Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
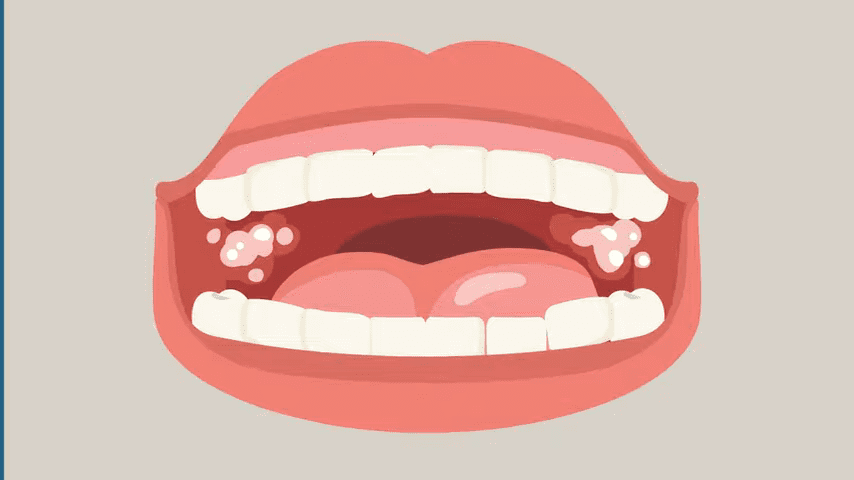
Get to Know the Signs: Early Detection of Oral Cancer. Learn the signs of oral cancer for early detection and timely treatment.
Oral cancer can manifest with various symptoms that individuals should be aware of to ensure timely detection and intervention. One common sign is the presence of persistent sores or ulcers in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks. These may appear as red or white patches and often lead to discomfort or pain while eating or speaking. Additionally, unexplained bleeding in the mouth, lumps or thickening of the oral tissues, difficulty in chewing, swallowing, or moving the jaw, and chronic hoarseness are all potential indicators of oral cancer.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Persistent mouth sore | A sore in the mouth that does not heal within a few weeks. |
| Red or white patches | Red or white patches in the mouth or on the lips. |
| Persistent sore throat | A sore throat that persists and does not go away despite treatment. |
| Difficulty swallowing | Difficulty or pain while swallowing, also known as dysphagia. |
| Changes in voice | Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or persistent voice changes. |
| Lump or mass | A lump, mass, or thickening in the mouth, throat, or neck. |
| Ear pain | Pain in one or both ears that does not result from an ear infection. |
| Loose teeth | Teeth that become loose for no apparent reason. |
| Jaw swelling or stiffness | Swelling, numbness, or stiffness in the jaw that does not resolve. |
| Unexplained weight loss | Significant weight loss without trying can be a sign of advanced oral cancer. |
| Bleeding | Unexplained bleeding in the mouth or gums. |
Moreover, individuals may experience persistent ear pain, numbness in the mouth or facial areas, or a change in their bite alignment without any apparent cause. It is crucial to note that these symptoms can sometimes be indicative of other oral health issues, but if they persist for an extended period or worsen over time, it is essential to seek prompt evaluation from a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Oral cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Understanding the risk factors associated with oral cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer, including tobacco use in all forms, excessive alcohol consumption, a diet low in fruits and vegetables, chronic sun exposure to the lips, and a history of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Genetics can also play a role, as individuals with a family history of oral cancer may have a higher risk of developing the disease.
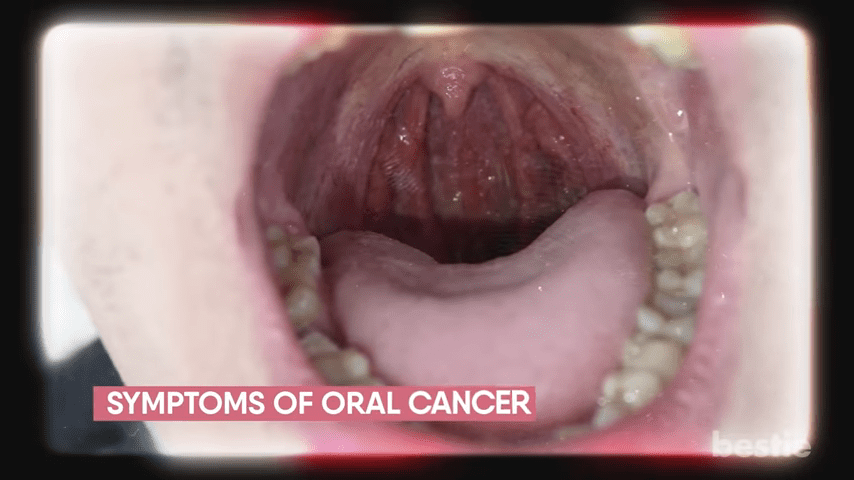
Moreover, other risk factors such as poor oral hygiene, chronic irritation from ill-fitting dentures or constant friction from sharp edges on teeth, and a weakened immune system can also contribute to the development of oral cancer. It is essential for individuals to be aware of these risk factors and take proactive steps to reduce their risk, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy diet, using lip protection when exposed to the sun for extended periods, and practicing good oral hygiene habits. By understanding and addressing these risk factors, individuals can help protect themselves against oral cancer and improve their overall oral health.
Early detection of oral cancer is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Detecting oral cancer in its initial stages significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and enhances prognosis. Regular screenings by dentists play a fundamental role in identifying any suspicious changes or abnormalities in the mouth that might indicate the presence of oral cancer.
By detecting oral cancer early, dentists can expedite the referral process to specialists for further evaluation and treatment. Timely diagnosis allows for less aggressive treatment options, reducing the overall impact on a patient’s quality of life. Ultimately, early detection not only improves survival rates but also ensures that patients can receive the necessary care and support promptly.
Oral cancer can manifest in various locations within the oral cavity, impacting different parts of the mouth and throat. Common locations where oral cancer may develop include the lips, the front two-thirds of the tongue, the gums, the floor of the mouth, the inner lining of the cheeks, the roof of the mouth (palate), and the tonsils.

Understanding these specific locations is crucial for early detection and effective treatment of oral cancer. By being aware of the common sites where oral cancer tends to arise, individuals can monitor these areas for any unusual changes or symptoms, prompting them to seek prompt evaluation and diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
Oral cancer diagnosis involves a series of steps to accurately detect and confirm the presence of cancerous cells in the oral cavity. Typically, the process begins with a comprehensive physical examination of the mouth, throat, and neck by a healthcare professional. This examination may include the use of a small mirror or a special light to closely inspect the mouth for any abnormalities, such as sores, lumps, or discolorations that could indicate the presence of cancerous tissue.
Following the initial examination, if there are any suspicious findings, a biopsy may be recommended to further evaluate the abnormal tissue. During a biopsy, a small sample of the suspicious area is removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the biopsy can help determine if cancer cells are present, the type of cancer present, and how aggressive the cancer is, guiding the healthcare team in developing an appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
Surgery is often the primary treatment for oral cancer, aiming to remove the tumor and surrounding tissues to prevent the cancer from spreading. Depending on the location and stage of the cancer, different surgical techniques may be utilized, such as excision of the tumor, neck dissection to remove affected lymph nodes, or reconstructive surgery to restore the appearance and function of the mouth. In some cases, surgery may be combined with radiation therapy or chemotherapy to improve outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Surgical removal of the tumor and affected tissue. |
| Radiation Therapy | High-energy rays to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. |
| Chemotherapy | Medications to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. |
| Targeted Therapy | Drugs that target specific abnormalities in cancer cells. |
| Immunotherapy | Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. |
| Palliative Care | Focuses on improving quality of life and managing symptoms. |
Radiation therapy is another common treatment modality for oral cancer, using high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be delivered externally through a machine aimed at the tumor site, or internally by placing radioactive materials directly into or near the tumor. Radiation therapy is often used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy to enhance effectiveness. However, it can also lead to side effects such as oral mucositis, dry mouth, and difficulty swallowing, which may require supportive care to manage.
Dentists play a crucial role in the early detection of oral cancer through regular screenings during routine dental check-ups. As frontline healthcare providers, dentists are trained to identify suspicious lesions or abnormalities in the mouth that could be indicative of oral cancer. By performing thorough oral examinations and utilizing diagnostic tools like tissue biopsies, dentists can help in the timely diagnosis and management of oral cancer cases, potentially improving patient outcomes and survival rates.

Furthermore, dentists serve as educators for their patients, raising awareness about the risk factors associated with oral cancer, such as tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Through open communication and patient education, dentists empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their oral health and lifestyle choices, thereby contributing to the prevention and early detection of oral cancer. By promoting regular dental visits and encouraging self-examinations, dentists play a vital role in the holistic approach towards combating oral cancer and promoting overall well-being.
Oral cancer is a serious health condition that can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early. Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing oral cancer. Avoiding tobacco and alcohol use is one of the most effective ways to prevent oral cancer. Tobacco use, including smoking and smokeless tobacco, is a major risk factor for oral cancer, while excessive alcohol consumption can also increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups can help in early detection of any potential issues.
Incorporating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables can also contribute to reducing the risk of oral cancer. Consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables not only provides essential nutrients for overall health but also contains antioxidants that protect cells from damage that can lead to cancer. It is essential to be aware of any changes in your mouth, such as persistent sores, lumps, or red or white patches, and to promptly seek medical attention if you notice any concerning symptoms. By following these preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining their oral health and reducing their risk of developing oral cancer.
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in influencing the risk of developing oral cancer. Factors such as tobacco use, whether smoking or smokeless, are known to increase the likelihood of oral cancer. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products can damage cells in the mouth and lead to the development of cancerous growths. Moreover, excessive alcohol consumption has also been linked to a higher risk of oral cancer. Alcohol can irritate the cells in the mouth, making them more susceptible to genetic mutations that can trigger cancer formation.
Furthermore, poor diet choices, specifically a lack of fruits and vegetables in one’s diet, can contribute to an increased risk of oral cancer. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins and antioxidants that help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of cancer development. On the contrary, a diet high in processed foods and lacking in nutritional value can weaken the body’s immune system and leave the oral tissues vulnerable to cancerous changes. Making informed decisions about lifestyle habits, such as quitting tobacco use, moderating alcohol consumption, and adopting a balanced diet, can play a crucial role in reducing the risk of oral cancer.
Genetics plays a crucial role in the development of oral cancer. Research has shown that certain genetic mutations and variations can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing this disease. Inherited genetic syndromes, such as Fanconi anemia and dyskeratosis congenita, are known to be associated with a higher risk of oral cancer, highlighting the significant impact of genetics on this condition.
Furthermore, studies have identified specific gene alterations that are linked to the development and progression of oral cancer. For instance, mutations in the TP53 gene, which plays a critical role in cell growth regulation, have been found to be prevalent in oral cancer patients. Understanding the genetic factors involved in oral cancer can help in the development of more personalized treatment approaches and targeted therapies for patients with this condition.
Support services for oral cancer patients play a crucial role in providing psychological, emotional, and practical support throughout their treatment journey. These services typically encompass counseling, support groups, educational resources, and financial assistance to alleviate the burden faced by patients and their families. The aim is to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care and guidance beyond just medical treatment, fostering a sense of community and empowerment during a challenging time.
Furthermore, organizations such as the Oral Cancer Foundation and CancerCare offer valuable resources, including online forums, helplines, and informational materials to help patients navigate their diagnosis and treatment process. These support services not only enhance the overall well-being of patients but also contribute to better treatment outcomes and quality of life post-treatment. By addressing the holistic needs of oral cancer patients, these support services play a pivotal role in promoting resilience and facilitating a smoother recovery journey.
Oral cancer, like many cancers, can have varying survival rates based on factors such as the stage at diagnosis, location of the tumor, and individual health status. The five-year survival rate for oral cancer can range from around 40% to 80%, depending on these variables. Early detection plays a crucial role in improving survival rates, as treatment outcomes are generally more favorable when the cancer is diagnosed in its earlier stages.
Additionally, the type of treatment received can also impact survival rates. Treatment options for oral cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these modalities. The effectiveness of these treatments in eradicating cancer cells and preventing recurrence can contribute to the overall survival rate for patients with oral cancer. It is essential for individuals to undergo regular screenings and seek prompt medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise to enhance their chances of early detection and successful treatment outcomes.
Oral cancer screening has been a topic of debate within the dental and medical communities. One controversy surrounding screening is the lack of standardization in guidelines for who should receive screenings and how often they should be conducted. Some experts argue that widespread screening may lead to unnecessary anxiety and invasive follow-up procedures for patients without significant risk factors. Conversely, proponents of routine screening emphasize the potential benefits of early detection in improving treatment outcomes and reducing mortality rates associated with oral cancer.
Another point of contention in oral cancer screening is the efficacy of certain screening methods in accurately detecting early signs of the disease. While visual examinations and physical assessments of the oral cavity are commonly used in screening protocols, there is ongoing discussion about the reliability and sensitivity of these methods. Some researchers advocate for the incorporation of adjunctive screening tools, such as salivary tests or advanced imaging techniques, to enhance the accuracy of early detection efforts. Critics, however, raise concerns about the cost-effectiveness and practicality of implementing these additional screening modalities on a widespread scale.
Recent advancements in the field of oral cancer research have brought about promising developments in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying this disease. Scientists are delving into the complexities of genetic mutations and biomarkers that may aid in early detection and personalized treatment strategies. For instance, emerging studies are exploring the role of specific genes, such as PTEN and TP53, in the progression of oral cancer, offering new insights into targeted therapies that could help improve patient outcomes.
Another area of focus in current oral cancer research involves investigating the impact of the tumor microenvironment on disease progression and treatment response. Researchers are studying how interactions between cancer cells, immune cells, and surrounding tissues influence the growth and spread of oral tumors. By deciphering these intricate relationships, novel therapeutic approaches like immunotherapy and targeted drug delivery systems are being explored to combat oral cancer more effectively.
Regular oral cancer screenings play a crucial role in early detection, which is key to successful treatment outcomes. These screenings involve a thorough examination of the mouth, gums, tongue, and throat by a qualified healthcare professional. Detecting oral cancer in its early stages significantly increases the chances of effective treatment and overall survival rates.
As with many types of cancer, oral cancer can often be asymptomatic in its initial stages, making regular screenings imperative for timely diagnosis. By undergoing routine screenings, individuals can proactively monitor their oral health and address any abnormalities or suspicious signs promptly. Remember, early detection through regular screenings can save lives and improve the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with oral cancer.
It is recommended to get screened for oral cancer at least once a year, especially if you have risk factors such as smoking or heavy alcohol consumption.
While genetics can play a role in oral cancer, most cases are linked to lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption. It is still important to get regular screenings, especially if you have a family history of oral cancer.
Some preventive measures for oral cancer include avoiding tobacco products, limiting alcohol consumption, practicing good oral hygiene, and getting regular screenings.
Yes, there are support services available for oral cancer patients, including counseling, support groups, and resources for managing treatment side effects.
The survival rates for oral cancer vary depending on the stage at which it is detected. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of survival. It is important to get regular screenings to catch any signs of oral cancer early.