Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
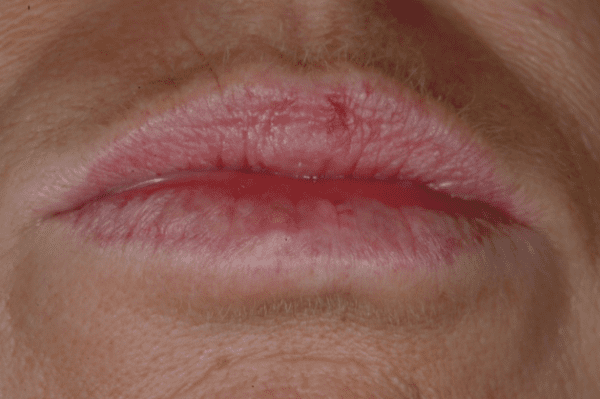
Learn about the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for lip cancer.
Lip cancer is a type of oral cancer that develops specifically on the lips. It is a relatively uncommon form of cancer, but its impact can be significant for those affected. Understanding the basics of lip cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Lip cancer can occur on the upper or lower lip and can vary in severity. It is most commonly seen in individuals over the age of 40, although it can affect people of all ages. The primary cause of lip cancer is prolonged sun exposure, particularly to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Other risk factors include tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and a weakened immune system.

Recognizing the symptoms of lip cancer is essential for early detection and prompt treatment. Common warning signs include persistent sores or lumps on the lips that do not heal, changes in the color or texture of the lips, persistent bleeding or pain, and difficulty swallowing or speaking. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a medical professional for a thorough examination and proper diagnosis.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricate anatomy of the lips and how lip cancer develops. We will also explore the various risk factors, causes, and diagnostic procedures associated with this condition. By equipping ourselves with knowledge, we can better understand and navigate the world of lip cancer, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for patients.
The lips are a vital part of our facial anatomy, serving both functional and aesthetic purposes. Composed of delicate and sensitive skin, the lips are characterized by a thin outer layer of skin known as the epidermis, and underneath lies the dermis, which contains blood vessels, nerve endings, and connective tissues. This unique structure makes the lips highly susceptible to various conditions, including cancer.
Cancer can develop in the lips when there is an abnormal growth of cells. The most common type of lip cancer is known as squamous cell carcinoma, which accounts for approximately 95% of all lip cancer cases. This type of cancer originates in the squamous cells that make up the thin, flat surface of the lips. Factors such as excessive sun exposure, tobacco use, and a weakened immune system can contribute to the development of lip cancer. Understanding the anatomy of the lips and how cancer develops is crucial in recognizing the early warning signs and seeking timely treatment.
It is crucial to recognize the early warning signs of lip cancer in order to obtain prompt diagnosis and treatment. While symptoms may vary from person to person, there are certain indications that should not be overlooked. One of the most common symptoms of lip cancer is the formation of sores or ulcers that do not heal within a reasonable amount of time. These sores may appear scaly or crusty, and they can be painful or tender to the touch. Another warning sign to be aware of is the presence of a lump or thickening on the lip that does not go away. This lump may be accompanied by swelling or redness.
In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, it is important to pay attention to any changes in the color or texture of the lips. Discoloration, such as a darkening or whitening of the skin, or abnormalities in the texture, such as roughness or thickening, should be examined by a healthcare professional. It is worth noting that persistent lip pain, numbness, or a tingling sensation can also be indicative of lip cancer. It is vital to remember that these warning signs alone do not confirm the presence of lip cancer, but they should be taken seriously and warrant further investigation. Early detection and diagnosis play a crucial role in ensuring successful treatment outcomes, so any concerns should be addressed promptly by a qualified healthcare professional.
There are several risk factors that can contribute to the development of lip cancer. One of the primary causes is excessive sun exposure. The lips are particularly vulnerable to harmful UV rays, and prolonged sun exposure without protection can increase the risk of developing lip cancer. This risk is even higher for individuals who work outdoors or participate in outdoor activities for extended periods of time.
Another significant risk factor is tobacco use. Smoking or chewing tobacco introduces harmful chemicals into the body, which can damage the cells of the lips and increase the likelihood of cancer formation. It is important to note that lip cancer can affect both smokers and non-smokers, although the risk is significantly higher for tobacco users.
| Risk Factors / Causes | Description |
|---|---|
| Sun Exposure | Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds increases the risk of lip cancer. |
| Tobacco Use | Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using smokeless tobacco increases the risk of developing lip cancer. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Heavy alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of lip cancer, especially when combined with tobacco use. |
| Human Papillomavirus (HPV) | Certain strains of HPV, especially HPV-16, are linked to an increased risk of developing lip cancer. |
| Immunosuppression | Weakened immune system due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive medications can increase susceptibility to lip cancer. |
| Genetic Factors | Some genetic factors may predispose individuals to develop lip cancer, although specific genes involved are not fully understood. |
| Chronic Irritation | Chronic irritation of the lips from ill-fitting dentures, rough teeth, or habitual lip biting may increase the risk of lip cancer. |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Neglecting oral hygiene may lead to chronic inflammation or infections in the mouth, which can contribute to the development of lip cancer. |
| Age | Lip cancer is more common in older individuals, with risk increasing with age. |
| Gender | Men are more likely to develop lip cancer compared to women, although the gender gap is narrowing. |
| Occupational Exposure | Certain occupations with exposure to chemicals, such as those found in certain manufacturing or construction industries, may increase the risk of lip cancer. |
Additionally, certain genetic factors may also contribute to the development of lip cancer. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of lip cancer may be at a higher risk of developing the disease themselves. Other risk factors include a weakened immune system, a history of certain viral infections, and a history of precancerous lip lesions.
Understanding the risk factors and causes of lip cancer is crucial for early detection and prevention. By avoiding excessive sun exposure, quitting tobacco use, and regularly visiting a healthcare professional for oral health screenings, individuals can reduce their risk of developing lip cancer.
Sun exposure plays a crucial role in the development of lip cancer. The lips are constantly exposed to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, making them particularly vulnerable to damage. Prolonged or excessive exposure to UV radiation can lead to genetic mutations in the cells of the lips, increasing the risk of cancerous growth.
Research has shown a strong correlation between sun exposure and the incidence of lip cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, up to 90% of lip cancers are attributed to sun exposure. This is especially true for the lower lip, which is more exposed to sunlight than the upper lip. Additionally, individuals who work outdoors or participate in outdoor activities without adequate sun protection are at an even higher risk.
UV radiation not only damages the skin on the lips but also weakens the immune system’s ability to defend against cancer cells. This makes it even more crucial to protect the lips from the sun’s harmful rays. Wearing wide-brimmed hats, using lip balms with SPF, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours are effective ways to minimize sun exposure and reduce the risk of lip cancer. By taking proactive measures to protect our lips, we can significantly decrease the chances of developing this potentially life-threatening condition.
Lip cancer is often associated with tobacco use, but it is important to note that non-smokers can also develop this condition. While the prevalence of lip cancer in non-smokers is relatively low, it is still a possibility that should not be overlooked.
Research suggests that non-smokers may be at increased risk for lip cancer due to other factors such as prolonged exposure to the sun, certain genetic predispositions, or even environmental factors like exposure to certain chemicals. Additionally, studies have shown that non-smokers who engage in heavy alcohol consumption are also at a higher risk for developing lip cancer.
| Aspect | Information |
|---|---|
| Prevalence | Uncommon |
| Risk Factors | UV exposure, genetics |
| Symptoms | Persistent lip sore, lump, discoloration |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, imaging tests |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Prognosis | Generally favorable with early detection |
| Prevention | Sun protection (lip balm, hats), avoid tanning |
Therefore, it is crucial for both smokers and non-smokers to be aware of the potential signs and symptoms of lip cancer, and to seek prompt medical attention if any abnormalities on the lips are noticed. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for individuals with lip cancer, regardless of their smoking status.
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for a variety of health conditions, including lip cancer. Studies have shown that smokers are at a significantly higher risk for developing lip cancer compared to non-smokers. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can cause DNA damage and impair the body’s ability to repair itself, leading to the development of cancerous cells in the lips. In fact, research has indicated that smokers are up to 10 times more likely to develop lip cancer than non-smokers.
It’s not just the act of smoking that increases the risk of lip cancer; the duration and intensity of smoking also play a role. The longer someone smokes and the more cigarettes they consume per day, the greater their risk becomes. The addictive nature of tobacco makes it difficult for smokers to quit, but it’s crucial to understand the potential consequences on oral health. By quitting smoking and seeking professional help, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing lip cancer and improve their overall health.
Lip cancer is a condition that can affect both men and women, although women may face some unique considerations and challenges in dealing with this disease. While lip cancer is more commonly seen in men, women are not exempt from its risks. Hormonal factors, such as fluctuations during pregnancy or menopause, can play a role in the development of lip cancer in women. Additionally, certain cosmetic products containing potentially harmful ingredients or excessive sun exposure without proper protection can increase the likelihood of lip cancer in women.
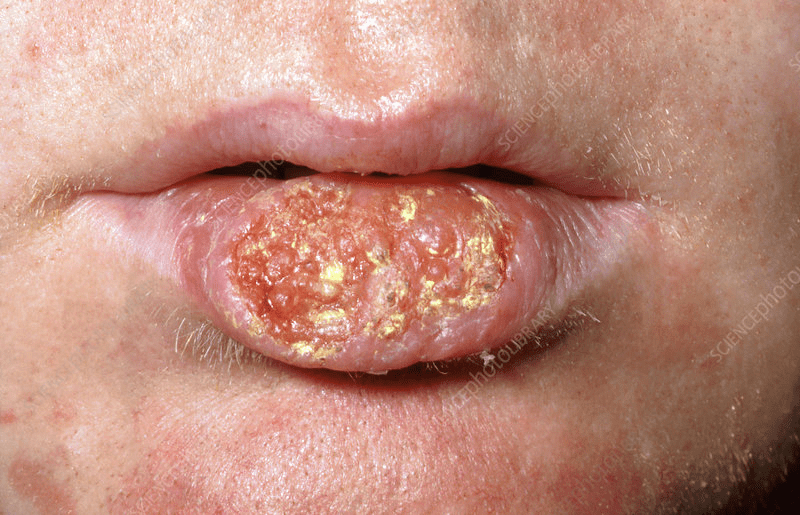
Furthermore, women may face additional challenges when diagnosed with lip cancer, particularly when it comes to physical appearance and body image. The lips play a significant role in facial aesthetics, and their alteration due to cancer treatment can impact self-confidence and emotional well-being. It is crucial for healthcare providers to understand and address these unique considerations, offering support and guidance throughout the treatment journey. By providing a comprehensive and holistic approach to care, we can help women facing lip cancer navigate these challenges and achieve the best possible outcomes.
In order to diagnose lip cancer, there are several common tests and procedures that medical professionals may use. These diagnostic methods are vital for accurately identifying the presence and extent of lip cancer, allowing for prompt and appropriate treatment.
One common test used for diagnosing lip cancer is a biopsy. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is taken from the lip area and examined under a microscope. This allows the medical team to determine whether the cells are malignant or benign, and if cancer is present, what type of cancer it is. Biopsies can be performed using different techniques, such as excisional biopsy or incisional biopsy, depending on the size and location of the suspected cancerous area.
Another procedure commonly employed in the diagnosis of lip cancer is imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans. These tests provide detailed images of the lip and surrounding structures, allowing for a closer look at any potential cancerous growths. Imaging tests can help determine the size, location, and spread of the cancer, aiding in treatment planning.
In conclusion, there are various tests and procedures that are used in the diagnosis of lip cancer. Biopsies and imaging tests are among the most common methods used by medical professionals to accurately identify and characterize the presence of lip cancer. These diagnostic techniques play a crucial role in guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
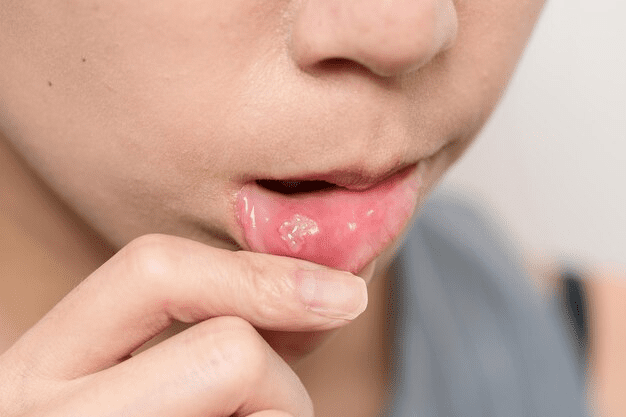
Lip cancer is a serious condition that requires proper diagnosis and staging to determine its severity and spread. Staging is a crucial step in understanding the extent of the disease and determining the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
The stages of lip cancer are determined based on several factors, including the size of the tumor, its depth of invasion, and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. The most commonly used staging system for lip cancer is the TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Node, and Metastasis. This system assigns a stage to the cancer based on the size and location of the tumor, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastasis.
Accurate staging of lip cancer allows healthcare professionals to provide tailored treatment options and to estimate the prognosis for the patient. It also helps in determining the need for additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or biopsies, to further evaluate the extent of the disease. Proper staging is, therefore, essential in guiding clinicians and patients towards the most effective and appropriate treatment strategies for lip cancer.
Treatment options for lip cancer vary depending on factors such as the stage of the cancer, the location of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient. Surgery is often the primary treatment for early-stage lip cancer. During surgical procedures, the surgeon removes the cancerous tumor, along with a margin of healthy tissue surrounding the tumor to ensure complete removal. In some cases, a skin graft may be necessary to reconstruct the lips after surgery.
Radiation therapy may be used as a primary treatment for lip cancer, particularly in cases where surgery is not possible or for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery. Radiation uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells and can be effective in destroying cancerous cells in the lips. This treatment may be used alone or in combination with surgery to increase the chances of successful treatment. Other treatment options, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies, may also be considered based on the specific characteristics of the cancer and the needs of the patient.
Surgical removal of lip cancer is a common treatment method used to effectively eliminate cancerous cells from the lips. There are several techniques and considerations that dentists and surgeons take into account when performing these procedures. One common approach is called Mohs micrographic surgery, which involves removing the cancerous tissue layer by layer while closely examining the margins under a microscope. This technique ensures precise removal of the cancerous cells while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
Another technique used for lip cancer removal is wide local excision. This involves removing the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue surrounding it. The extent of the excision may vary depending on the size and stage of the cancer. In some cases, reconstructive surgery may be required to restore the appearance and function of the lips after removal of the cancerous tissue.
When considering surgical procedures for lip cancer removal, it is important to take into account factors such as the location and size of the tumor, the stage of the cancer, and the overall health of the patient. The goal is not only to effectively remove the cancer but also to ensure the best possible cosmetic and functional outcome for the patient. Collaborating with a multidisciplinary team, including oral surgeons, dermatologists, and plastic surgeons, can help provide comprehensive care and improve the prognosis for individuals with lip cancer.
Radiation therapy is a crucial treatment option for individuals who are diagnosed with lip cancer. This therapy involves the use of high-energy X-rays to destroy cancer cells and prevent their growth. The benefits of radiation therapy for lip cancer are substantial, as it effectively targets and eliminates cancer cells in the affected area. By doing so, radiation therapy can prevent the spread of cancer to nearby tissues and organs, ultimately improving the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
In addition to its effectiveness, radiation therapy for lip cancer has relatively few side effects compared to other treatment modalities. While it is normal for patients to experience some temporary skin redness, swelling, or dryness in the treated area, these symptoms typically subside after the completion of treatment. Serious side effects are rare but may include radiation burns, oral sores, or changes in taste sensation. However, it’s worth noting that these side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with appropriate medical care. Overall, radiation therapy offers a promising approach for treating lip cancer, providing both beneficial outcomes and manageable side effects.
Adjuvant therapies play a crucial role in enhancing the outcomes of lip cancer treatment. These additional treatments are administered after primary surgical removal of the cancerous tissue, and they aim to eradicate any remaining cancer cells, reduce the risk of local recurrence, and improve overall survival rates.
One commonly used adjuvant therapy for lip cancer is radiation therapy. Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It can be delivered externally through a machine or internally through implantation of small radioactive seeds or wires. Radiation therapy is especially beneficial in cases where the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other distant sites.
In addition to radiation therapy, chemotherapy may be recommended as an adjuvant treatment for lip cancer. Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body, including those that may have spread beyond the lips. This systemic treatment approach can help eliminate any hidden cancer cells and reduce the risk of distant metastasis. However, it is important to note that the specific combination and duration of chemotherapy regimens vary depending on the individual case and the stage of lip cancer.
By implementing these adjuvant therapies, healthcare professionals can maximize the effectiveness of lip cancer treatment and improve long-term outcomes for patients. The decision to use adjuvant therapies will be based on various factors, such as the stage and extent of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and individualized treatment plans developed by a multidisciplinary team of specialists. Close monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure the ongoing success of these strategies in enhancing lip cancer treatment outcomes.
Recovery and rehabilitation are crucial aspects of the treatment journey for individuals who have undergone lip cancer treatment. After treatment, it is important to focus on overall well-being and regain normalcy in daily life. While the exact rehabilitation process may vary depending on the individual’s specific situation, there are some common factors to consider.
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the rehabilitation process, helping individuals regain strength and functionality in the affected area. Therapists may recommend exercises and stretches that target the muscles and tissues around the lips, promoting improved movement and flexibility. Additionally, speech and swallowing therapy might be necessary if lip cancer treatment has affected these functions. These therapy sessions focus on relearning proper techniques and strengthening the muscles involved. Alongside physical therapy, emotional support and counseling can also be beneficial, providing individuals with the tools to cope with any psychological challenges they may face during recovery.
Sun protection and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in preventing lip cancer. The primary cause of lip cancer is excessive sun exposure, particularly to the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Therefore, protecting your lips from the sun’s rays is essential for reducing the risk of developing this type of cancer.
One of the most effective ways to protect your lips from the sun is by wearing lip balm or sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF). Look for products that offer broad-spectrum protection, which shields against both UVA and UVB rays. Additionally, wearing a wide-brimmed hat, using a lip balm with SPF, and seeking shade during peak sun hours can further safeguard your lips from the damaging effects of the sun. Engaging in healthy lifestyle choices, such as avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption, also contributes to the prevention of lip cancer. By adopting these sun protection measures and making positive lifestyle choices, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing lip cancer.
Lip cancer is relatively rare compared to other types of cancer. However, it is still important to be aware of the risk factors and take preventative measures.
Yes, lip cancer can occur in non-smokers. While smoking increases the risk, sun exposure and other factors can also contribute to the development of lip cancer.
Lip cancer can affect both men and women, but there are some unique considerations and challenges for women. It is important for everyone to take protective measures against lip cancer.
Early warning signs of lip cancer may include persistent lip sores, lumps, or patches, changes in lip color or texture, and difficulty in lip movement. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if any concerning symptoms are experienced.
Lip cancer can be diagnosed through various tests and procedures, including a physical examination, biopsy, imaging tests, and lymph node evaluation. These diagnostic methods help determine the presence and severity of lip cancer.
The treatment options for lip cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, and adjuvant therapies. The choice of treatment depends on the stage and spread of the cancer, as well as the individual’s overall health.
Sun exposure plays a significant role in the development of lip cancer. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds increases the risk of lip cancer. It is crucial to protect the lips from sun damage by using lip balm with SPF, wearing hats, and seeking shade when the sun is strongest.
Radiation therapy is used as a treatment option for lip cancer. It can effectively target and destroy cancer cells. However, it may also cause side effects such as skin irritation, dry mouth, and fatigue. The benefits and risks of radiation therapy are evaluated on an individual basis.
Preventing lip cancer involves practicing sun protection measures, such as wearing lip balm with SPF, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and using protective clothing and accessories. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying hydrated can also reduce the risk of lip cancer.
The recovery process after lip cancer treatment varies depending on the individual and the specific treatment received. It may involve post-operative care, physical therapy, and regular follow-up appointments to monitor for any potential recurrence. Rehabilitation and recovery can take time, and it is important to adhere to the healthcare professional’s guidance for the best outcome.