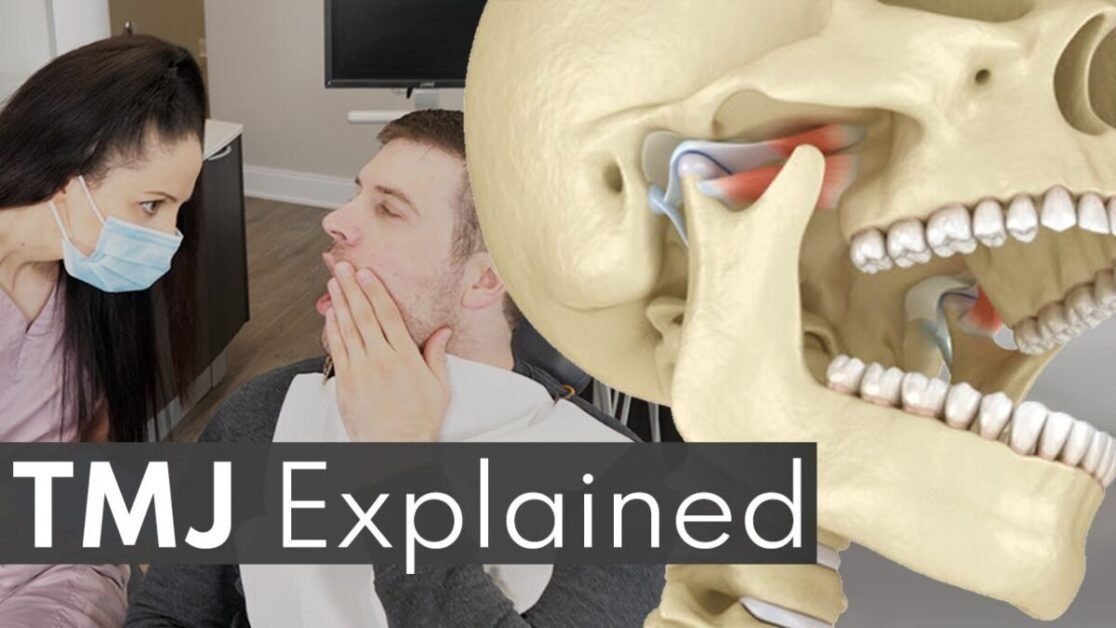
What’s Causing Your Morning Jaw Pain? Understanding and Managing TMJ. Learn about the causes of morning jaw pain and how to manage TMJ effectively.
The jaw is a complex and remarkable part of our anatomy, TMJ playing a crucial role in our ability to eat, speak, and express emotions. Understanding the structure and function of the jaw is essential for diagnosing and treating various conditions, including temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ).
At its core, the jaw consists of two main components: the mandible, which is the lower jaw bone, and the maxilla, which forms the upper jaw and houses the upper teeth. These two bones are connected by the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), a bilateral joint that allows for the opening and closing of the mouth. The TMJ is surrounded by a complex network of muscles, ligaments, and tendons, all working together to facilitate smooth movement and stability.
In addition to its role in facilitating basic functions like chewing and speaking, the jaw also has a significant impact on overall facial aesthetics. The position and alignment of the jaw can affect the appearance of the face and contribute to a person’s self-confidence. Furthermore, the jaw’s structure can influence the airway and, therefore, breathing patterns during sleep.
To fully comprehend the complexities of the jaw and its function, it is important to delve deeper into its anatomy and understand how it interacts with other components of the face and body. With this understanding, we can better recognize and address issues related to the jaw, such as TMJ disorders, leading to improved dental health and overall well-being.

TMJ, or temporomandibular joint disorder, is a condition that affects the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. It can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Recognizing the signs and signals of TMJ is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
One of the most common symptoms of TMJ is jaw pain, which can be felt on one or both sides of the face. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be aggravated by chewing, talking, or even opening the mouth widely. Other common symptoms include jaw stiffness, difficulty in opening or closing the mouth, and clicking or popping sounds when moving the jaw. Some individuals may also experience headaches, ear pain, facial pain, or neck and shoulder pain. It’s important to note that these symptoms may vary from person to person and can be intermittent or persistent. Being aware of these signs and signals can help individuals seek appropriate dental care and management for TMJ.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Jaw pain or tenderness | Pain or tenderness in the jaw joint area, often aggravated by chewing, yawning, or other movements of the jaw. |
| Difficulty or discomfort while chewing | Difficulty or discomfort experienced while chewing food, especially hard or tough foods. |
| Clicking, popping, or grating sounds | Audible sounds such as clicking, popping, or grating noises during jaw movement, particularly when opening or closing the mouth. |
| Locking of the jaw | Temporary or prolonged locking of the jaw joint, causing difficulty in opening or closing the mouth fully. |
| Jaw muscle stiffness | Stiffness or tightness in the muscles surrounding the jaw joint, often leading to difficulty in jaw movement or discomfort. |
| Facial pain or discomfort | Pain or discomfort in the face, particularly around the jaw joint area, cheeks, temples, or ears. |
| Earaches or ringing in the ears (tinnitus) | Ear-related symptoms such as earaches, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or feelings of fullness or pressure in the ears. |
| Headaches, neck pain, or shoulder pain | Headaches, neck pain, or shoulder pain that may be associated with the tension and muscle strain resulting from TMJ disorder. |
| Changes in bite alignment | Changes in the way the upper and lower teeth fit together (malocclusion) or alterations in the bite pattern, which may lead to discomfort or difficulty in biting. |
| Facial swelling | Swelling or puffiness in the face, particularly around the jaw area, which may be accompanied by tenderness or discomfort. |
Stress is an inevitable part of modern life, and its impact on our physical and mental well-being is well-documented. But did you know that stress can also play a significant role in the development and exacerbation of temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)? TMJ is a condition that affects the hinge joint connecting the jaw to the skull, causing pain, discomfort, and limited jaw movement. While numerous factors contribute to TMJ, stress has emerged as a key player in its onset and progression.
When we experience stress, our bodies undergo a cascade of physiological reactions, including increased muscle tension. This tension can extend to the muscles that control the jaw, leading to clenching, grinding, and ultimately, TMJ symptoms. Additionally, stress can disrupt our sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and further exacerbating jaw pain. It is crucial to understand the link between stress and TMJ to effectively manage and treat this condition. By addressing stress levels and adopting stress-reduction techniques, individuals with TMJ can minimize symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Oral hygiene plays a crucial role in the overall health of the jaw and can significantly impact jaw pain associated with TMJ. Maintaining good dental health is essential for preventing and managing TMJ symptoms. Poor oral hygiene can lead to various dental issues that can contribute to jaw pain, such as tooth decay and gum disease. These conditions can cause inflammation and infection, putting additional pressure on the temporomandibular joint and exacerbating TMJ symptoms.
Taking care of your teeth and gums through regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help prevent dental problems that may contribute to TMJ. Proper oral hygiene practices, like using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing technique, promote a healthy oral environment and reduce the risk of dental issues. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and limiting sugary foods and drinks can further support oral health and alleviate TMJ-related discomfort. By prioritizing dental hygiene, individuals can reduce the likelihood of experiencing jaw pain associated with TMJ and enhance their overall oral well-being.

Identifying Triggers: Foods and Habits that Can Aggravate TMJ
When it comes to managing and alleviating temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain, it is important to identify and address potential triggers. Certain foods and habits can exacerbate TMJ symptoms, leading to increased discomfort and difficulty in jaw movement. By understanding and avoiding these triggers, individuals with TMJ can better manage their condition and experience relief.
One common trigger for TMJ pain is consuming hard or chewy foods. These can require excessive jaw movement and strain the already sensitive TMJ joint. Foods like nuts, popcorn, and chewy candies should be consumed with caution, or better yet, avoided altogether. It is also important to be mindful of habits such as nail biting or chewing pen caps, as these repetitive motions can place unnecessary stress on the jaw.
| Triggers | Description |
|---|---|
| Chewy Foods | Foods that require excessive chewing, such as gum, tough meats, or hard candies, can strain the jaw and aggravate TMJ. |
| Sticky Foods | Sticky foods like caramel or taffy can cause the jaw to overwork while trying to chew and dislodge them. |
| Hard Foods | Hard foods like nuts, seeds, and raw vegetables may require intense chewing motions that strain the jaw muscles. |
| Crunchy Snacks | Crunchy snacks like chips or pretzels can put stress on the jaw joints, especially if eaten in excess. |
| Excessive Chewing | Chewing gum or pen caps habitually can overwork the jaw muscles and exacerbate TMJ symptoms. |
| Clenching | Habitual clenching or grinding of teeth, often done subconsciously, can contribute to TMJ issues. |
| Stress | Stress can lead to increased muscle tension in the jaw and facial muscles, worsening TMJ symptoms. |
| Poor Posture | Poor posture, especially when sitting or standing, can affect the alignment of the jaw and contribute to TMJ discomfort. |
| Nail Biting | Nail biting can put undue stress on the jaw joints and exacerbate TMJ symptoms over time. |
| Jaw Resting on Hand | Resting the jaw on the hand while sitting or lying down can strain the jaw muscles and worsen TMJ pain. |
TMJ, or temporomandibular joint disorder, can cause a wide range of symptoms, including jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty in opening or closing the mouth. If you are experiencing persistent jaw pain, it is important to determine whether it is related to TMJ or if it is being caused by other factors.
One of the first steps in diagnosing TMJ is to consult with a qualified healthcare professional, such as a dentist or an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. They will perform a thorough examination, which may include evaluating your medical history, conducting a physical examination of the jaw and surrounding areas, and ordering additional tests if necessary. These tests may include dental X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to get a more detailed view of the jaw joint and surrounding structures. Through these assessments, they will be able to determine if your jaw pain is indeed related to TMJ or if it is being caused by other conditions. They will then be able to develop an appropriate treatment plan for you.
It is worth noting that TMJ pain can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions, such as toothaches, sinus infections, or even heart problems. Therefore, it is crucial to seek professional guidance to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection and treatment of TMJ can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. In the next section, we will explore various treatment options available for managing TMJ and providing relief from jaw pain.
Table 1: Diagnostic Techniques for TMJ
| Technique | Description |
|—————————-|————————————————————————————————-|
| Medical History | Assessment of your medical history, including previous dental and jaw-related problems |
| Physical Examination | Evaluation of the jaw joint and surrounding areas through palpation and range of motion tests |
| Dental X-rays | Imaging tests to assess the structure and alignment of the teeth and jaw bones |
| CT Scan | Detailed images of the jaw joint to evaluate its internal structures and surrounding tissues |
| MRI Scan | High-resolution images of the TMJ and surrounding tissues to identify potential abnormalities |
Treatment for TMJ can vary depending on the severity of symptoms and individual circumstances. From home remedies to professional interventions, there are multiple options available to help manage and alleviate TMJ-related pain and discomfort.
One of the most commonly recommended home remedies is applying a cold or warm compress to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and relieve muscle tension. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or meditation can help decrease stress levels that may contribute to TMJ symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can also be effective in providing temporary relief.
However, in more severe cases, professional interventions may be necessary. Dentists may suggest the use of oral appliances, such as splints or mouthguards, to help alleviate pressure on the jaw joint and prevent teeth grinding or clenching. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, as it focuses on strengthening and stretching the muscles around the jaw to improve joint stability. In some cases, more invasive treatments such as corticosteroid injections or surgery may be considered.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dentist or oral surgeon, to discuss which treatment options are best suited for individual needs. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, consider the severity and underlying causes of TMJ, and recommend an appropriate course of action. With the right treatment approach, individuals with TMJ can find relief and improve their overall quality of life.

Jaw exercises are an essential component of managing temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders and providing relief from jaw pain. Strengthening and stretching the jaw muscles can help improve their flexibility and decrease muscle tension, leading to reduced discomfort and improved jaw function. These exercises target the muscles surrounding the jaw joint, including the temporalis, masseter, and pterygoid muscles.
One effective jaw exercise is the resisted opening and closing technique. To perform this exercise, place your thumb under your chin and apply gentle pressure as you slowly try to open your mouth against the resistance. Hold this position for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat this exercise several times a day to strengthen the jaw muscles. Another beneficial exercise is the gentle stretching of the jaw muscles by opening your mouth as wide as possible and then slowly closing it. Hold this stretch for a few seconds before relaxing. Regularly incorporating these exercises into your routine can help alleviate TMJ symptoms and promote overall jaw health.
Bite alignment refers to the way your teeth fit together when you close your mouth. It plays a crucial role in the overall health and function of your jaw. When your bite is properly aligned, the forces exerted during chewing and speaking are evenly distributed, preventing excessive stress on your temporomandibular joints (TMJ). However, when your bite is misaligned, it can lead to various issues, including TMJ disorders.
A misaligned bite can put undue pressure on your TMJ, causing inflammation, pain, and discomfort. This can result in a range of symptoms, including jaw pain, headaches, earaches, and difficulty opening and closing the mouth. Additionally, a misaligned bite can affect the position and movement of your jaw, potentially leading to clicking or popping noises when you open or close your mouth. Furthermore, an imbalanced bite can contribute to bruxism (teeth grinding), which can exacerbate TMJ symptoms. Therefore, understanding the relationship between bite alignment and TMJ is crucial in diagnosing and treating TMJ disorders effectively.
TMJ, or temporomandibular joint disorder, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can affect both men and women, there is evidence to suggest that women may be more prone to developing TMJ. This gender disparity is thought to be related to hormonal influences, specifically the fluctuation of estrogen levels throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Estrogen is known to play a role in pain perception and inflammation, and its levels can vary significantly during different stages of a woman’s menstrual cycle. Research has shown that women are more likely to experience symptoms of TMJ, such as jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds, headaches, and difficulty in opening or closing the mouth, at specific times during their cycle when estrogen levels are highest or lowest. This suggests that hormonal imbalances may contribute to the development or exacerbation of TMJ symptoms in women.
While the exact mechanisms behind the hormonal influences on TMJ are still being studied, understanding the link between estrogen levels and jaw pain in women is an important step towards better management and treatment of the condition. By recognizing the potential impact of hormonal fluctuations on TMJ symptoms, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans and interventions to address these specific needs in women.
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on people’s overall well-being, affecting their ability to get a good night’s rest and function optimally during the day. One particular sleep disorder that is often associated with jaw pain and discomfort is nighttime jaw clenching, also known as sleep bruxism. This involuntary gripping or grinding of the teeth can lead to various complications, including temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
The link between sleep disorders and TMJ is multifaceted. The repetitive motion and excessive pressure exerted on the jaw joint during bruxism episodes can cause inflammation and damage to the TMJ. This can result in jaw pain, headaches, earaches, and even difficulties in fully opening or closing the mouth. Additionally, the strain on the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and nerves can contribute to sleep disruptions, further exacerbating the cycle of sleep disorders and TMJ-related symptoms. It is crucial for individuals experiencing these issues to seek professional evaluation and appropriate treatment to address both the sleep disorder and TMJ concerns.
Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, is a common condition that affects many individuals. In relation to temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ), bruxism plays a significant role in contributing to jaw pain and discomfort. Bruxism is classified as the involuntary clenching, grinding, or gnashing of teeth, often occurring during sleep or periods of stress.
The connection between bruxism and TMJ lies in the excessive pressure that is placed on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) during teeth grinding. The repetitive and forceful movements can lead to strain and inflammation in the jaw joint, resulting in pain and stiffness. Individuals with TMJ who also experience bruxism may find their symptoms intensify, causing increased jaw pain and difficulty in performing everyday activities such as eating and speaking.
Alternative Therapies for TMJ: Exploring Non-Conventional Treatment Options
When it comes to managing TMJ, traditional treatment options like medication, physical therapy, and dental interventions are often recommended. However, for those seeking alternative approaches, there are non-conventional therapies that may provide some relief.
One such therapy is acupuncture. Derived from traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to restore the flow of energy and promote healing. Some studies have shown that acupuncture can help reduce TMJ pain and improve jaw function, although further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness. Additionally, relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and biofeedback have been explored as potential remedies for TMJ. These practices focus on reducing stress, tension, and muscle tightness, all of which can contribute to jaw pain. While there is limited scientific evidence supporting their efficacy, many people find these techniques helpful in managing their TMJ symptoms.
Overall, alternative therapies for TMJ offer potential options for those who may not find relief with traditional treatments. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified practitioner to ensure these therapies are safe and suitable for your specific condition.
Lifestyle Changes for TMJ Management: Stress Reduction and Self-Care
Managing TMJ symptoms can often involve making lifestyle changes that help reduce stress and promote self-care. Stress has long been recognized as a significant contributor to TMJ pain and discomfort. When we experience stress, our muscles tend to tense up, including those in the jaw. This increased tension can exacerbate TMJ symptoms and lead to further pain and discomfort.
To effectively manage TMJ, it is essential to incorporate stress reduction techniques into your daily routine. This can include practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as yoga or tai chi. Additionally, finding healthy outlets for stress, such as engaging in hobbies or spending time with loved ones, can have a positive impact on TMJ symptoms.
Self-care is another vital component in managing TMJ. Proper oral hygiene is key in preventing oral health issues that can aggravate TMJ symptoms. Regular brushing and flossing, along with routine dental check-ups, can help maintain optimal dental health and reduce the risk of TMJ flare-ups. Additionally, using relaxation techniques, such as warm compresses or gentle jaw stretching exercises, can provide relief and promote healing in the jaw muscles.
By incorporating stress reduction techniques and prioritizing self-care, individuals with TMJ can take a proactive role in managing their symptoms. These lifestyle changes, when combined with appropriate medical interventions, can help alleviate pain, improve jaw function, and enhance overall quality of life. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific TMJ management plan.
Jaw pain caused by Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorder can be a debilitating condition that affects many aspects of daily life. Patients often wonder about the long-term outlook for TMJ and whether they can find complete relief from their jaw pain. While every individual case may vary, it is important to understand that with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle changes, significant improvement and even elimination of jaw pain is possible.
The journey towards eliminating jaw pain begins with a thorough understanding of the underlying causes and triggers of TMJ disorder. Factors such as stress, dental health, bite alignment, and even hormonal influences can contribute to the development and persistence of TMJ symptoms. By addressing these factors and seeking appropriate treatment options, individuals can effectively manage their TMJ and work towards long-term resolution. With the guidance of a healthcare professional, patients can identify personalized strategies and therapies that cater to their specific needs, promoting healing and restoring jaw function.
While complete elimination of jaw pain may not be guaranteed for every individual, it is important to recognize that managing and reducing TMJ symptoms is achievable. With the right combination of lifestyle changes, professional interventions, and ongoing care, patients can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of TMJ disorder on their daily activities. By taking proactive steps towards understanding and addressing the root causes of TMJ, individuals can strive towards long-term relief and regain control over their oral health and well-being.
Stay tuned for more information in the upcoming sections of this article, as we delve into the various treatment options, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies that can contribute to the long-term outlook for TMJ.
TMJ can be caused by a variety of factors, including jaw injury, arthritis, teeth grinding, and misalignment of the jaw.
In some cases, TMJ symptoms may resolve on their own with self-care and lifestyle changes. However, it is important to seek treatment if the symptoms persist or worsen.
Yes, there are several home remedies that may provide temporary relief from TMJ pain, such as applying a warm or cold compress, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding hard or chewy foods.
Yes, stress is often linked to TMJ symptoms and can exacerbate jaw pain. Managing stress through techniques like exercise, meditation, and therapy may help alleviate TMJ symptoms.
Yes, TMJ can lead to sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea, especially if nighttime teeth grinding or jaw clenching is present. Treating the underlying TMJ condition may improve sleep quality.
Yes, hormonal fluctuations in women, particularly during menstruation and pregnancy, can affect TMJ symptoms and potentially worsen jaw pain. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help manage these hormonal influences.
Yes, teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, is commonly associated with TMJ. Addressing bruxism through treatments like mouthguards or dental interventions may help alleviate TMJ symptoms.
Yes, some alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy, have shown promise in relieving TMJ symptoms. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
While complete elimination of jaw pain is not guaranteed, many individuals with TMJ find relief through a combination of treatments, lifestyle changes, and self-care practices. Working with healthcare professionals can help improve symptoms and manage TMJ in the long term.