Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
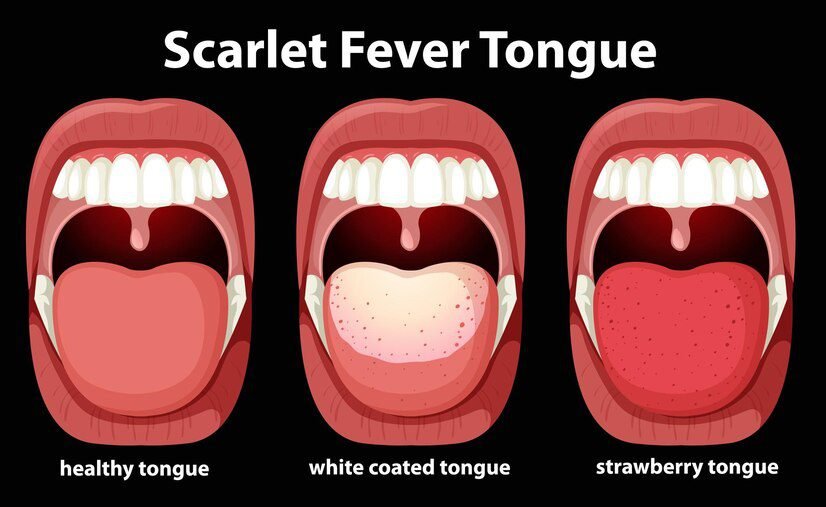
What Does Your Tongue Say About Your Health? Understanding Tongue Signs and Symptoms. Find out what your tongue can reveal about your health and how to interpret its signs.
The condition of our tongue can be an indicator of our overall health. There are various possible tongue conditions and understanding their meanings can provide valuable insights into our well-being. Here, we will explore some common tongue conditions and what they could potentially signify.
One common tongue condition is thrush, also known as oral candidiasis. This condition is characterized by the presence of white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks. It is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus and can occur due to factors such as weakened immune system, certain medications, or poor oral hygiene. Detecting thrush on the tongue can alert us to the presence of an underlying health issue or the need for better oral care. Seeking medical attention is important to properly diagnose and treat this condition.
Another tongue condition to be aware of is glossitis, which refers to inflammation of the tongue. It can cause the tongue to appear swollen, red, and smooth. Glossitis can develop as a result of various factors, including infections, allergies, nutritional deficiencies, or tongue trauma. Identifying glossitis can indicate the presence of an underlying health issue or nutritional imbalance that requires attention. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the cause of glossitis and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
By understanding possible tongue conditions and their meanings, we can proactively monitor our oral health and address any potential underlying issues. It is important to remember that any persistent or concerning tongue changes should be evaluated by a medical professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.

Tongue discoloration can be a cause for concern, as it may indicate an underlying health issue. There are several common causes of tongue discoloration, ranging from harmless to more serious conditions. One possible cause is the accumulation of surface debris and bacteria, which can give the tongue a yellowish or white coating. This can be easily resolved with proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and tongue scraping.
Another common cause of tongue discoloration is the consumption of certain foods and beverages. For example, regularly consuming dark-colored foods like berries, chocolate, and coffee can stain the tongue. Additionally, tobacco use, both smoking and chewing, can also lead to discoloration. In these cases, tongue discoloration is usually harmless and can be resolved by avoiding or limiting the consumption of these substances.
It is important to note that tongue discoloration can also be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. For instance, a black or hairy tongue may be an indication of an overgrowth of bacteria or yeast in the mouth. This condition, known as black hairy tongue, is often harmless but can be caused by poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, or certain medications. In more severe cases, tongue discoloration can be a sign of anemia, vitamin deficiencies, or even oral cancer.
If you notice any changes in the color of your tongue that are persistent or accompanied by other symptoms, it is essential to seek professional dental care. A dentist or oral healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a balanced diet, and scheduling regular dental check-ups can also help prevent tongue discoloration and promote overall oral health.
Tongue texture can provide valuable insights into a person’s overall health. The surface of the tongue can reveal important information about various health issues, ranging from nutritional deficiencies to digestive problems. By examining the texture of the tongue, dental professionals can identify potential underlying health concerns and recommend appropriate treatment.
A healthy tongue should have a smooth and uniform surface. However, changes in texture can indicate an array of health conditions. For example, a rough or bumpy tongue may be a sign of dehydration or a deficiency in essential vitamins and minerals. On the other hand, a fissured or grooved tongue might indicate a genetic condition or a weakened immune system. By paying close attention to the texture of the tongue, dental professionals can provide early intervention, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Understanding the relationship between tongue texture and health is crucial for both dental professionals and individuals concerned about their well-being. By recognizing these indicators, we can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal health and preventing potential complications. Let us now delve deeper into specific tongue textures and their possible implications for our overall health.
Dehydration occurs when your body doesn’t have enough water to function properly. It can happen for various reasons, including excessive sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, or simply not drinking enough fluids. While it’s important to replenish your body with water when dehydrated, did you know that your tongue can also provide valuable clues about your hydration levels?
One of the signs of dehydration that can be observed through your tongue is dryness. When you are dehydrated, your body prioritizes the distribution of available water to essential organs, leaving your mouth and tongue to feel dry and parched. In severe cases, your tongue may appear shriveled or stick to the roof of your mouth. This is an important indication that you should increase your fluid intake to prevent further dehydration. Additionally, a dehydrated tongue may lack the normal pink color and appear pale or have a whitish coating. This could indicate a need for immediate rehydration to restore the health of your body and prevent potential complications.
The coating on your tongue can provide valuable insights into the health of your digestive system. Often overlooked, the condition of your tongue can indicate underlying issues that require attention. A healthy tongue should appear pink in color and have a thin, transparent layer of coating. However, variations in color, thickness, and texture of the tongue coating can reveal potential digestive problems.
A thick, white coating on the tongue, for example, may suggest an overgrowth of bacteria or yeast in the digestive tract. This can be indicative of conditions such as oral thrush or candida overgrowth, which can affect the balance of good bacteria in your gut. On the other hand, a yellow coating on the tongue may indicate liver dysfunction or gallbladder issues. Understanding these different coatings can help identify the root cause of digestive discomfort and guide appropriate treatment options. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dentist to accurately diagnose and address any concerns related to the coating on your tongue.
Geographic tongue, also known as benign migratory glossitis, is a common condition that affects the surface of the tongue. It is called “geographic” because of the characteristic appearance of irregular, map-like patches on the tongue’s surface. While the exact cause of geographic tongue is unknown, it is believed to be a result of the loss of small bumps on the tongue called papillae. These papillae normally serve to provide friction and house taste buds, so their absence can lead to changes in the smoothness and appearance of the tongue.
The implications of geographic tongue vary from person to person. Some individuals with geographic tongue may experience no discomfort or symptoms at all, while others may notice mild to moderate sensitivity or a burning sensation on the affected areas. In rare cases, geographic tongue may be associated with other conditions such as psoriasis or lichen planus. It is important to note that geographic tongue is not contagious or a sign of any serious underlying health issue. If you notice any changes in the appearance or sensation of your tongue, it is always best to consult with a dental professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Oral hygiene plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of our mouths. While most people are aware of the importance of brushing and flossing their teeth, many might overlook the significance of tongue health in their oral care routine. The tongue is not only responsible for taste and speech, but it also harbors a significant amount of bacteria and food debris. Neglecting tongue hygiene can lead to unpleasant odors and oral health issues. Therefore, it is imperative to understand the link between tongue health and oral hygiene, and incorporate proper tongue cleaning techniques into our daily oral care regimen.
Bacteria and food particles can accumulate on the surface of the tongue, leading to the formation of a white or yellowish coating. This coating can not only cause bad breath but also serve as a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. It is essential to clean the surface of the tongue regularly to remove this coating and maintain a healthy oral environment. Tongue cleaning tools, such as tongue scrapers or brushes, can be used to effectively remove the buildup. Incorporating tongue cleaning into our oral hygiene routine can help prevent oral health issues such as cavities, gum diseases, and oral infections.
In conclusion, proper oral hygiene extends beyond brushing and flossing our teeth. The link between tongue health and oral hygiene is undeniable, as neglecting tongue cleaning can lead to various oral health issues. By incorporating tongue cleaning techniques into our daily oral care regimen, we can maintain a healthy oral environment, prevent bad breath, and reduce the risk of oral diseases. Remember, a healthy tongue is essential for a healthy smile.
Oral thrush, also known as candidiasis, is a common fungal infection that can affect the tongue and other areas of the mouth. It is caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans, which is normally present in small amounts in the mouth. However, certain factors can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and fungi in the mouth, leading to the development of thrush.
The signs of oral thrush on the tongue can vary, but they often include white patches or plaques that may resemble cottage cheese. These patches can be easily wiped off, revealing a sore, red, and sometimes bleeding surface underneath. In some cases, the tongue may also appear swollen or have a burning sensation. It is important to note that oral thrush can occur in individuals of all ages, from infants to the elderly, but it is most commonly seen in infants, those with weakened immune systems, and individuals taking certain medications, such as antibiotics or corticosteroids. Early recognition and prompt treatment of oral thrush are crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and causing discomfort or further complications.
| Signs of Oral Thrush on the Tongue | Description |
|---|---|
| White patches or plaques | Creamy, white lesions resembling cottage cheese on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, gums, or tonsils. These patches may be difficult to scrape off. |
| Redness or inflammation | The affected areas of the tongue may appear red and inflamed, especially around the white patches. |
| Soreness or discomfort | Patients may experience pain, soreness, or discomfort in the affected areas, particularly while eating or drinking acidic or spicy foods. |
| Loss of taste | Some individuals with oral thrush may notice a loss of taste sensation or changes in taste perception. |
| Bleeding or cracking | In severe cases, the tongue may bleed or develop cracks or fissures, especially if the lesions are scraped or irritated. |
| Cotton-like appearance | The white patches may have a cotton-like appearance and can sometimes spread to the throat, causing difficulty swallowing. |
Tongue ulcers, also known as canker sores, are a common oral condition that can cause significant discomfort and irritation. These small, shallow lesions can appear on the surface of the tongue, as well as on the inner cheeks and lips. While their exact cause is still not fully understood, several factors have been identified as potential triggers for tongue ulcers.
One of the primary causes of tongue ulcers is tissue injury or trauma. Accidentally biting the tongue or the inside of the cheek can lead to the formation of ulcers. Other possible causes include stress, hormonal changes, certain foods and drinks, nutritional deficiencies, and even allergies. Moreover, medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and compromised immune system can also contribute to the development of tongue ulcers.
Treatment options for tongue ulcers mainly focus on relieving pain and promoting healing. Over-the-counter ointments and gels that contain ingredients like benzocaine or hydrogen peroxide can help alleviate discomfort. Additionally, using antimicrobial mouthwashes and avoiding spicy, acidic, or rough-textured foods can aid in the healing process. In severe cases, a dentist or healthcare professional may prescribe topical or systemic medications to manage the ulcers effectively.
It is important to note that tongue ulcers typically resolve on their own within a week or two. However, if they persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The appearance of your tongue can provide valuable insights into your overall nutritional status. A healthy tongue typically appears pink, moist, and covered with tiny bumps called papillae. However, deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can manifest as changes in the color, texture, and coating of your tongue.
One common indication of nutritional deficiencies is a pale or white tongue. This may suggest a lack of iron, vitamin B12, or folate in your diet, which are all important for the production of red blood cells. Additionally, a bright red tongue could indicate a deficiency in niacin or vitamin B3.
It’s important to note that while your tongue can provide clues about potential nutritional deficiencies, further testing and consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis. A comprehensive assessment of your diet, lifestyle, and medical history is necessary to make appropriate dietary adjustments and ensure overall well-being.
| Tongue Condition | Nutritional Status Indicator |
|---|---|
| Pink and moist | Generally healthy |
| Pale | Iron deficiency anemia |
| Bright red | Vitamin B12 deficiency |
| Smooth | Folate or iron deficiency |
| Swollen | Vitamin B12 deficiency |
| White coating | Oral thrush, candida infection, dehydration, or poor oral hygiene |
| Yellow coating | Jaundice, liver issues, or poor digestion |
| Cracks | Vitamin B complex deficiency, especially B2 (riboflavin) |
| Soreness or ulcers | Vitamin B complex deficiency, iron deficiency, or immune system issues |
| Geographic tongue | Vitamin B complex deficiency or immune system issues |
| Burning sensation | Vitamin B complex deficiency, particularly B3 (niacin) |
| Tenderness | Vitamin B complex deficiency, especially B6 (pyridoxine) |
The health of our tongue is often overlooked, but it plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. It serves as a powerful tool for communication, taste perception, and proper digestion. Yet, many fail to recognize that the condition of our tongue can indicate underlying health issues that may affect our entire body.
A healthy tongue is moist, pink, and covered with tiny bumps called papillae. Any deviation from this normal appearance could be a sign of an underlying health problem. For instance, a white coating on the tongue may indicate a fungal infection called oral thrush, which can be a symptom of a weakened immune system. On the other hand, a red or sore tongue could be a sign of deficiencies in certain vitamins or minerals.
As we delve deeper into the connection between tongue health and overall well-being, it becomes evident that our tongues can act as a mirror reflecting our internal health. By paying attention to the condition, texture, and color of our tongues, we can potentially detect early signs of various health issues and take appropriate action. Whether it’s maintaining good oral hygiene, addressing nutritional deficiencies, or seeking medical attention when necessary, taking care of our tongues can contribute to our overall well-being in remarkable ways. Stay tuned as we explore this fascinating topic further.
Tongue sores can be uncomfortable and concerning, but they can also serve as indicators of potential health problems. In some cases, tongue sores may simply be a result of minor irritation or injury, such as accidentally biting the tongue or consuming overly hot foods. However, persistent or recurrent tongue sores may be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires attention.
One potential cause of tongue sores is a condition called oral thrush. This fungal infection is caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus in the mouth. Along with tongue sores, oral thrush may also cause white patches or a creamy coating on the tongue, as well as discomfort or a burning sensation. It is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or taking certain medications.
Another possible cause of tongue sores is a condition called aphthous ulcers, also known as canker sores. These small, shallow sores can appear on various areas of the mouth, including the tongue. While the exact cause of aphthous ulcers is unclear, they may be triggered by factors such as stress, certain foods or allergies, hormonal changes, or a weakened immune system.
As with any oral health concern, it is important to consult with a dental professional if you are experiencing persistent or recurrent tongue sores. They can properly diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment or further evaluation if necessary. Early detection and intervention can help prevent potential complications and ensure optimal oral health.
Tongue bumps can be a cause for concern, as they can indicate underlying health issues or simply be a temporary irritation. These bumps can take various forms, such as small white or red spots, raised bumps, or even painful ulcers. While most tongue bumps are harmless and resolve on their own, it’s important to understand the possible causes behind them.
One common cause of tongue bumps is oral thrush, a fungal infection that results in creamy white patches on the surface of the tongue. This condition occurs when the naturally occurring yeast in the mouth overgrows. Another possible cause is canker sores, which are small, painful ulcers that typically develop on the soft tissues of the mouth, including the tongue. Other factors that can contribute to the development of tongue bumps include viral infections, such as herpes simplex virus, and irritation from biting or burning the tongue. In rare cases, tongue bumps can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as oral cancer or autoimmune disorders.
While tongue bumps can be uncomfortable and concerning, it’s important to seek professional dental care if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms. A dentist or oral health professional can evaluate your condition, provide a definitive diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Remember, early detection and intervention are crucial for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being.
Tongue sensitivity is an important aspect of oral health that often goes unnoticed. The tongue is not only responsible for taste, but it also plays a crucial role in speech and swallowing. When the tongue becomes sensitive, it can indicate underlying health issues that should not be ignored.
There are various factors that can contribute to tongue sensitivity, including dental problems, oral infections, and certain medical conditions. For instance, a condition known as glossitis, which causes inflammation of the tongue, can result in heightened sensitivity. Additionally, tongue sensitivity can be a symptom of nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of vitamin B12 or iron.
It is essential to pay attention to any changes in tongue sensitivity and seek professional dental or medical advice if needed. By understanding the implications of tongue sensitivity, we can better address potential health issues and take appropriate steps to maintain optimal oral health.
Tongue Piercings: Potential Risks and Complications
Oral piercings, particularly tongue piercings, have become popular forms of self-expression in recent years. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and complications that can arise from these procedures. While each individual may have a unique experience, it is essential to understand the common dangers associated with tongue piercings.
One major concern is the risk of infection. The mouth harbors a wide array of bacteria, and introducing a foreign object through piercing creates an entry point for these microorganisms. Infections can lead to pain, swelling, and even more severe complications such as abscess formation or the involvement of nearby structures like the salivary glands. Additionally, poor oral hygiene, improper aftercare, and frequent contact with oral contaminants like food particles can increase the risk of infection.
Another potential issue is damage to teeth and gums. Tongue piercings have been known to cause trauma to the oral tissues, leading to gum recession, tooth fractures, and enamel erosion. The constant presence of the jewelry can also result in tooth chipping or cracking, particularly when biting on hard objects or during sleep. Furthermore, metal jewelry can attract plaque and tartar buildup, which can contribute to gum disease if not properly addressed.
While tongue piercings may be visually appealing to some, it is crucial to weigh the potential risks against the desire for self-expression. Consulting with a dental professional before getting a tongue piercing can provide valuable insight into individual risk factors and promote a better understanding of the necessary precautions and aftercare. By making informed decisions and prioritizing oral health, individuals can minimize the likelihood of complications associated with tongue piercings.
Tongue piercings can lead to several risks, including infection, swelling, pain, damage to teeth or gums, difficulty speaking or eating, nerve damage, and allergic reactions.
The healing time for a tongue piercing can vary, but it generally takes about 4 to 6 weeks. However, complete healing may take several months.
Yes, a tongue piercing can potentially cause speech problems, especially during the initial healing period. It may affect pronunciation and clarity of speech.
While it is rare, a tongue piercing can potentially damage taste buds. This may temporarily or permanently alter a person’s sense of taste.
Yes, aftercare for tongue piercings is crucial. It typically involves rinsing with an alcohol-free mouthwash after meals, avoiding oral contact with bodily fluids, maintaining proper oral hygiene, and avoiding smoking or alcohol consumption during the healing period.
Yes, tongue piercings can cause tooth or gum damage. The jewelry can accidentally hit and chip teeth, or it may irritate the gums, leading to gum recession or periodontal disease if not properly cared for.
The risk of infection with a tongue piercing is relatively high. Poor oral hygiene, improper aftercare, or introducing bacteria during the piercing process can increase the chances of infection.
Yes, there can be long-term complications from tongue piercings. These may include ongoing infections, gum recession, tooth damage, nerve damage, and even speech or swallowing difficulties in rare cases.
Yes, some individuals may have an allergic reaction to the metal used in tongue piercings, such as nickel. It is important to choose hypoallergenic materials to minimize this risk.
Yes, it is possible to remove a tongue piercing if complications occur. However, it is recommended to consult with a professional piercer or healthcare provider before doing so to ensure proper care and minimize potential risks.