Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Learn the importance of dental X-rays for accurate oral health diagnosis.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in oral health diagnosis, providing valuable insights that are not visible to the naked eye. These diagnostic images are a key tool used by dentists to detect and evaluate a wide range of dental conditions. From tooth decay and cavities to gum disease and abnormalities, dental X-rays help dentists make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans.
One of the main advantages of dental X-rays is their ability to detect oral health issues in their early stages. By capturing detailed images of the teeth, jaws, and supporting structures, dentists can identify problems before they become more complex and difficult to treat. This early detection allows for prompt intervention, helping to prevent further damage and potential complications. Dental X-rays also enable dentists to monitor the progression of certain conditions, ensuring that the chosen treatment is effective and adjustments can be made if necessary.
Overall, dental X-rays are an invaluable tool in the field of dentistry. Whether it’s aiding in early detection, guiding treatment plans, or uncovering hidden problems, these diagnostic images provide valuable information that helps dentists deliver optimal oral health care to their patients.

Dental X-rays are an invaluable tool in the diagnosis of oral health conditions. They provide dentists with a clear and detailed view of the teeth and underlying structures that may not be visible during a routine dental examination. This is particularly critical in detecting problems that are hidden beneath the surface, such as cavities, impacted teeth, and bone loss.
By using dental X-rays, dentists can accurately identify and diagnose oral health issues at an early stage. This allows for prompt and targeted treatment, minimizing the risk of further complications and ensuring optimal outcomes for patients. In fact, studies have shown that dental X-rays can detect dental caries (cavities) at least 20% more effectively than a visual examination alone.
Furthermore, dental X-rays play a vital role in assessing the overall oral health and development of pediatric patients. Children’s teeth and jaw structures are constantly changing, and X-rays provide dentists with a comprehensive evaluation of their dental health. This is crucial for identifying any abnormalities or potential issues that may affect their oral development. Additionally, dental X-rays can assist dentists in planning orthodontic treatments and monitoring the progress of ongoing dental procedures.
In conclusion, the importance of dental X-rays in oral health diagnosis cannot be overstated. They enable dentists to accurately and efficiently detect oral health conditions that may not be visible during a regular exam. By identifying issues early on, dental X-rays contribute to proactive and effective treatment planning, ultimately leading to improved oral health outcomes for patients of all ages.
Dental X-rays are an integral part of the diagnostic process in oral health care. They provide valuable insights into the structure and condition of teeth, gums, and bones that are not visible to the naked eye. But have you ever wondered how dental X-rays actually work?
Dental X-rays, also known as radiographs, utilize a form of electromagnetic radiation called X-rays. These X-rays pass through the oral cavity and are absorbed differently by various oral tissues. Dense tissues, such as tooth enamel and bone, absorb more X-rays and appear white on the resulting image. In contrast, less dense tissues, like gums and soft tissues, allow more X-rays to pass through, resulting in darker areas on the X-ray image.
By capturing these X-ray images, dentists can accurately diagnose a wide range of dental conditions, including cavities, gum disease, infections, and abnormalities in tooth and bone structure. They can also evaluate the position and alignment of teeth, assess the health of the underlying jawbone, and detect any signs of oral cancer or other abnormalities. With this understanding of how dental X-rays work, we can appreciate the immense value they bring to the field of oral health diagnosis.

Dental X-rays play a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of various oral health issues. There are several types of dental X-rays that dentists use depending on the specific needs of the patient. One commonly used type is the bitewing X-ray. This type of X-ray allows dentists to capture images of the upper and lower teeth in a single image, making it useful for detecting tooth decay, cavities, and bone loss.
Another type of dental X-ray is the periapical X-ray. This X-ray provides a detailed view of a specific tooth from root to crown, making it ideal for diagnosing problems such as abscesses, cysts, and abnormalities in the tooth root. Additionally, panoramic X-rays provide a comprehensive view of the entire mouth, including the jaw, teeth, sinuses, and temporomandibular joints. This type of X-ray is particularly useful for evaluating impacted teeth, jawbone irregularities, and the placement of dental implants.
By utilizing different types of dental X-rays, dentists can gain valuable insights into the oral health of their patients and make informed treatment decisions. These X-rays allow dentists to examine areas that are not visible during a regular dental examination, and they provide a detailed and comprehensive view of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding structures. With the help of dental X-rays, dentists can accurately diagnose various oral health issues and provide appropriate and timely treatment, ensuring the overall oral health and well-being of their patients.
| Type of Dental X-ray | Specific Use |
|---|---|
| Bitewing X-rays | Detecting cavities between teeth |
| Periapical X-rays | Showing the entire tooth from crown to root tip |
| Panoramic X-rays | Providing an overview of the entire mouth and jaw |
| Occlusal X-rays | Revealing the placement of teeth in the upper or lower jaw |
| Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) | Detailed 3D imaging for dental surgeries and implants |
| Orthodontic X-rays | Assessing the position of teeth and roots for orthodontic treatment |
| Cephalometric X-rays | Analyzing the relationship between the teeth and jawbone for orthodontic planning |
| Digital X-rays | Using digital sensors for enhanced image quality and reduced radiation exposure |
Advancements in dental x-ray technology have revolutionized the field of oral health diagnosis, providing numerous benefits for patients. One significant advancement is the introduction of digital radiography, which has replaced traditional film-based x-rays. Digital x-rays offer a host of advantages, including reduced radiation exposure, improved image quality, and faster processing.
With digital x-rays, patients are exposed to significantly lower levels of radiation compared to traditional film-based x-rays. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who require frequent or regular dental x-rays, such as those undergoing orthodontic treatment or individuals with certain medical conditions. Additionally, the images produced by digital x-rays are sharper and more detailed, allowing dentists to detect even the smallest abnormalities or early signs of oral health issues. This improved image quality enables dentists to make more accurate diagnoses and create more precise treatment plans for their patients.
Furthermore, the digital format of these x-rays allows for faster processing and immediate accessibility. With traditional film-based x-rays, patients would have to wait for the films to be developed and for the images to be manually examined. However, with digital x-rays, the images are available within seconds and can be viewed on a computer screen. This not only saves valuable time for both the patient and the dentist but also enhances communication and enables the dentist to discuss the findings with the patient in real-time. Overall, the advancements in dental x-ray technology have greatly improved the diagnostic capabilities and overall experience for patients, making it an invaluable tool in oral health care.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in the early detection of oral health issues. Through the use of X-rays, dentists are able to uncover problems that may not be visible to the naked eye, allowing for timely diagnosis and treatment. This is especially important as many oral health conditions, such as tooth decay and gum disease, can progress silently without causing noticeable symptoms.
One of the main benefits of dental X-rays is their ability to detect tooth decay in its early stages. X-rays can identify the presence of cavities between teeth or in areas that are difficult to see, such as beneath fillings or between teeth crowns. By catching decay early on, dentists can intervene before the damage becomes more severe, potentially saving the affected teeth from further deterioration or even extraction. Furthermore, dental X-rays can also aid in the detection of other oral health issues, such as periodontal disease, bone loss, and even tumors or abnormalities. Overall, dental X-rays serve as a valuable tool for dentists to provide comprehensive and proactive care for their patients’ oral health.
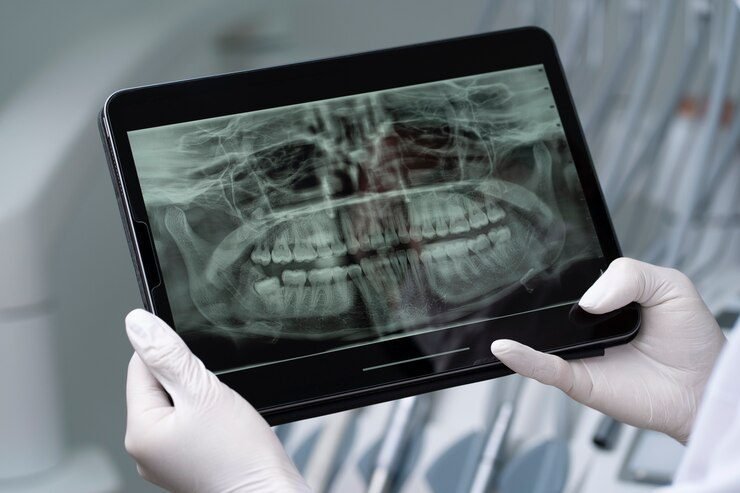
In order to ensure the safety of patients during dental x-ray procedures, several safety measures are implemented. Firstly, the dental office should have appropriate shielding in place to protect patients from unnecessary radiation exposure. This includes lead aprons or thyroid collars that can be worn by the patient to shield vital organs from radiation.
Furthermore, dental professionals should adhere to the As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principle when taking x-rays. This means that they should use the lowest possible radiation dose necessary to obtain the diagnostic information needed. Modern x-ray equipment also includes features like collimation and filtration to further limit radiation exposure.
In addition to these precautions, dental professionals should take accurate and standardized radiographs, ensuring proper positioning and technique. This not only reduces the need for retakes and additional exposures but also improves the diagnostic quality of the images. Moreover, dental offices should regularly inspect and maintain their x-ray equipment to guarantee its optimal performance and safety.
By implementing these safety measures, dental professionals can minimize the risks associated with dental x-ray procedures and ensure the well-being of their patients. It is important for patients to feel confident that their oral health examinations are being conducted with their safety as a top priority.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in the early detection of tooth decay and cavities. While visual examination by a dentist can identify some visible signs of decay, X-rays provide a more comprehensive view by revealing decay that may be hidden beneath the tooth’s surface. This is particularly important in identifying cavities between teeth or in areas not easily visible to the naked eye.
By using dental X-rays, dentists can accurately diagnose tooth decay and cavities at their earliest stages. This allows for prompt treatment, preventing further damage to the tooth and potentially avoiding the need for more extensive procedures such as root canals or extractions. Furthermore, early intervention can help preserve the natural tooth structure, ensuring optimal oral health and reducing the risk of complications in the future.
In addition to their diagnostic benefits, dental X-rays also aid in monitoring the progression of tooth decay and cavities over time. By comparing X-rays taken at different intervals, dentists can assess the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments to ensure successful outcomes. This enables dentists to provide personalized care tailored to each patient’s specific needs, ultimately contributing to better oral health outcomes.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in identifying and diagnosing periodontal disease, a serious oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. This diagnostic tool helps uncover hidden problems that may not be visible during a routine dental examination.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, starts with the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Over time, this can lead to inflammation of the gums, causing them to pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These pockets become a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to further infection and damage to the gum tissue and bone.
Dental X-rays provide a deeper insight into the extent of the disease by capturing images of the underlying structures, including the bones that support the teeth. This allows dentists to assess the severity of bone loss and identify any hidden areas of infection. By detecting periodontal disease early through X-rays, dentists can develop a tailored treatment plan to prevent further damage and improve the overall oral health of their patients.
Please note that this is just a sample section for the given article. The section complete in itself and does not have a conclusion as per the instructions provided. The actual content and structure of the article should be developed considering the complete scope and requirements of the topic.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in assessing bone health, particularly in the evaluation of jawbone and tooth support. X-rays allow dentists to obtain detailed images of the bone structure, providing valuable information about its density, quality, and overall health. By examining these images, dentists can detect and diagnose various conditions such as bone loss, fractures, infections, and abnormalities that may otherwise go unnoticed.
One of the key benefits of dental X-rays in assessing bone health is their ability to help dentists evaluate the level of support that the jawbone provides to the teeth. This is particularly important in cases where dental implants or other tooth replacements are being considered. By assessing bone health through X-rays, dentists can determine whether the jawbone has sufficient thickness and density to support dental implants, or if additional procedures, such as bone grafting, are necessary to ensure successful implant placement.
Additionally, dental X-rays are used to monitor bone health over time, allowing dentists to detect any changes or deterioration that may require intervention. This enables dentists to provide appropriate treatment and prevent further complications in patients with compromised bone health.
Dental x-rays play a crucial role in the planning and monitoring of orthodontic treatment. They provide orthodontists with essential information about the alignment and positioning of teeth, the growth and development of jaws, and the overall oral health of the patient.
By using dental x-rays, orthodontists can accurately assess the underlying structures that support the teeth, including the roots, jawbone, and surrounding tissues. This information is vital for creating an effective treatment plan and ensuring precise adjustments throughout the orthodontic journey.
Furthermore, dental x-rays allow orthodontists to monitor the progress of treatment over time. By comparing x-rays taken at different stages, orthodontists can evaluate how teeth are shifting, measure the effectiveness of braces or aligners, and make necessary adjustments to achieve optimal results.
In summary, dental x-rays provide orthodontists with valuable insights into a patient’s oral health, enabling them to plan and monitor orthodontic treatment with precision. By utilizing this valuable tool, orthodontists can guide patients towards a healthy and beautiful smile.
In the field of oral surgery, dental x-rays play a crucial role in guiding procedures for optimal outcomes. These imaging techniques provide invaluable information that helps dentists and oral surgeons assess the condition of the patient’s teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. By using dental x-rays, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose and plan the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
One of the key benefits of dental x-rays in oral surgery is their ability to provide detailed and precise images of the patient’s oral structures. This allows dentists to identify any potential abnormalities or complications that may affect the success of the surgical procedure. Whether it’s the positioning of impacted teeth, the presence of cysts or tumors, or the evaluation of bone density, dental x-rays provide essential information that helps guide the surgeon in making informed decisions.
Furthermore, dental x-rays also enable dentists to visualize the root structure and surrounding tissues, which is particularly important in procedures such as tooth extractions, dental implant placements, or orthodontic treatments. By having a clear understanding of the patient’s oral anatomy, surgeons can minimize the risk of complications, ensure optimal placement of dental appliances or devices, and ultimately provide the best possible outcomes for patients undergoing oral surgery.
In summary, dental x-rays serve as an indispensable tool in oral surgery as they provide detailed images and vital information to guide procedures and optimize patient outcomes. With the ability to assess the condition of teeth, gums, bone, and surrounding structures, dental x-rays allow skilled professionals to make accurate diagnoses and plan the most appropriate treatment plans. By utilizing this valuable resource, dentists and oral surgeons can enhance the safety, effectiveness, and success of oral surgical procedures.
| Procedure | Guidelines for Optimal Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Oral Surgery | 1. Thorough pre-operative assessment including medical history and risk factors |
| 2. Adequate anesthesia and pain management protocols | |
| 3. Sterile techniques and infection control during the procedure | |
| 4. Careful handling of tissues to minimize trauma and bleeding | |
| 5. Clear communication with the patient regarding post-operative care | |
| 6. Post-operative follow-up to monitor healing and address any complications | |
| Dental X-rays | 1. Proper patient positioning to ensure accurate imaging |
| 2. Use of appropriate radiation shielding for patient safety | |
| 3. Selection of the correct type and angle of X-ray for diagnostic purposes | |
| 4. Regular calibration and maintenance of X-ray equipment | |
| 5. Minimization of radiation exposure through appropriate settings and techniques | |
| 6. Interpretation of X-ray results by qualified professionals for accurate diagnosis |
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in detecting tumors and abnormalities within the oral cavity. These diagnostic tools are valuable in identifying conditions that may not be visible during a routine oral examination. By capturing detailed images of the teeth, jawbones, and surrounding tissues, dental X-rays enable dentists to detect any irregularities or signs of disease.
One of the most common abnormalities detected through dental X-rays is oral cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, this form of cancer can start as small, painless lumps or white patches that may go unnoticed during a visual examination. However, with the help of X-rays, dentists can identify these early signs and prompt patients to seek further medical evaluation and treatment. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery, emphasizing the vital role dental X-rays play in overall healthcare.
Moreover, dental X-rays are also effective in detecting abnormalities within the jawbone, such as cysts and tumors. These growths may develop unnoticed, causing significant damage and discomfort if left untreated. X-rays provide dentists with a detailed view of the jaw’s internal structures, allowing them to identify and monitor any potential issues. This early detection helps dentists determine the most appropriate treatment plan and ensures the best possible outcomes for their patients’ oral health.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders, providing valuable insight into the condition of the jaw joint and surrounding structures. TMJ disorders can cause a range of symptoms, including jaw pain, headaches, popping or clicking sounds, and difficulty with jaw movement. While a clinical examination can provide some information, dental X-rays offer a more comprehensive view of the joint, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
One of the key benefits of dental X-rays for TMJ disorders is their ability to identify structural abnormalities and changes. X-rays can reveal any misalignments or degenerative changes in the joint, as well as assess the position of the disc that cushions the joint. This information is vital in determining the underlying cause of the TMJ disorder and guiding appropriate treatment options. Additionally, dental X-rays can help identify any other potential contributing factors, such as tooth misalignment or bite issues, which may be exacerbating the TMJ disorder. By capturing detailed images of the joint, dental X-rays provide dentists with essential information to make informed decisions about the appropriate course of treatment for TMJ disorders.
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in ensuring the healthy dental development of pediatric patients. As children’s teeth and jaw structures are still developing, X-rays can provide valuable insight into any potential issues that may arise. X-rays allow dentists to detect problems that may not be noticeable during a visual examination, such as tooth decay, abnormalities in tooth formation, or improper alignment of teeth.
By using dental X-rays, dentists can accurately diagnose and create a personalized treatment plan for children, ensuring that their dental health is effectively managed. X-rays help in identifying potential dental problems at an early stage, which can be crucial in preventing further complications. Moreover, detecting and addressing dental issues early on can also help in minimizing the need for invasive procedures or more extensive treatments later in life.
However, it is important to note that the use of dental X-rays in pediatric patients is done with utmost care and caution. Dentists take into consideration the child’s age, size, and individual dental needs when determining the frequency and type of X-rays to be taken. Protective measures, such as the use of lead aprons and collars, are always employed to minimize radiation exposure and ensure the safety of the child. Additionally, advancements in dental X-ray technology have greatly reduced radiation levels, making them even safer for pediatric patients.
In conclusion, dental X-rays are an invaluable tool in ensuring the healthy dental development of pediatric patients. By enabling dentists to detect and address dental issues early on, X-rays contribute to the overall oral health and well-being of children. However, it is crucial that X-rays are used judiciously and with safety measures in place to minimize radiation exposure. With the proper use of dental X-rays, dentists can provide optimal and personalized care to pediatric patients, setting a strong foundation for their lifelong dental health.
Radiation exposure is a concern for many patients when it comes to dental x-rays. However, it is important to understand that the amount of radiation used in dental x-rays is extremely low and poses minimal risk to patients. In fact, the radiation exposure from dental x-rays is equivalent to the amount of radiation a person receives from their natural surroundings in a day.
The American Dental Association (ADA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have established guidelines and regulations to ensure the safety of dental x-ray procedures. These guidelines include using the lowest possible radiation dose, using lead aprons and collars to shield the body, and employing digital radiography, which further reduces radiation exposure. Additionally, dentists only recommend x-rays when necessary and based on a patient’s individual situation, taking into consideration their age, oral health, and risk factors.
It is also worth noting that the benefits of dental x-rays far outweigh the minimal risks associated with radiation exposure. Dental x-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing oral health issues such as tooth decay, cavities, periodontal disease, and even tumors or abnormalities. They allow dentists to detect problems at an early stage when they are easier and less expensive to treat. By having regular dental x-rays, patients can ensure that their oral health is being properly monitored and any potential issues are addressed promptly.
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on various factors such as age, oral health condition, and risk of dental problems. Your dentist will determine the appropriate interval for X-ray examinations based on your individual needs.
Yes, dental X-rays are considered safe. The amount of radiation exposure from dental X-rays is minimal and within the acceptable range. Dentists also take necessary precautions to minimize radiation exposure by using lead aprons and collars.
Although dental X-rays are generally safe, pregnant women should try to avoid them, especially during the first trimester. However, if there is an urgent dental issue, your dentist may still perform X-rays using proper lead shielding to protect the abdomen.
Children are more sensitive to radiation than adults, but the amount of radiation from dental X-rays is very low. Dentists use pediatric-sized X-ray equipment and take additional precautions to minimize radiation exposure in children.
Yes, dental X-rays can help in the detection of tumors and abnormalities in the oral cavity. However, it is important to note that dental X-rays alone cannot diagnose oral cancer. Additional tests and evaluations may be required for a definitive diagnosis.
No, dental X-rays do not cause cavities or tooth decay. They are diagnostic tools used to detect and diagnose these conditions at an early stage, allowing for timely treatment.
The duration of a dental X-ray procedure may vary depending on the type of X-ray being taken. In most cases, intraoral X-rays can be completed within minutes, while panoramic or full-mouth X-rays may take slightly longer.
While dental X-rays primarily focus on the teeth and supporting structures, they can also reveal signs of gum disease such as bone loss and tartar buildup. However, a comprehensive examination by a dentist is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
The amount of radiation exposure from dental X-rays is minimal, and the benefits of early detection and diagnosis far outweigh the potential risks. Dentists follow strict safety protocols to ensure minimal radiation exposure during X-ray procedures.
In general, dental X-rays are safe for individuals with medical conditions. However, it is important to inform your dentist about any existing medical conditions or concerns to determine the appropriate precautions or alternative imaging methods if necessary.